Enzymatic hydrolysis buffer solution for promoting acetone-butanol-ethanol fermentation production of fibers and application thereof
A technology of buffer solution and enzymatic hydrolysis solution, which is applied in the field of lignocellulose resource utilization, can solve problems such as the inability to realize the promotion and improvement of butanol metabolism, and achieve the effect of promoting efficient production and simplifying the preparation scheme
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
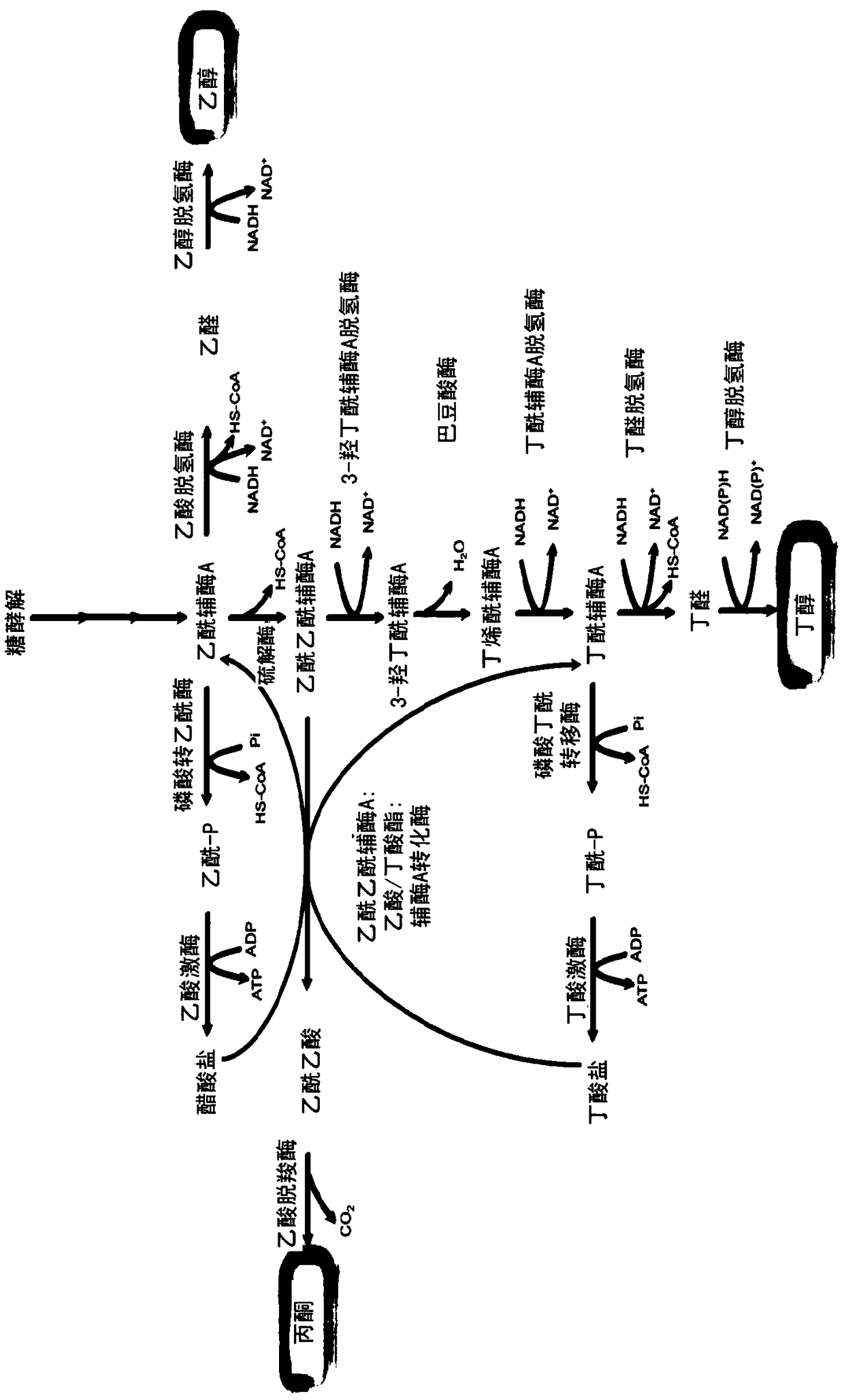
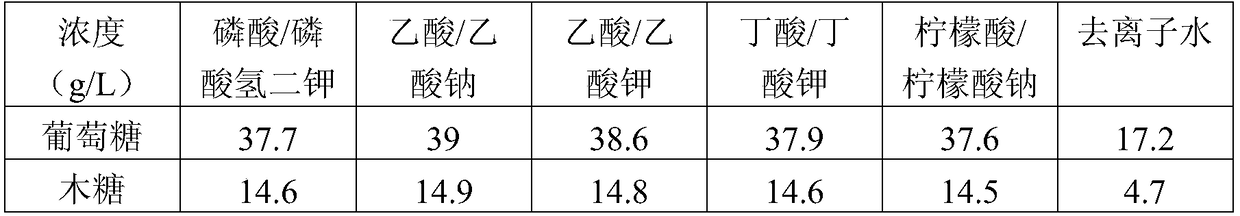
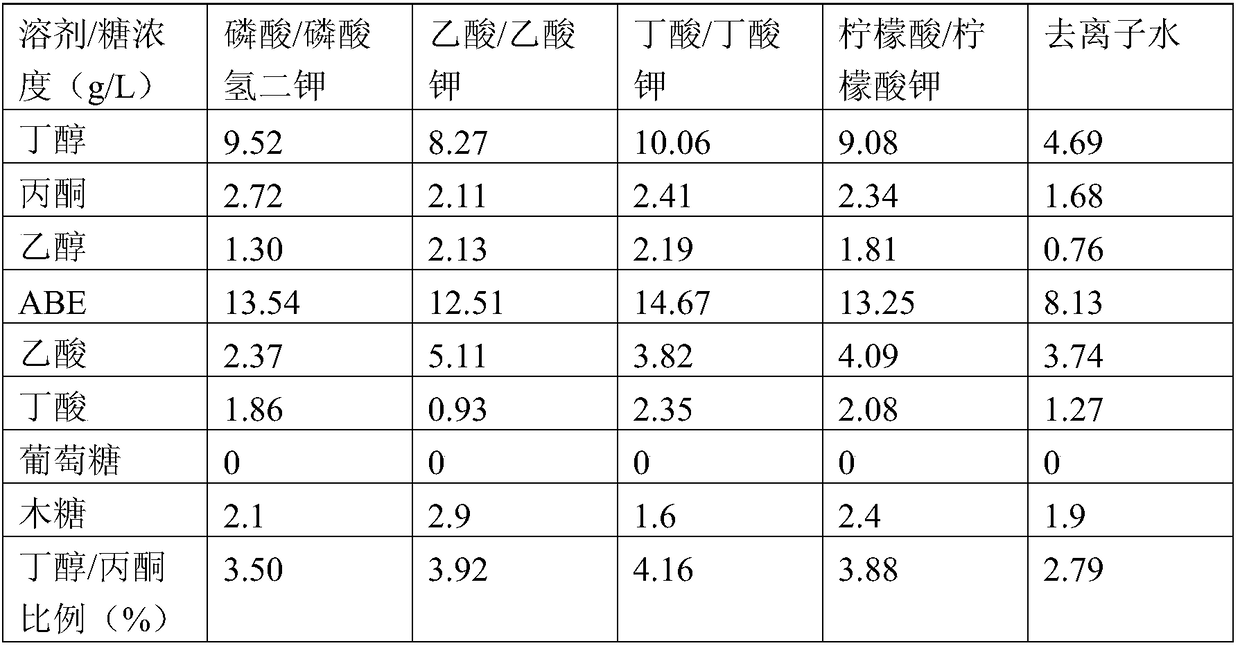
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0116] Example 1: Using acetic acid / butyric acid dilute solution to prepare fiber enzymatic hydrolysis buffer and realize enzymatic saccharification and ABE fermentation of sugarcane straw residue after ethylenediamine pretreatment
[0117] (1) Rinse the juiced sugarcane stalks with deionized water until there is no residual free sugar on the surface, and dry at 105° C. to absolute dryness. Then crush until the particle size is below 40 mesh. The sugarcane straw residue was fully mixed with a pre-prepared 10% (w / v) aqueous solution of ethylenediamine, and pretreated at 120° C. for 1 hour. Afterwards, the reactor was cooled to room temperature, and centrifuged at 10000 rpm to obtain solid sugarcane stalk pretreatment residue. Rinse the pretreatment residue with deionized water until the surface is neutral. The obtained neutral pretreatment residue was baked to absolute dryness at 105°C. The measured solid yield was 49.8%, and the contents of cellulose, hemicellulose and lign...
Embodiment 2
[0124] Example 2: Utilizing the organic acid in the ABE fermentation broth to prepare an enzymatic hydrolysis buffer, and carrying out batch ABE fermentation.
[0125] Get the ABE fermentation broth in Example 1, and suspend steaming at 45° C. under 20 kPa until the volume of the concentrated fermentation broth is half of the original fermentation broth. After that, add deionized water to the decompressed concentrated fermented liquid, so that the volume of the fermented liquid remains consistent with the volume before concentration. The concentration of ethanol in the diluted concentrated fermented liquid detected by gas chromatography is 0.6 g / L, the concentrations of acetic acid and butyric acid are 2.5 g / L and 1.5 g / L, and the pH of the fermented liquid is 4.3.
[0126]Add concentrated ammonia water to the diluted concentrated fermented liquid to adjust the pH to 5. Afterwards, the neutral sugarcane stalk residue obtained by pretreatment and washing with the ethylenediami...
Embodiment 3
[0127] Example 3: Using different concentrations of butyric acid / ammonium butyrate enzymatic hydrolysis buffer to enzymolyze wheat straw and carry out free ABE fermentation
[0128] (1) The wheat straw was crushed until the particle size was below 40 meshes, and then fully mixed with 5% (w / v) dilute sulfuric acid prepared in advance, and pretreated at 120°C for 1 hour. Afterwards, the reactor was cooled to room temperature and centrifuged at 10000 rpm to obtain solid wheat straw pretreatment residue. Rinse the residue with deionized water until the surface is neutral. The resulting neutral residue was dried to absolute dryness at 105°C. 4 groups in parallel.
[0129] (2) Add 25mM, 50mM, 75mM and 100mM butyric acid / ammonium butyrate buffer solution to the 4 groups of pretreatment residues obtained by the reaction respectively according to the solid addition amount of 10% (w / v), the pH of the buffer solution is 4.8 . After thorough mixing, 30 FPU / g of residual cellulase was ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com