Method for preparing steroid drug intermediate by mixed bacterial fermentation transformation of phytosterol
A technology of phytosterols and steroidal drugs, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, fermentation, etc., can solve the problems of difficult temperature and high enzyme activity, and achieve shortened conversion cycle, high product formation rate, and reduced The effect of production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
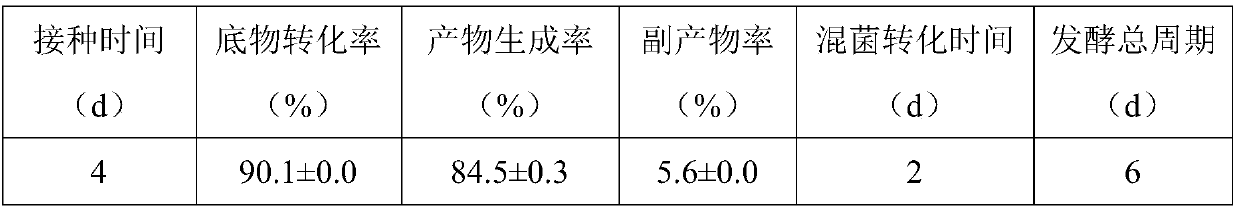
[0024] Example 1: Effect of Ochraus inoculum Size on Sequential Transformation of Phytosterols to Produce 11α-OH AD
[0025] (1) Mycobacterium (M.neoaurum) TCCC 11028M3 (MNR M3) was used as the production strain, the strain taken from the glycerol tube was streaked on the slant medium, cultured at 29°C for 3-4d, and the slant was activated twice;
[0026] (2) Mycobacterium TCCC 11028M3 (MNR M3) seed culture: pour a certain amount of 0.5% Tween 80 sterile aqueous solution into the solid medium of step (1) under aseptic operation to wash the slant seeds, so that the thalline OD 600The value is controlled at 1.0±0.2, inoculated into 30mL seed medium with 3% inoculum size, and cultured at 28°C and 200r / min until the logarithmic growth phase (36-48h);
[0027] (3) Mycobacterium TCCC 11028M3 (MNR M3) fermentation culture: Accurately weigh an appropriate amount of phytosterols so that the final concentration in the fermentation medium is 3g / L, and inoculum the seeds in step (2) by 8...
Embodiment 2
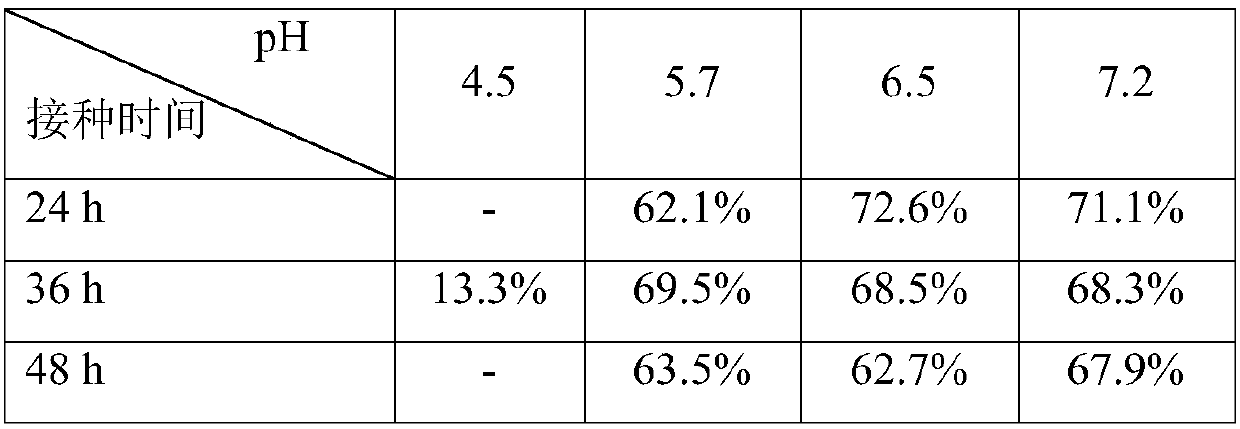
[0041] Example 2: Effect of Ochrae inoculation time on sequential transformation of phytosterol production (11α-OH AD)
[0042] Except the following content, other is the same as embodiment 1.
[0043] In the sequential transformation system, considering that molds have obvious advantages over the growth and reproduction of mycobacteria, the mycobacteria grow to a certain stage and the side chain degrades phytosterols to generate a certain concentration of androst-4-ene-3 ,17-diketone (AD), it is beneficial to the whole flora system to insert A.
[0044] (1) Biotransformation: After the side chain of mycobacteria degrades phytosterols to generate a certain concentration of androst-4-ene-3,17-dione, it is the 1d, 2d, 3d, and 4d of mycobacterial transformation, respectively. 50% of the inoculum was added to Ochrae sp. CICC41473 cells for subsequent transformation experiments, the culture temperature was 28°C, and the transformation was carried out at a speed of 200r / min for 2 d...
Embodiment 3
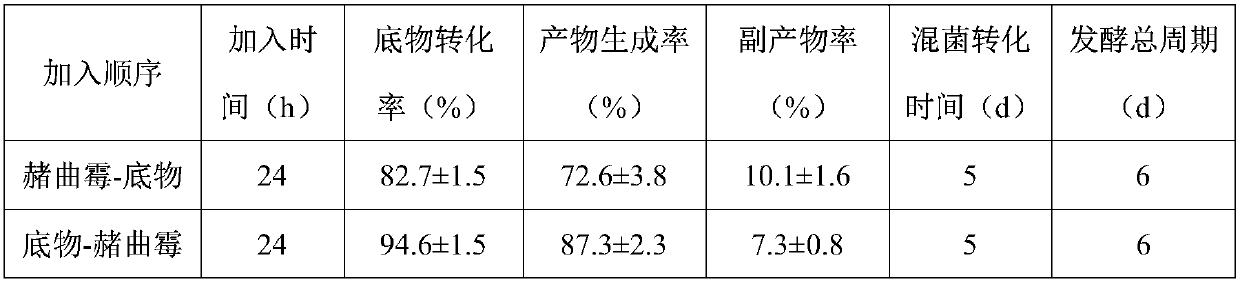
[0051] Example 3: Research on mixed culture transformation of phytosterols to generate 11α-OH AD
[0052] Except the following content, other is the same as embodiment 1.
[0053] (1) Biotransformation: Mycobacterium TCCC 11028M3 seed culture solution was inserted in 50mL fermentation medium by 8% inoculum, and the spore suspension of prepared Ochraus ochraci CICC 41473 was 10% at the final concentration of spores. 6 The inoculation amount of each / mL was inserted into the fermentation medium, and then phytosterols with a final concentration of 3g / L were added at 24h, 36h, and 48h respectively, the culture temperature was 28°C, and the transformation was carried out at a speed of 200r / min for 5d;
[0054] Described fermentation medium consists of: glucose 30g / L, citric acid 2g / L, ferric ammonium citrate 0.05g / L, magnesium sulfate 0.5g / L, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.5g / L, diammonium hydrogen phosphate 3.5 g / L, corn steep liquor 40g / L, silkworm chrysalis powder 2g / L, cyclod...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com