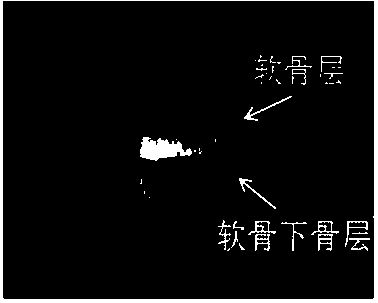
Cartilage-bone repair support with bionic gradient and preparation method thereof
A bone repair and subchondral bone technology, applied in tissue regeneration, medical science, prosthesis, etc., can solve the problem of poor interface bonding, inability to simulate the characteristics of continuous gradient distribution, and the bonding force between scaffold layers and layers Weakness and other problems, to achieve the effect of convenient operation, good in situ induction of cartilage tissue growth, biocompatibility in situ induction of cartilage growth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] 1. Preparation of cartilage layer composite precursor solution
[0050] (1) Dissolve 50 mg of sodium hyaluronate in 10 mL of deionized water, and magnetically stir for 30 min in a water bath at 45-60°C until completely dissolved to obtain an aqueous solution of sodium hyaluronate;
[0051] (2) Dissolve 0.5 g of chitosan in an acetic acid solution with a volume fraction of 1%, and stir magnetically for 30 minutes in a water bath at 37°C to obtain chitosan acetic acid solution A;
[0052] (3) Under the condition of magnetic stirring, slowly add the sodium hyaluronate aqueous solution obtained in step (1) into the chitosan acetic acid solution A obtained in step (2), and fully stir to form a uniform mixed solution;
[0053] (4) Add 4.5 mL, 4 mg / mL of EDC and 5.6 mL, 1 mg / mL of NHS to the mixture obtained in step (3), and cross-link at room temperature for 4 h to obtain the precursor solution of the cartilage layer complex;
[0054] 2. Preparation of Subchondral Bone Layer...
Embodiment 2
[0065] 1. Preparation of cartilage layer composite precursor solution
[0066] (1) Dissolve 100 mg of sodium hyaluronate in 10 mL of deionized water, and magnetically stir for 30 min in a water bath at 45-60°C until completely dissolved to obtain a sodium hyaluronate aqueous solution;
[0067] (2) Dissolve 0.75 g of chitosan in an acetic acid solution with a volume fraction of 1.5%, and magnetically stir for 30 minutes in a water bath at 37°C to obtain chitosan acetic acid solution A;
[0068] (3) Under the condition of magnetic stirring, slowly add the sodium hyaluronate aqueous solution obtained in step (1) into the chitosan acetic acid solution A obtained in step (2), and fully stir to form a uniform mixed solution;
[0069] (4) Add 4.5 mL, 4 mg / mL of EDC and 5.6 mL, 1 mg / mL of NHS to the mixture obtained in step (3), and cross-link at room temperature for 4 h to obtain the precursor solution of the cartilage layer complex;
[0070] 2. Preparation of Subchondral Bone Layer...
Embodiment 3
[0081] 1. Preparation of cartilage layer composite precursor solution
[0082] (1) Dissolve 150 mg of sodium hyaluronate in 10 mL of deionized water, and magnetically stir for 30 min in a water bath at 45-60°C until completely dissolved to obtain a sodium hyaluronate aqueous solution;
[0083] (2) Dissolve 1.0 g of chitosan in an acetic acid solution with a volume fraction of 2%, and stir magnetically for 30 minutes in a water bath at 37°C to obtain chitosan acetic acid solution A;
[0084] (3) Under the condition of magnetic stirring, slowly add the sodium hyaluronate aqueous solution obtained in step (1) into the chitosan acetic acid solution A obtained in step (2), and fully stir to form a uniform mixed solution;
[0085] (4) Add 4.5 mL, 4 mg / mL of EDC and 5.6 mL, 1 mg / mL of NHS to the mixture obtained in step (3), and cross-link at room temperature for 4 h to obtain the precursor solution of the cartilage layer complex;
[0086] 2. Preparation of Subchondral Bone Layer Co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com