Myrtle polysaccharide P3, separation method thereof and application of myrtle polysaccharide P3 in blood-lipid-lowering drugs
A technology of myrtle and polysaccharide, applied in the field of natural products, can solve the problems of low level of processing and utilization, low utilization rate of development and the like, and achieve the effects of good physical and chemical stability, low cost and high yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
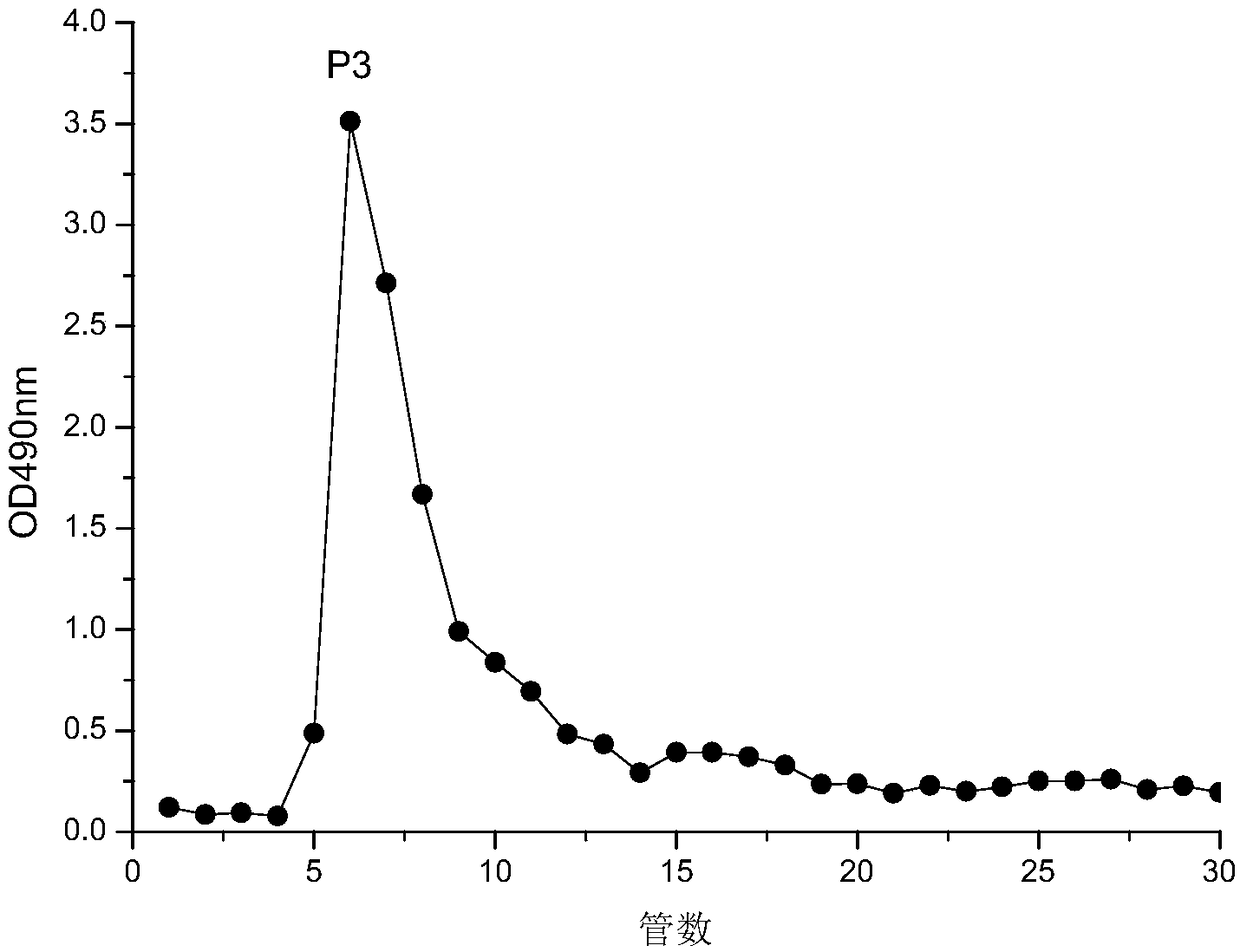
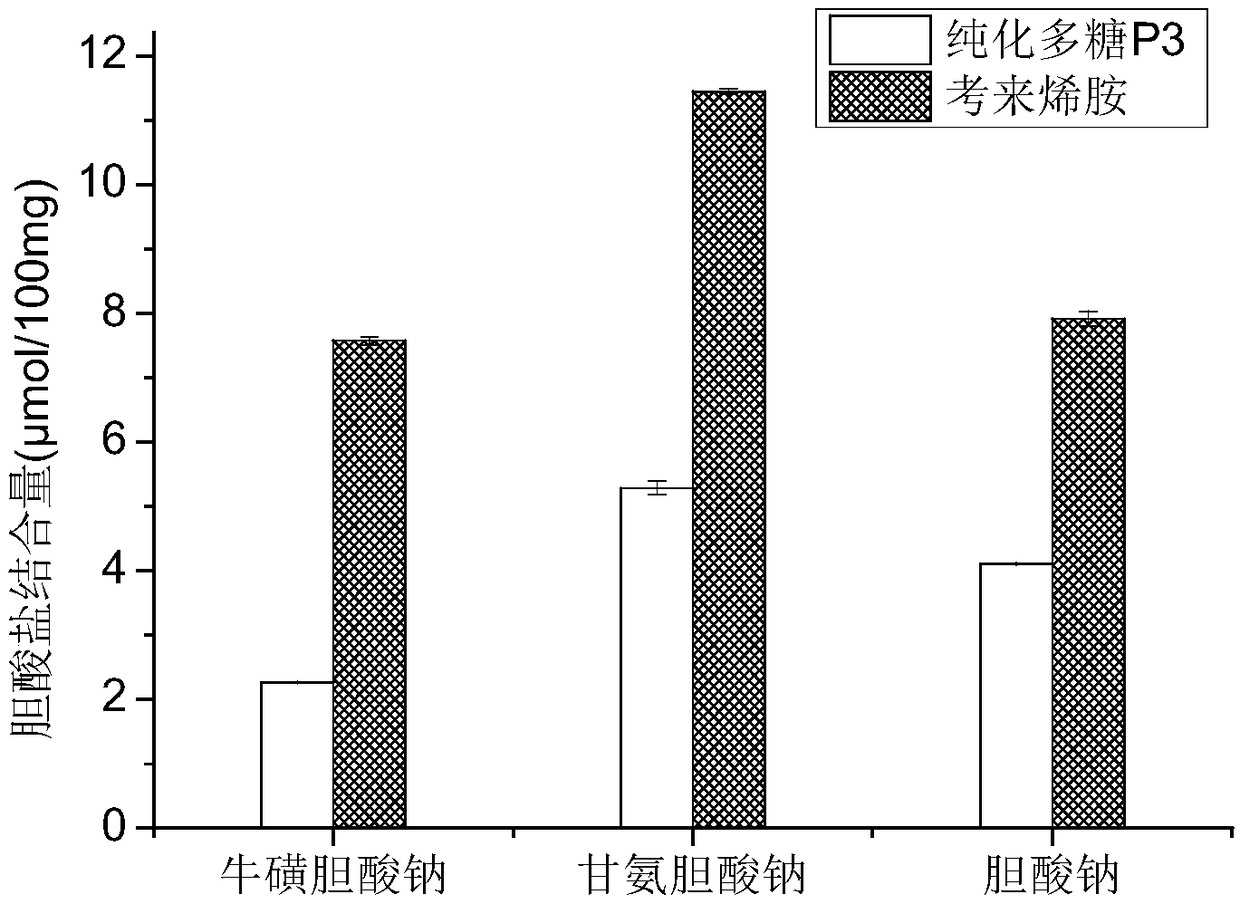
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] A method for extracting and isolating and purifying polysaccharides from myrtle fruit, comprising the following steps:
[0044](1) Extract polysaccharides from myrtle fruit: Weigh 110g of dried myrtle fruit and crush them, pass through a 40-mesh sieve, weigh 100g of dry powder, add 1000mL of distilled water, boil in a reflux device for 4h, and take the filter residue after suction filtration Then add 1000 mL of distilled water, boil for 4 h in a reflux device, combine the supernatants, and concentrate under reduced pressure. Slowly add 4 times the volume of 95% (V / V) ethanol to the concentrated solution, and keep stirring with a glass rod to uniformly precipitate the polysaccharide, then put it in a refrigerator at 4°C for 12 hours, and then centrifuge at 5000r / min for 15 minutes to collect the precipitate. After drying, myrtle fruit crude polysaccharide is obtained;
[0045] (2)H 2 o 2 Decolorization method: Weigh 20g myrtle fruit crude polysaccharide, add 100mL dis...
Embodiment 2
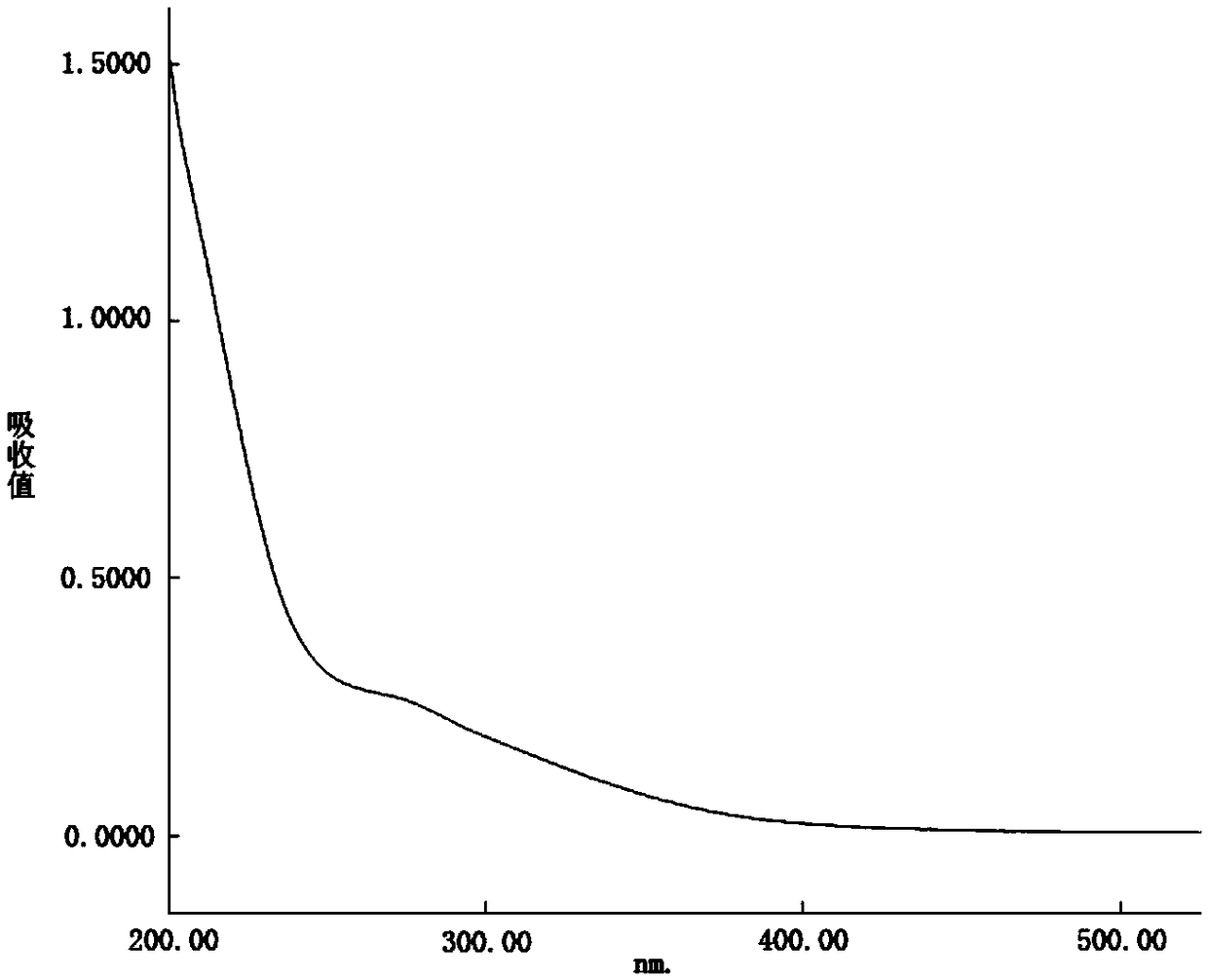
[0055] The myrtle fruit polysaccharide P3 obtained in Example 1 was analyzed by ultraviolet spectrum, and 1 mg polysaccharide sample was weighed to prepare a 1 mg / mL polysaccharide solution, and the ultraviolet spectrum was scanned in the range of 200-500 nm.
[0056] figure 2 It is the ultraviolet spectrogram of P3, and the results show that this component has no obvious absorption peaks at 260nm and 280nm, indicating that it does not contain protein and nucleic acid substances.
Embodiment 3
[0058] Carry out polysaccharide molecular weight analysis to the myrtle fruit polysaccharide P3 that embodiment 1 obtains, concrete experimental method is as follows:
[0059] Molecular weights were determined using gel permeation chromatography (GPC). Take 2 mg of polysaccharide sample, add 0.02 mol / L phosphate buffer solution to dissolve, prepare 2.0 mg / mL solution, filter with 0.22 μm sterile filter membrane, and take the filtrated liquid for later use. Chromatographic conditions: column temperature 35°C, 0.02mol / L phosphate buffer as mobile phase, flow rate 0.6mL / min, injection volume 20μL, Waters 2410 differential refractive index detector for detection. Prepare a series of dextran solutions with different molecular weights (700, 400, 200, 100, 50, 30, 10, 5kD) as standards, draw a standard curve, and calculate the molecular weight of the sample according to its corresponding elution volume against the standard curve .
[0060] The measured molecular weight of the myrtl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com