Method for improving efficiency of killing retained bacteria by aminoglycoside antibiotics through low ion shock
An aminoglycoside and antibiotic technology, applied in botanical equipment and methods, chemicals for biological control, biocides, etc., can solve problems such as long contact time and bacterial resistance, reduce side effects, eliminate Bacterial persistence, the effect of reducing bacterial tolerance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
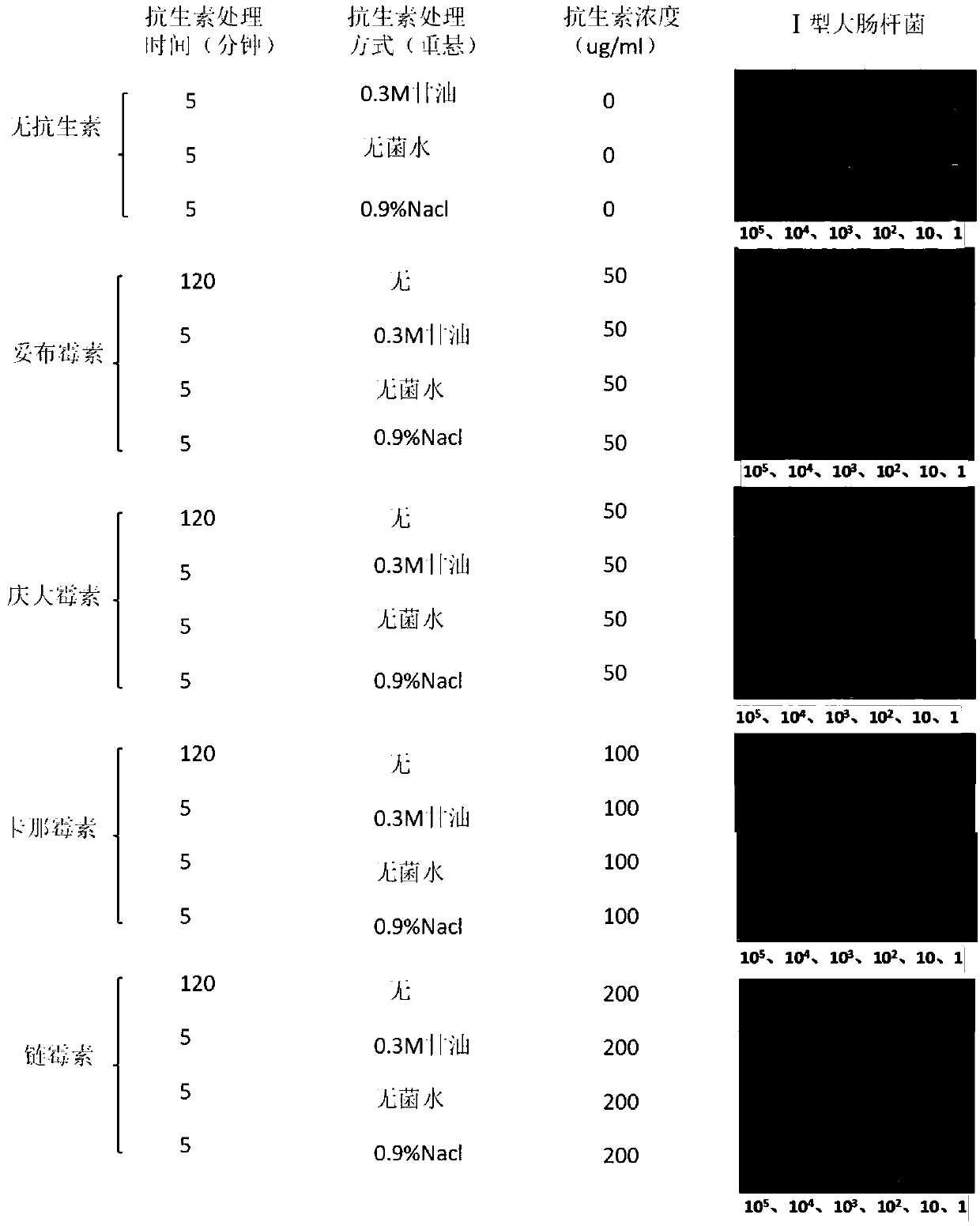
[0024] Low ion shock enhances the efficiency of aminoglycoside antibiotics in killing type Ⅰ Escherichia coli
[0025] 1. Activate the Escherichia coli standard strain (E.coli BW25113). Draw 1 μl of bacterial solution stored in a -80°C refrigerator with 40% glycerol, and inoculate it in 1ml M9 plus glucose liquid medium (configuration components: M9 medium, 5g / L glucose, 1.5g / L (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 , 1mg / L VB 1 , PH=7.3), cultured on a shaker (220rpm) at 37°C to the plateau phase, re-diluted 1000 times and inoculated in 10ml M9 plus glucose liquid medium, and cultivated to the logarithmic phase (OD 600 = 0.5-0.6). Take two 5ml EP tubes, put 4ml bacterial solution into each tube and centrifuge (5000g, 4℃, 5min), remove the supernatant; resuspend and centrifuge with the same volume of 4℃ pre-cooled M9 liquid medium (5000g, 4℃, 5min ), remove the supernatant; use 1ml normal temperature M9 liquid medium (PH=7.3) to resuspend and centrifuge (5000g, 4°C, 5min), remove the supernatant...
Embodiment 2
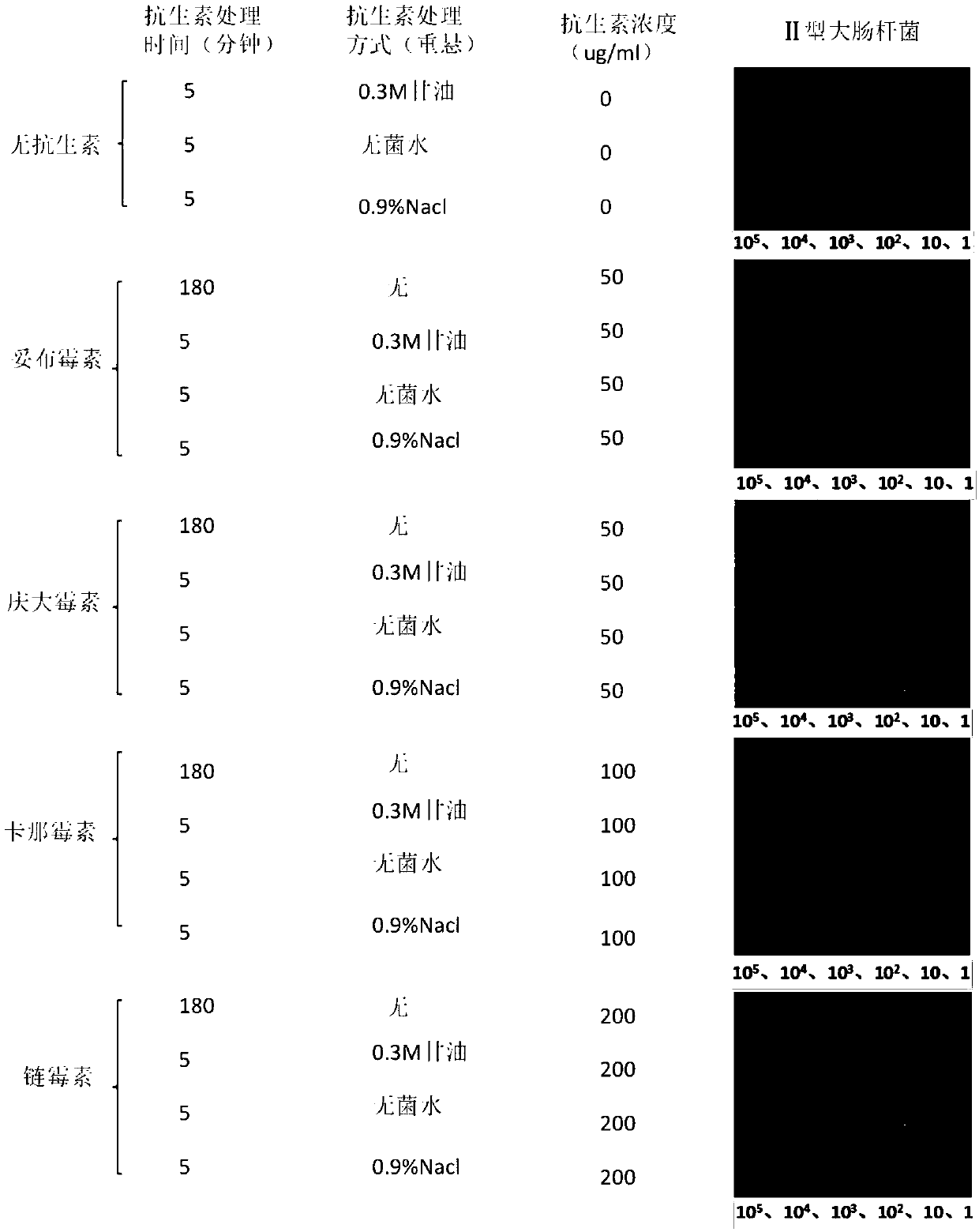
[0037] Low ion shock enhances the efficiency of aminoglycoside antibiotics in killing type Ⅱ Escherichia coli
[0038] 1. Activate the Escherichia coli standard strain (E.coli BW25113). Take 1 μl of bacterial solution stored in a -80°C refrigerator with 40% glycerol, inoculate it in 1ml of MHB liquid medium (Mueller-Hinton broth), and culture it on a shaker (220rpm) at 35°C for 24 hours (plateau period 10 9 CFU / ml), re-diluted 1000 times and inoculated in 2ml MHB liquid medium, cultured on a shaker (220rpm) at 35°C for 24h (plateau stage 10 9 CFU / ml). Take a 1.5ml EP tube, absorb 1ml of bacterial liquid and centrifuge (13000g, 2min), remove the supernatant; resuspend with 1ml of M9 carbon-free liquid medium and transfer 9ml of M9 carbon-free liquid medium into sterilized shake flasks (i.e.: the bacterial solution is 10 8 Concentration of CFU / ml (Continue culturing in a medium using M9 carbon-free liquid medium as a substrate), treat on a shaker (220rpm) at 37°C for 5h and t...
Embodiment 3
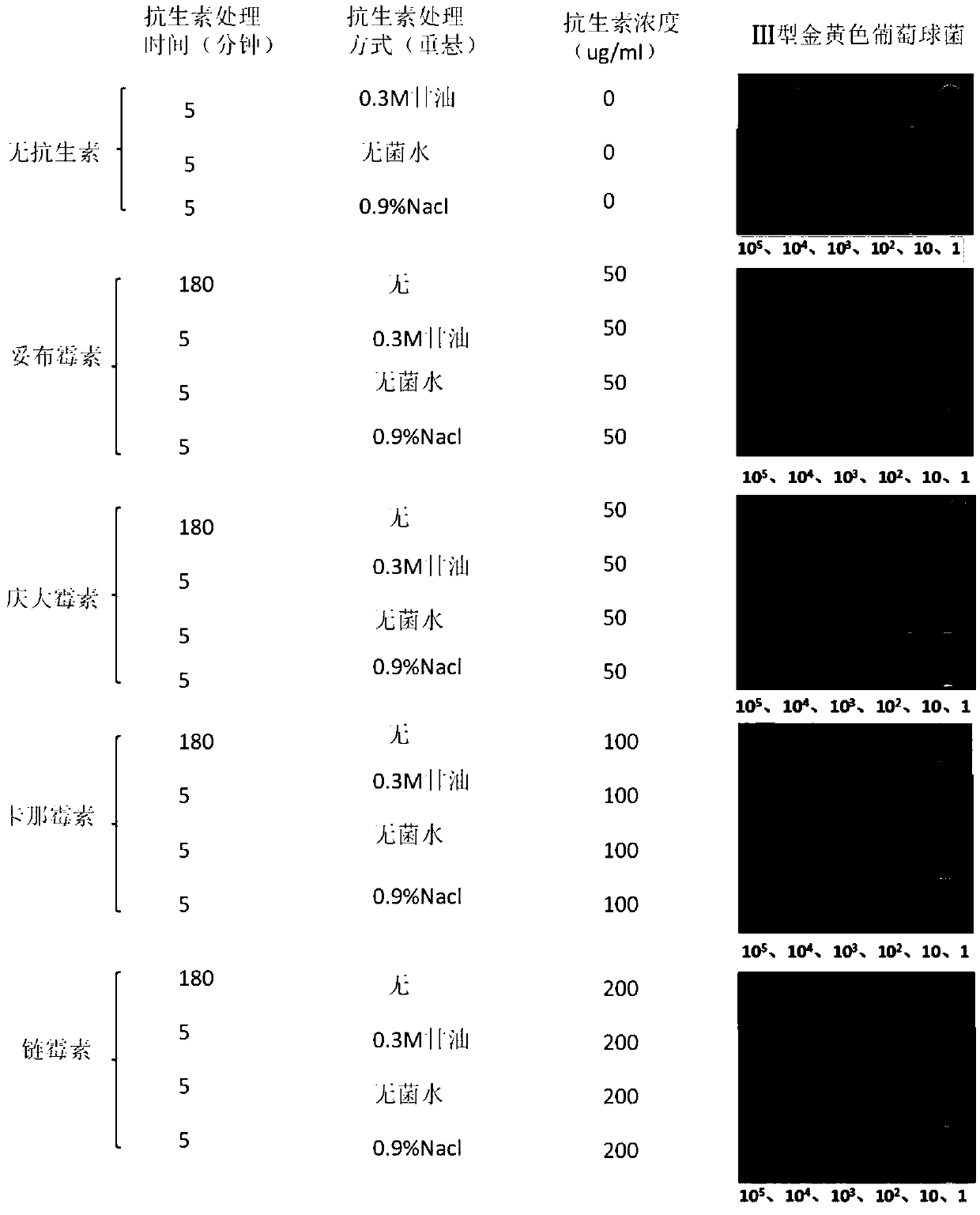
[0050] Hypoionic shock enhances the efficiency of aminoglycoside antibiotics in killing type Ⅲ Staphylococcus aureus
[0051] 1. Activate the standard strain of Staphylococcus aureus (S.aureus ATC25923). Take 1 μl of bacterial solution stored in a -80°C refrigerator with 40% glycerol, inoculate it in 1ml of MHB liquid medium (Mueller-Hinton broth), and culture it on a shaker (220rpm) at 35°C for 24 hours (plateau period 10 9 CFU / ml), re-diluted 1000 times and inoculated in 2ml MHB liquid medium, cultured on a shaker (220rpm) at 35°C for 24h (plateau stage 10 9 CFU / ml). Take a 1.5ml EP tube, absorb 1ml of the bacterial liquid and centrifuge (13000g, 2min), remove the supernatant; use 1ml of YNB carbon source-free liquid medium (Yeast nitrogen base broth, without anamino acid) to resuspend and 9ml of YNB carbon source-free liquid The culture medium was transferred into sterilized shake flasks respectively (that is, the bacterial solution was divided into 10 8 The concentratio...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com