Preparation method of lithium iron phosphate battery material
A lithium iron phosphate battery, phosphoric acid technology, applied in battery electrodes, secondary batteries, nanotechnology for materials and surface science, etc., can solve the difficulty of increasing raw material screening, high magnetic foreign matter in lithium iron phosphate, battery cycle Issues such as lifetime and safety performance impact
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
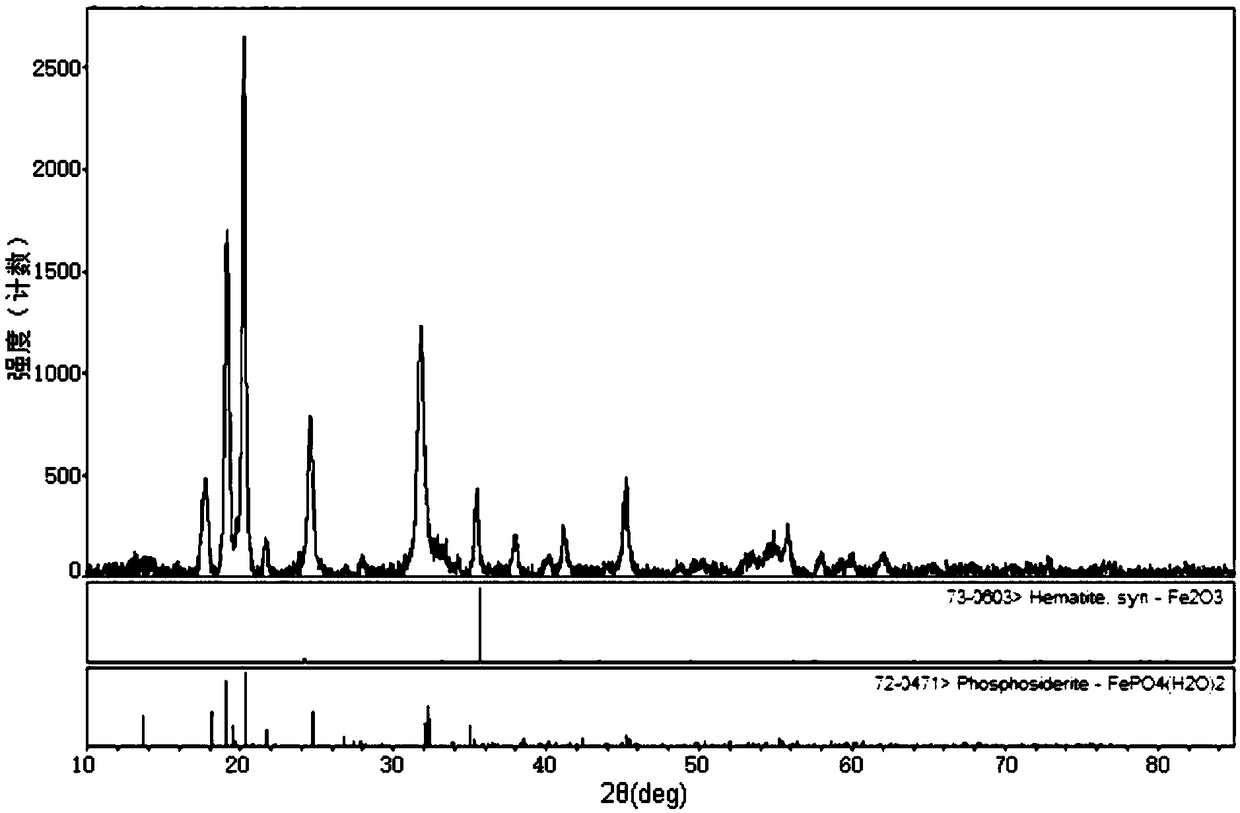
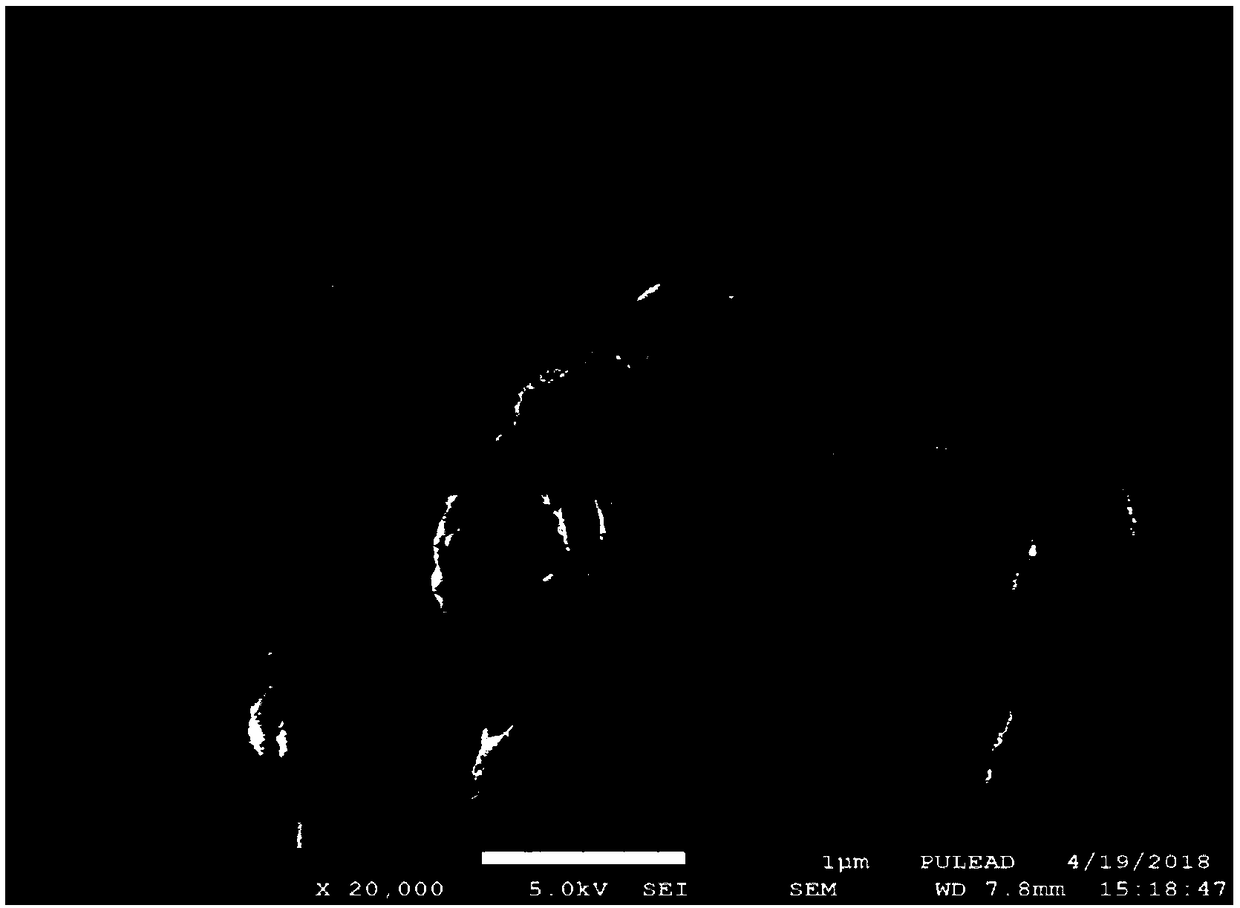
[0047] Mix iron source (ferrous sulfate), phosphorus source (phosphoric acid + ammonium dihydrogen phosphate) and plasticizer (sodium hydroxide) in a molar ratio of 0.9:(0.5+0.5):0.9 and dissolve in 500ml deionized water, The concentration of Fe ions is 1mol / L; all materials are mixed evenly and transferred to a 1L three-necked flask, and placed in an electric heating mantle for heating, using an electric stirrer to stir at a speed of 200rpm, and the temperature of the solution system rises to 50 ° C, adding 0.15molH 2 o 2 (30% of the molar amount of iron source) to make Fe 2+ Fully oxidize, heat the oxidized solution system to 85°C for 4 hours, and obtain xFePO 4 (H 2 O) 2 ·(1-x)Fe 2 o 3 The pink precipitate was analyzed by X-ray diffractometer software and x was 0.928; the pink precipitate was pre-fired in a muffle furnace at 550°C for 5 hours to obtain 0.928FePO 4 0.072 Fe 2 o 3 Composite; the X-ray diffraction spectrum, field emission electron microscopy and parti...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Iron source (ferrous sulfate + ferrous chloride), phosphorus source (ammonium dihydrogen phosphate) and plasticizer (NaHCO 3+NaOH) according to the molar ratio (0.2+0.65):1:(0.3+0.3) and dissolved in 600ml of deionized water for mixing, in which the concentration of Fe ions is 1.1mol / L, and all materials are mixed evenly and then transferred to a 1L three-necked flask , and placed in an electric heating mantle for heating, using an electric stirrer to stir at a speed of 200rpm, so that the temperature of the solution system rose to 60 ° C, adding 0.198molH 2 o 2 (30% of the molar amount of iron source) to make Fe 2+ Fully oxidize, heat the oxidized system to 90°C for 2 hours to obtain xFePO 4 (H 2 O) 2 ·(1-x)Fe 2 o 3 Pink precipitate; x equal to 0.911 calculated from X-ray diffractometer software.
[0052] The white precipitate was pre-fired in a muffle furnace at 550°C for 4 hours to obtain 0.911FePO 4 0.089Fe 2 o 3 complex; the complex, Li 2 CO 3 , NH 4 h...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Mix iron source (ferrous sulfate), phosphorus source (ammonium dihydrogen phosphate) and plasticizer (sodium carbonate) in a molar ratio of 1.05:1:0.1 and dissolve in 700ml of deionized water, wherein the Fe ion concentration is 0.5mol / L, all materials were mixed evenly and transferred to a 1L three-neck flask, and placed in a water bath with magnetic stirring for heating, the speed was adjusted to 400rpm, the temperature of the solution system rose to 55°C, and 0.175molH 2 o 2 (50% of the molar amount of iron source) to make Fe 2+ Fully oxidize, heat the oxidized system to 85°C for 10 hours to obtain xFePO 4 (H 2 O) 2 ·(1-x)Fe 2 o 3 Pink precipitate; x equal to 0.935 calculated from X-ray diffractometer software.
[0056] The white precipitate was pre-fired in a muffle furnace at 600°C for 3 hours to obtain 0.935FePO 4 0.065 Fe 2 o 3 complex; the complex, LiOH and phosphorus source supplement ((NH 4 ) 2 HPO 4 +NH 4 h 2 PO 4 ) is mixed in molar ratio acc...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Compaction density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com