Method for efficiently separating lignin based on dilute acid preimpregnation
A lignin and pre-impregnation technology, which is applied in the field of biomass separation and conversion, can solve the problems of low yield, long-term mechanical action, fracture, etc., and achieve the effects of high yield, pollution reduction and cost reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
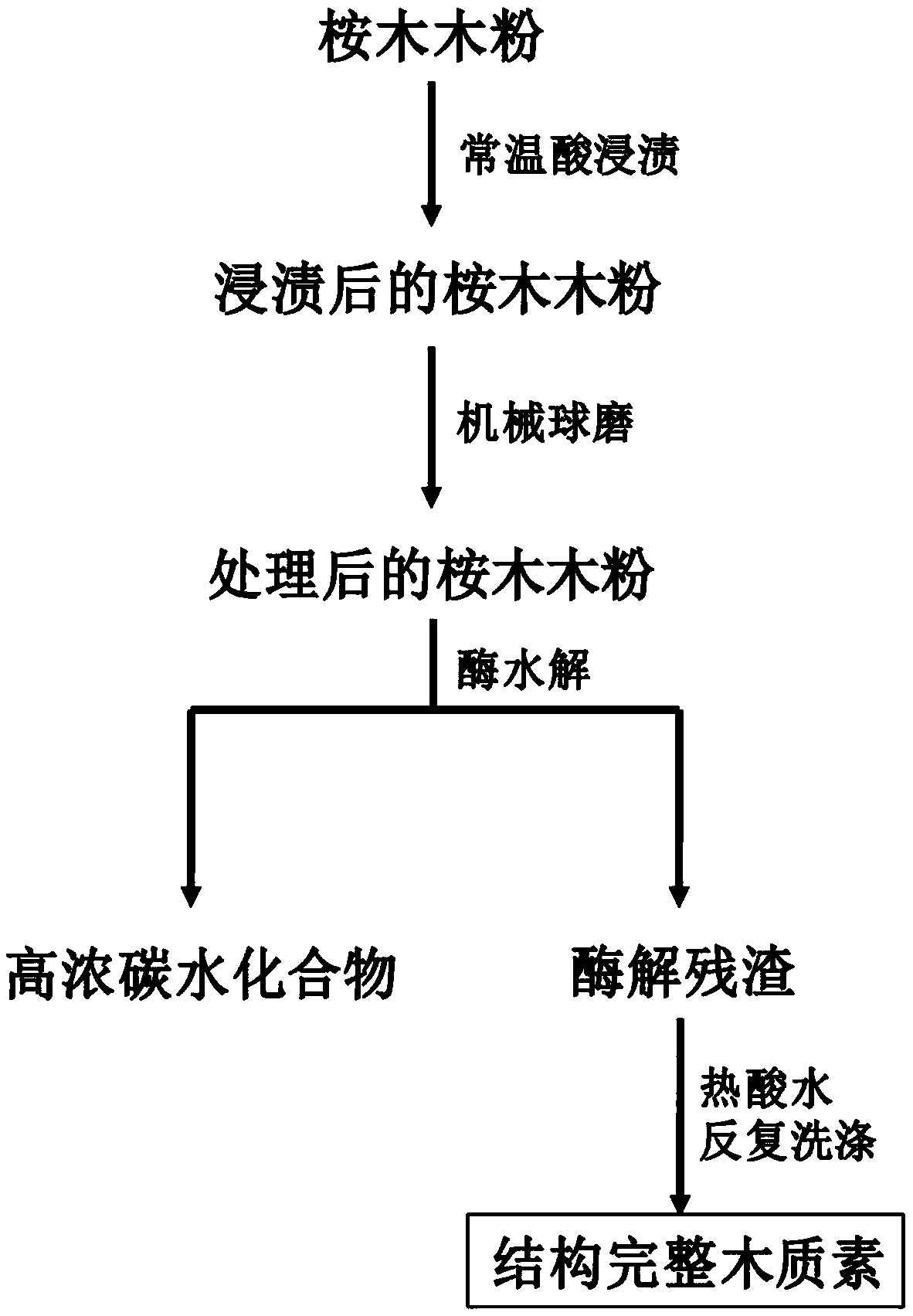
[0026] (1) Raw material pretreatment stage: crush the eucalyptus wood raw material to 20-100 mesh, and dry it.
[0027] (2) Pre-impregnation-ball milling stage: mix eucalyptus raw material with 5% dilute acetic acid solution at a ratio of 1g: 4ml, stand for impregnation at room temperature for 12h (overnight), freeze-dry it after impregnation, and then freeze-dry The eucalyptus raw material was ball milled (450-500rpm) for 2 hours to obtain the ball milled eucalyptus raw material.
[0028] (3) Enzymatic hydrolysis of treated eucalyptus raw materials: add sodium acetate buffer to the milled eucalyptus raw materials, adjust the pH to 4.8 with acetic acid, then add 10FPU / g cellulose compound enzyme, and enzymatically hydrolyze at 50°C 48h. After the enzymatic hydrolysis, the mixture was centrifuged to remove carbohydrates to obtain an enzymatic hydrolysis residue.
[0029] (4) The enzymolysis residue was repeatedly washed with hot acid water (pH=2) to remove polysaccharides and...
Embodiment 2
[0031] (1) Raw material pretreatment stage: crush the eucalyptus wood raw material to 20-100 mesh and dry it.
[0032] (2) Pre-impregnation-ball milling treatment stage: mix eucalyptus raw material with 2.5% dilute acetic acid solution in a ratio of 1g:3ml, stand for impregnation at room temperature for 12h (overnight), freeze-dry it after impregnation, and then freeze-dry The eucalyptus raw material was ball milled (450-500rpm) for 2 hours to obtain the ball milled eucalyptus raw material.
[0033] (3) Enzymolysis of treated raw materials: Add sodium acetate buffer to ball-milled eucalyptus raw materials, adjust pH to 4.8 with acetic acid, then add 10 FPU / g cellulose compound enzyme, and enzymolyze at 50°C for 48 hours. After the enzymatic hydrolysis, the mixture was centrifuged to remove carbohydrates to obtain an enzymatic hydrolysis residue.
[0034] (4) The enzymolysis residue was repeatedly washed with hot acid water (pH=2) to remove polysaccharides and monosaccharides,...
Embodiment 3
[0036] (1) Raw material pretreatment stage: crush the eucalyptus wood raw material to 20-100 mesh, and dry it.
[0037] (2) Pre-impregnation-ball milling treatment stage: mix eucalyptus raw material with 1% dilute acetic acid solution at a ratio of 1g:5ml, stand for impregnation at room temperature for 12h (overnight), freeze-dry it after impregnation, and then freeze-dry The eucalyptus raw material was ball milled (450-500rpm) for 2 hours to obtain the ball milled eucalyptus raw material.
[0038] (3) Enzymolysis of treated raw materials: Add sodium acetate buffer to ball-milled eucalyptus raw materials, adjust pH to 4.8 with acetic acid, then add 10 FPU / g cellulose compound enzyme, and enzymolyze at 50°C for 48 hours. After the enzymatic hydrolysis, the mixture was centrifuged to remove carbohydrates to obtain an enzymatic hydrolysis residue.
[0039] (4) The enzymolysis residue was repeatedly washed with hot acid water (pH=2) to remove polysaccharides and monosaccharides, an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com