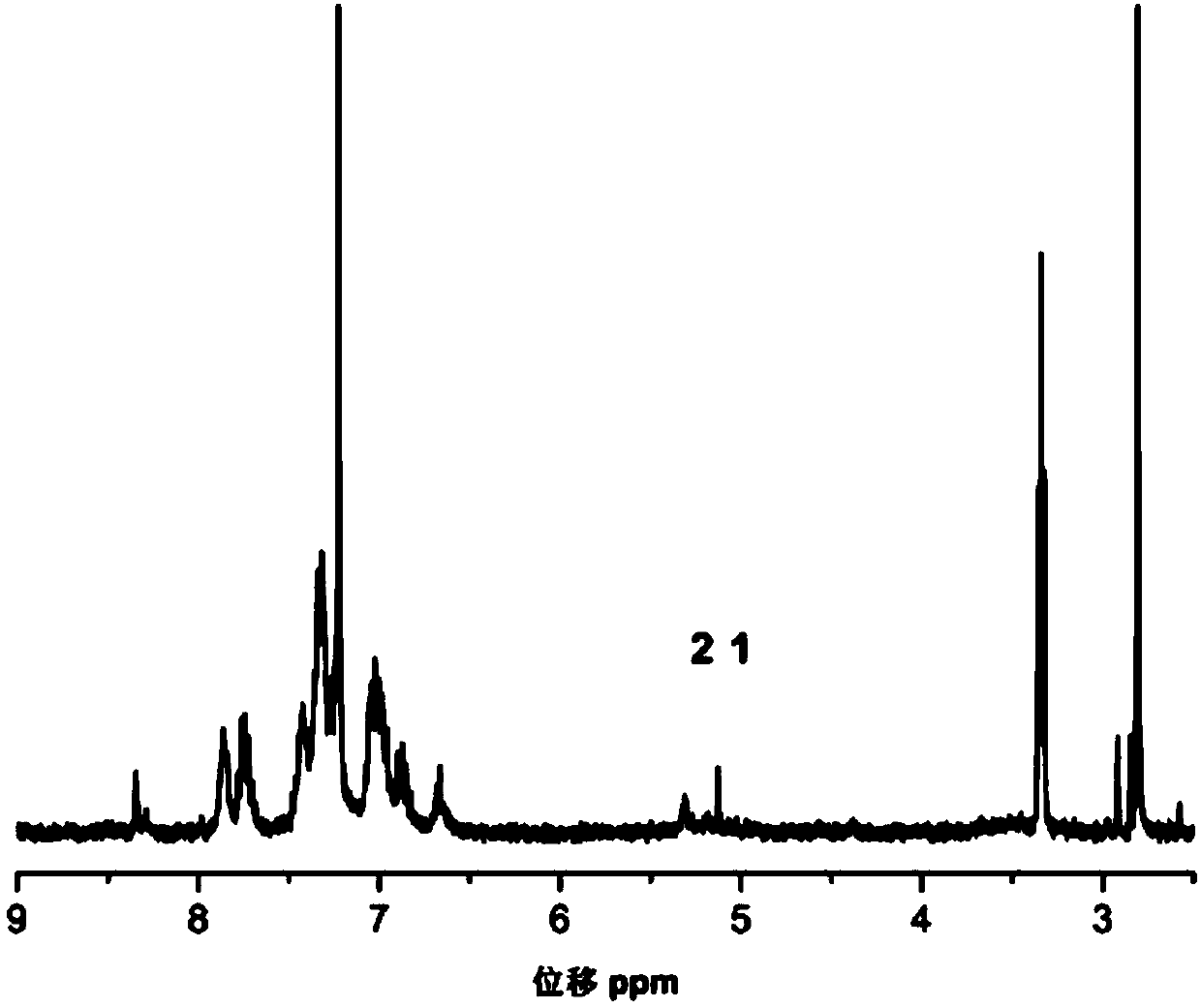
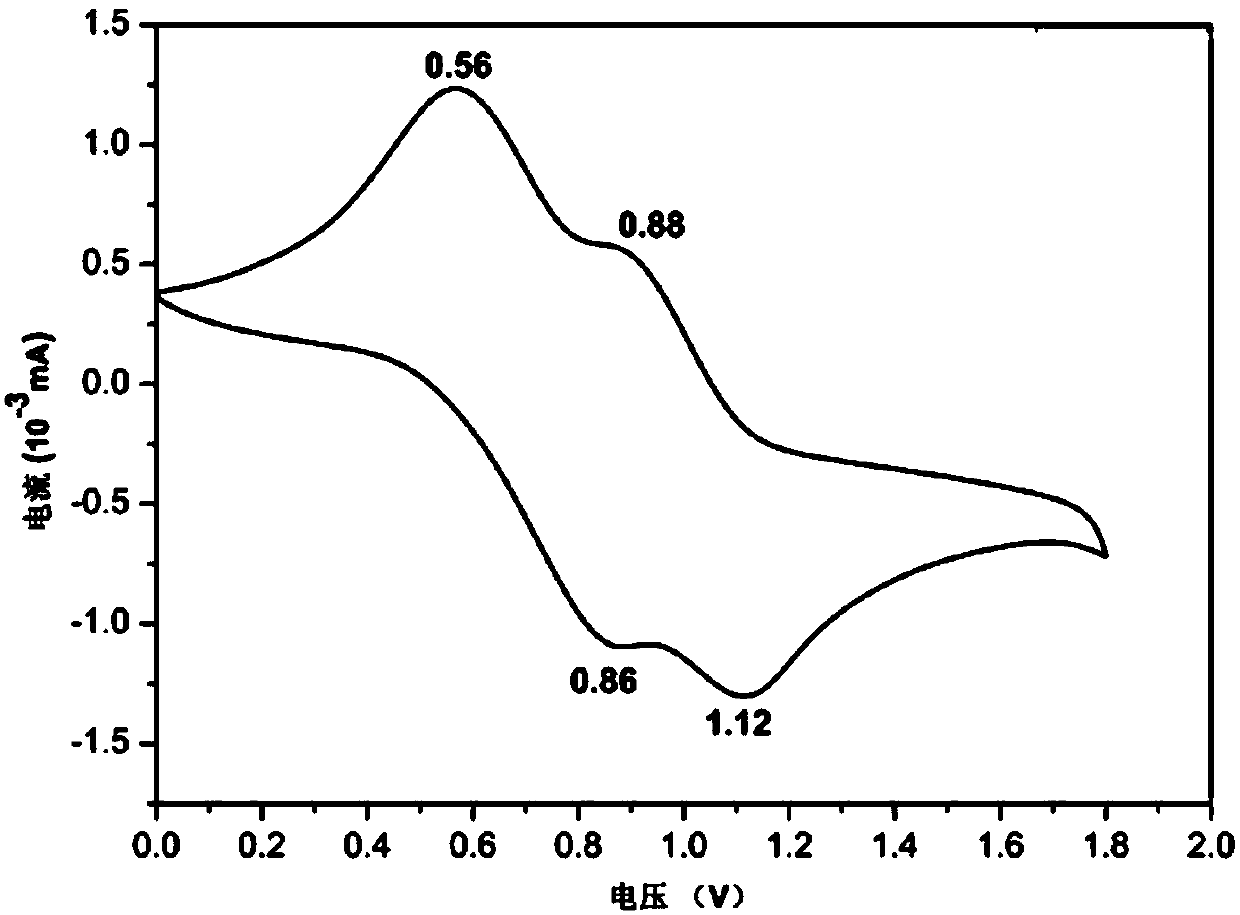
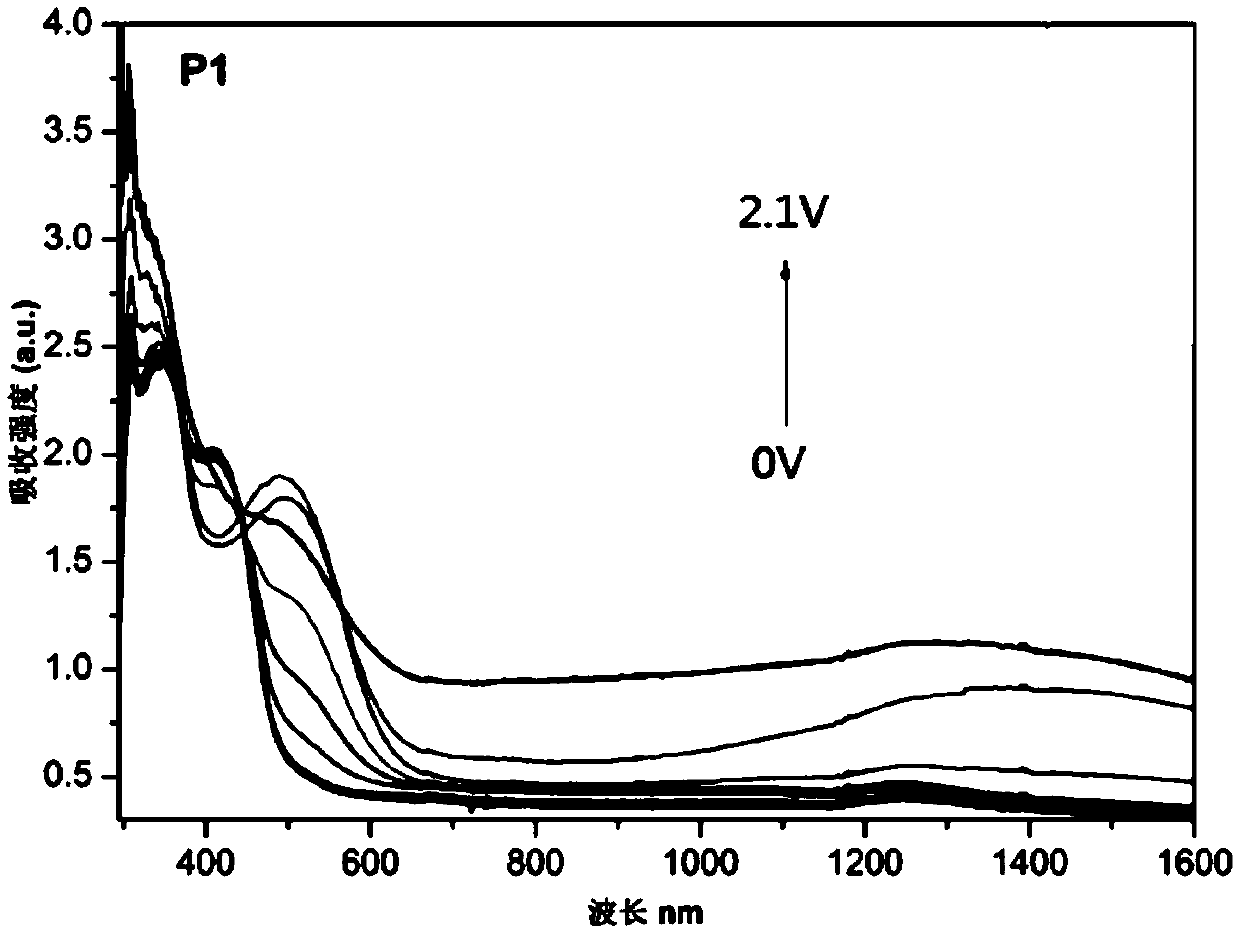
Triphenylamine-based polymer containing benzoxazine structure, as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology based on triarylamines and benzoxazines, applied in chemical instruments and methods, analysis through chemical reactions of materials, fluorescence/phosphorescence, etc., can solve the problem of poor film adhesion and durability of electrochromic polymer films Poor thermal performance and other problems, to achieve excellent electrochromic performance, excellent memory performance, and improve the effect of bonding strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0042] Specific embodiment 1: In this embodiment, the triarylamine-based polymer containing a benzoxazine structure is a triarylamine-based polymer containing a benzoxazine structure P1 or a triarylamine-based polymer containing a benzoxazine structure P2;
[0043] The structural formula of the triarylamine-based polymer P1 containing a benzoxazine structure is as follows:
[0044] In the formula, n is an integer of 3 to 10;
[0045] The structural formula of the triarylamine-based polymer P2 containing a benzoxazine structure is as follows:
[0046] , where n is an integer from 3 to 10.
[0047] In this embodiment, triphenylamine-based monomers are first prepared. In this embodiment, N,N-diphenyl-1,4-phenylenediamine and N,N'-diphenyl-biphenylenediamine are used as raw materials and then It reacts with p-fluoronitrobenzene to achieve nitration, and then reduces the nitro group to amino group. Using bisphenol A, paraformaldehyde, and triphenylamine-based monomers as raw ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0054] Specific embodiment two: the preparation method of triarylamine-based polymer P1 containing benzoxazine structure in this embodiment is as follows: 1. Synthesis of N, N'-bis(4-aminophenyl)-N, N'-diphenyl Base-1,4-phenylenediamine monomer: ①, in N 2 Under the atmosphere, put N,N-diphenyl-1,4-phenylenediamine monomer, sodium hydride and anhydrous N,N-dimethylformamide in a three-necked flask, and stir at 1~2 per second Add p-fluoronitrobenzene at the dropping rate, raise the temperature to 114-115°C, carry out constant temperature reaction, and then cool down; put the reaction product in water at 24-25°C until the crude product is precipitated, then filter the crude product, and use 99-100 Wash the crude product with water at ℃ for 2 to 3 times, dry the obtained crude product in a vacuum drying oven, and then recrystallize with ethanol, filter out the crystallized product after recrystallization, and vacuum dry the crystallized product to obtain a yellow powder M1; where...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0060] Specific embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 2 is that the yellow powder M1 described in step ① is N, N'-bis(4-nitrophenyl)-N, N'-diphenyl -1,4-Phenylenediamine. Others are the same as in the second embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com