Ethanol gas sensor based on zinc ferrite nano-sensitive material and preparation method thereof
A gas sensor and sensitive material technology, applied in the fields of nanotechnology, nanotechnology, analytical materials, etc. for materials and surface science, it can solve the problems of gas-sensing performance differences such as sensitivity, selectivity, and working temperature, and achieve improved gas sensitivity. The effect of sensitive performance, simple method and easy availability of raw materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] The preparation method of the ethanol gas sensor based on the zinc ferrite nano-sensitive material comprises the following steps:
[0026] (1) Preparation of precursor Zn, Fe-MOF nanomaterials
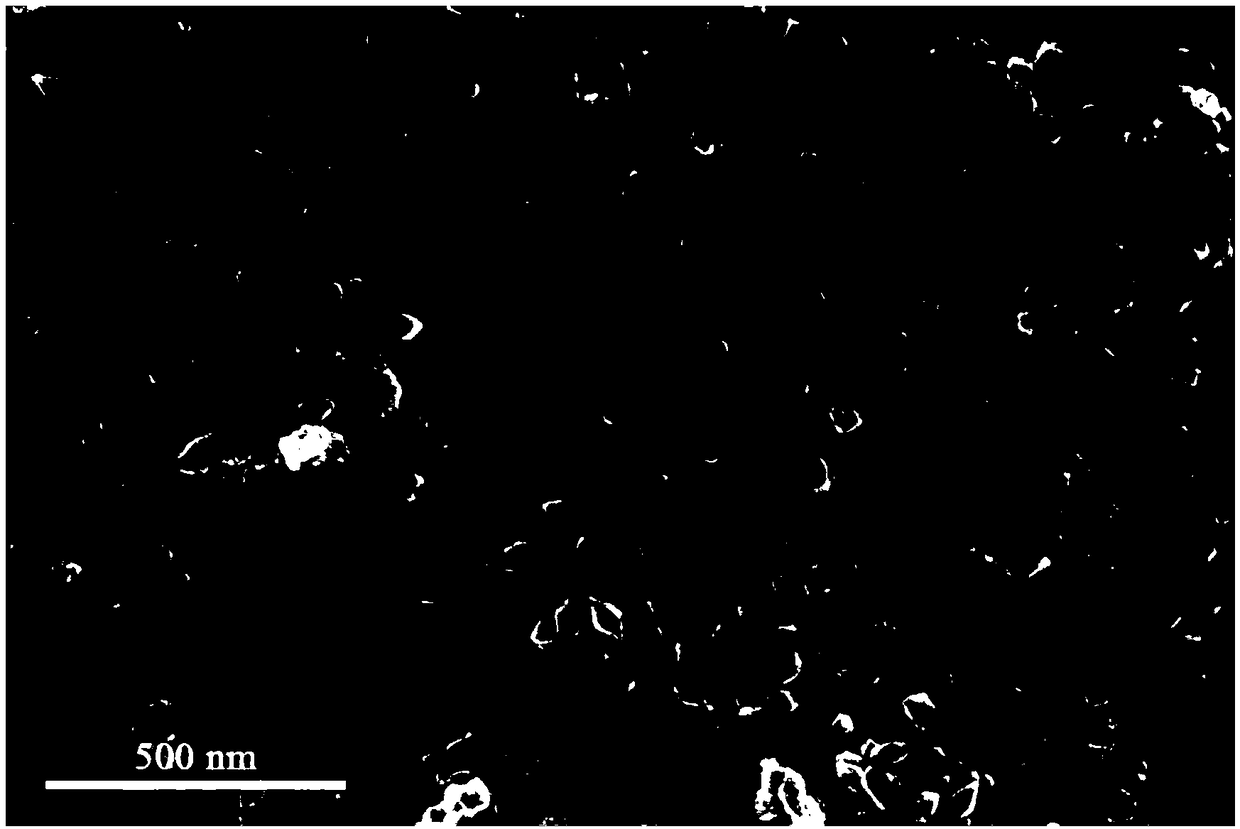
[0027] Zinc nitrate hexahydrate (74.4 mg), ferric nitrate nonahydrate (202 mg), fumaric acid (928.6 mg) were dissolved in 10 mL N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) solution and sonicated until uniform. Stir the above mixture at room temperature for 10 minutes, then transfer the obtained solution to a 20mL reactor and heat at 100°C for 8h, centrifuge the obtained product, wash it with DMF and ethanol successively, and then put it in a vacuum drying oven at 60°C After drying for 8 hours, the precursor Zn,Fe-MOF nanomaterials were obtained. The morphology of the obtained Zn, Fe-MOF nanomaterials was characterized by scanning electron microscopy. Such as figure 1 As shown, the obtained Zn, Fe-MOF nanomaterials have a spindle structure with a particle size of about 200nm.
[0028] (2) Pr...
Embodiment 2
[0036] (1) The steps for preparing Zn, Fe-MOF nanomaterials are the same as in Example 1.
[0037] (2) Preparation of ZnFe 2 o 4 nanomaterials
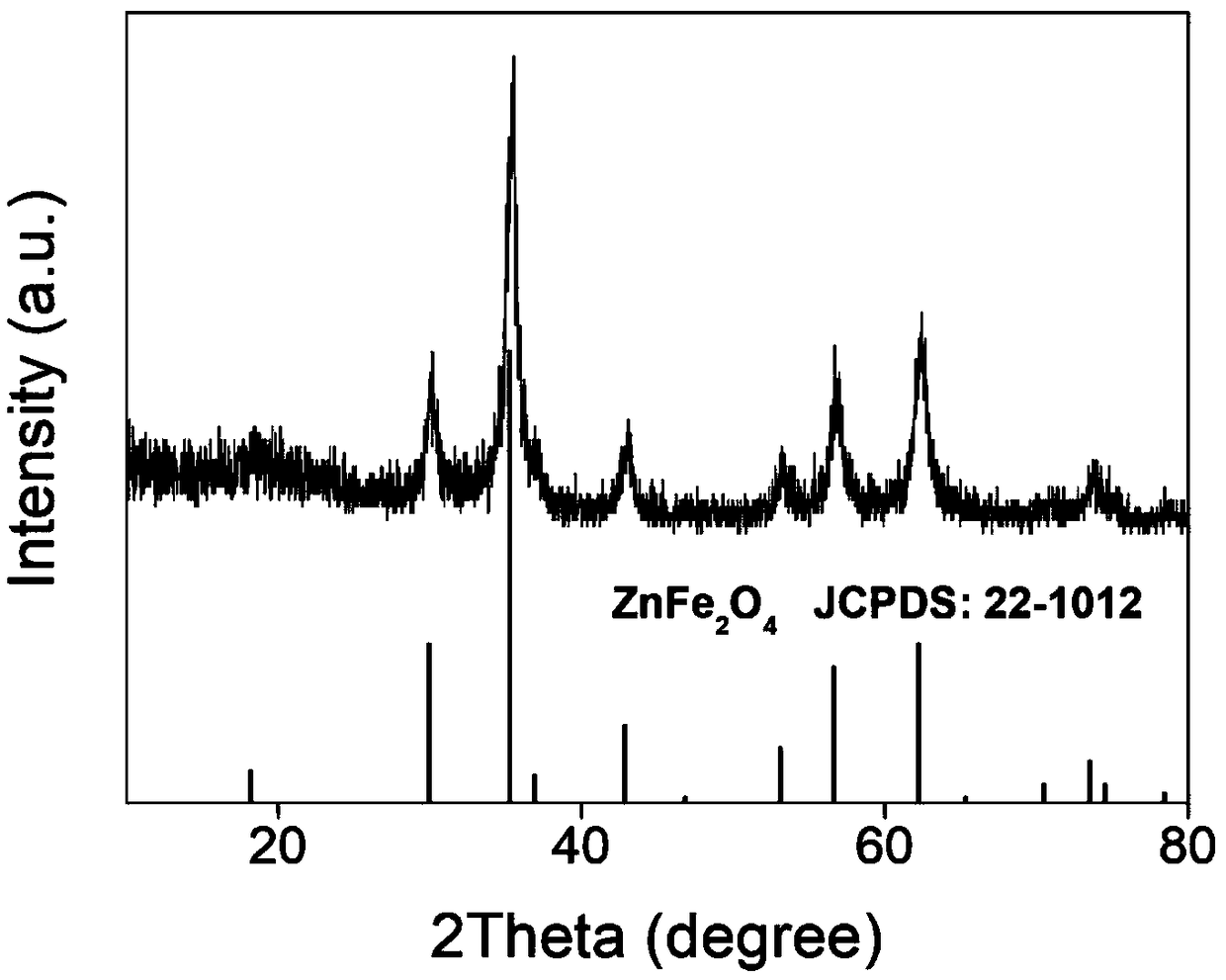
[0038] The Zn, Fe-MOF nanomaterial (100 mg) obtained in Example 1 was put into a crucible, placed in a muffle furnace, and calcined at a high temperature in an air atmosphere. The calcination temperature is 550°C, the heating rate is 1°C / min, and the calcination time is 2h. ZnFe 2 o 4 The structure and morphology of the nanomaterials are similar to those in Example 1.
[0039] (3) The steps of preparing the ethanol gas sensor are the same as those in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0041] (1) Preparation of Zn, Fe-MOF nanomaterials
[0042] At room temperature, zinc nitrate hexahydrate (82mg), ferric nitrate hexahydrate (130mg), fumaric acid (935mg) were dissolved in 12ml N,N-dimethylformamide DMF, and the mixed solution was sonicated until uniform. Move the homogeneous solution into a reaction kettle, heat and react at 120°C for 7 hours, then cool to room temperature, wash the obtained product with DMF and ethanol several times, put it in a vacuum box, and dry it at 80°C for 6 hours. Obtain the precursor material.
[0043] (2) Preparation of ZnFe 2 o 4 nanomaterials
[0044] The obtained Zn, Fe-MOF nanomaterial (100 mg) was put into a crucible, placed in a muffle furnace, and calcined at a high temperature in an air atmosphere. The calcination temperature is 350°C, and the calcination time is 6h. ZnFe 2 o 4 The structure and morphology of the nanomaterials are similar to those in Example 1.
[0045] (3) The steps of preparing the ethanol gas sen...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com