Pseudomonas rhodesiae PYQ4 for highly producing exopolysaccharide and preparation method and application of exopolysaccharide
A technology of Pseudomonas Roche and extracellular polysaccharide is applied in the field of microorganisms to achieve the effects of repairing post-sun damage, low price, and simple and easy-to-obtain active ingredients
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0019] Example 1: Extraction and Content Determination of Exopolysaccharides Produced by Pseudomonas Roche PYQ4
[0020] An appropriate amount of the above strains were picked from the sugar-producing solid medium and inoculated into the sugar-producing fermentation medium. The fermentation broth was obtained by shaking culture for 48h in a shaker with a rotational speed of 150rpm at 30°C. figure 1 It is the plate culture character of the strain PYQ4 of the present invention.
[0021] Among them, the used sugar-producing solid medium components are: sucrose 20g / L, tryptone 10g / L, yeast powder 5g / L, Na 2 HPO 4 ·12H 2 O 3g / L, agar 20g / L, the balance is distilled water. The components of the sugar-producing fermentation broth used are: sucrose 50g / L, tryptone 5g / L, yeast powder 1g / L, Na 2 HPO 4 ·12H 2 O 3g / L, the balance is distilled water.
[0022] The fermentation broth was centrifuged at 4000 g for 10 min to remove bacterial cells to obtain a supernatant. 1 / 4 volume o...
example 2
[0024] Example 2: Identification of the microbial strains of the present invention
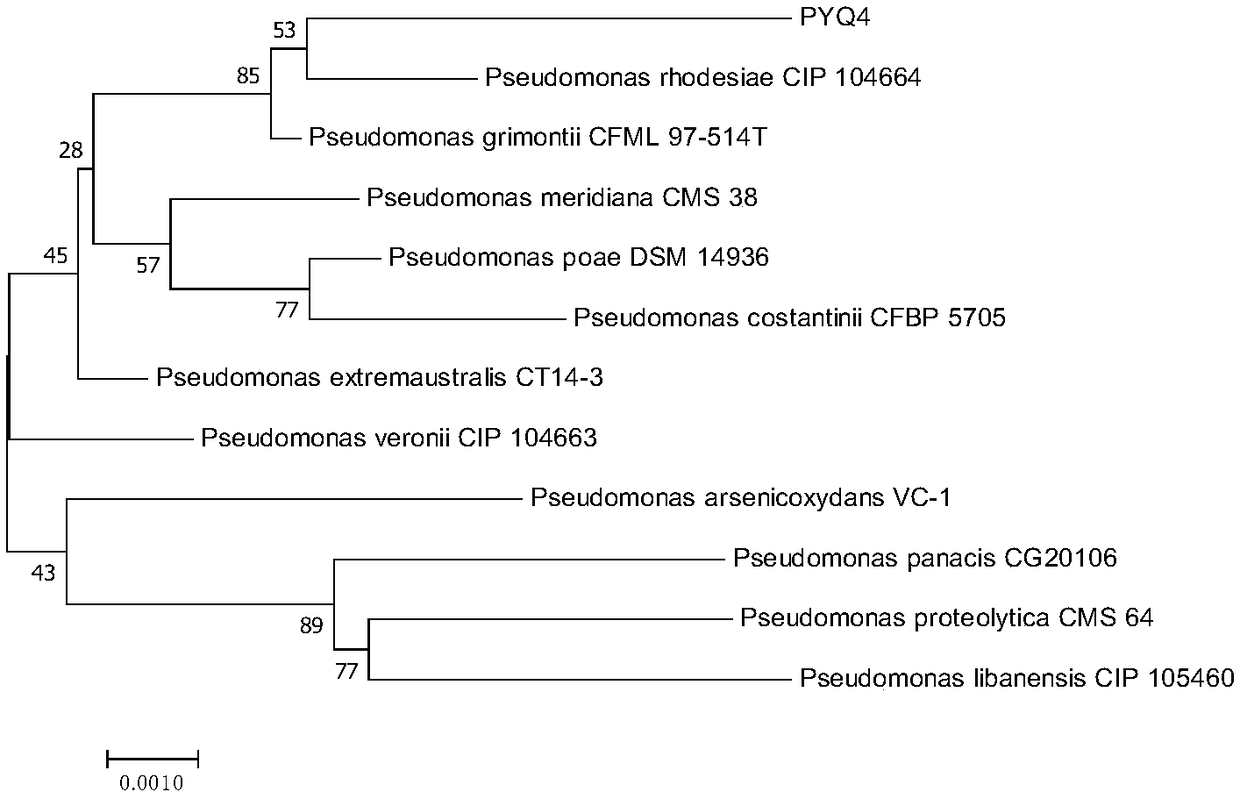
[0025] This strain is red by Gram staining and is a Gram-negative bacteria. The total DNA of the strain of the present invention was extracted according to the steps of the Takara Bacteria Genomic DNA Extraction Kit, and the 16S rDNA gene of the strain was amplified with the universal primers 27F and 1492R. Sequencing, and bacterial species identification by determining the sequence of 16S rDNA. The obtained sequence results were compared by Blast at NCBI, and the recognized standard sequence data homologous to the 16S rDNA of the strain was obtained from the database of GenBank. The MEGA software was used to calculate the sequence similarity and the Neighbor-Joining algorithm was used as the system. Developmental Analysis.
[0026] The constructed phylogenetic tree of the strain is as follows figure 2 As shown, it has the highest homology with Pseudomonas rhodesiae, so the strain describe...
example 3
[0027] Example 3: Application of above-mentioned polysaccharide as post-sun damage repairing agent
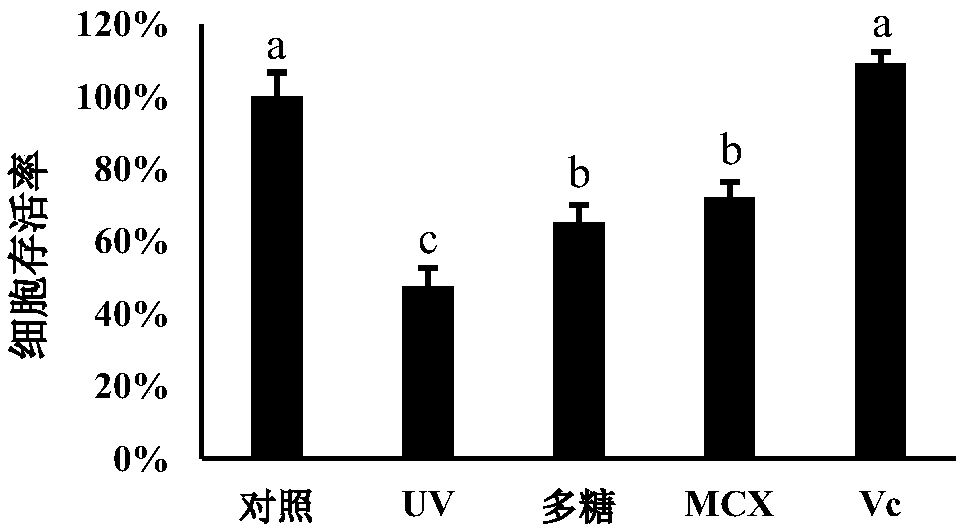
[0028] HaCaT cells in log phase were collected and seeded in a 96-well plate, 5000 cells per well, at 37°C, 5% CO. 2 Cultivated in an incubator. The cells were divided into control group, UV model group, polysaccharide group (1mg / mL), ethylhexyl methoxycinnamate (MCX) group (8%) and ascorbic acid (Vc) group (1mg / mL), of which the latter two. The group was the positive control, and each group was replicated with 3 wells. After the cells were cultured for 24 h, the medium was changed to phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and then irradiated with UV, and the control group was wrapped with tin foil to protect from light. Aspirate PBS, add the medium, the medium of the polysaccharide group contains 1 mg / mL of the above-mentioned strains to produce extracellular polysaccharides, the medium of the MCX group contains 8% ethylhexyl methoxycinnamate, and the Vc group is cultured The base...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com