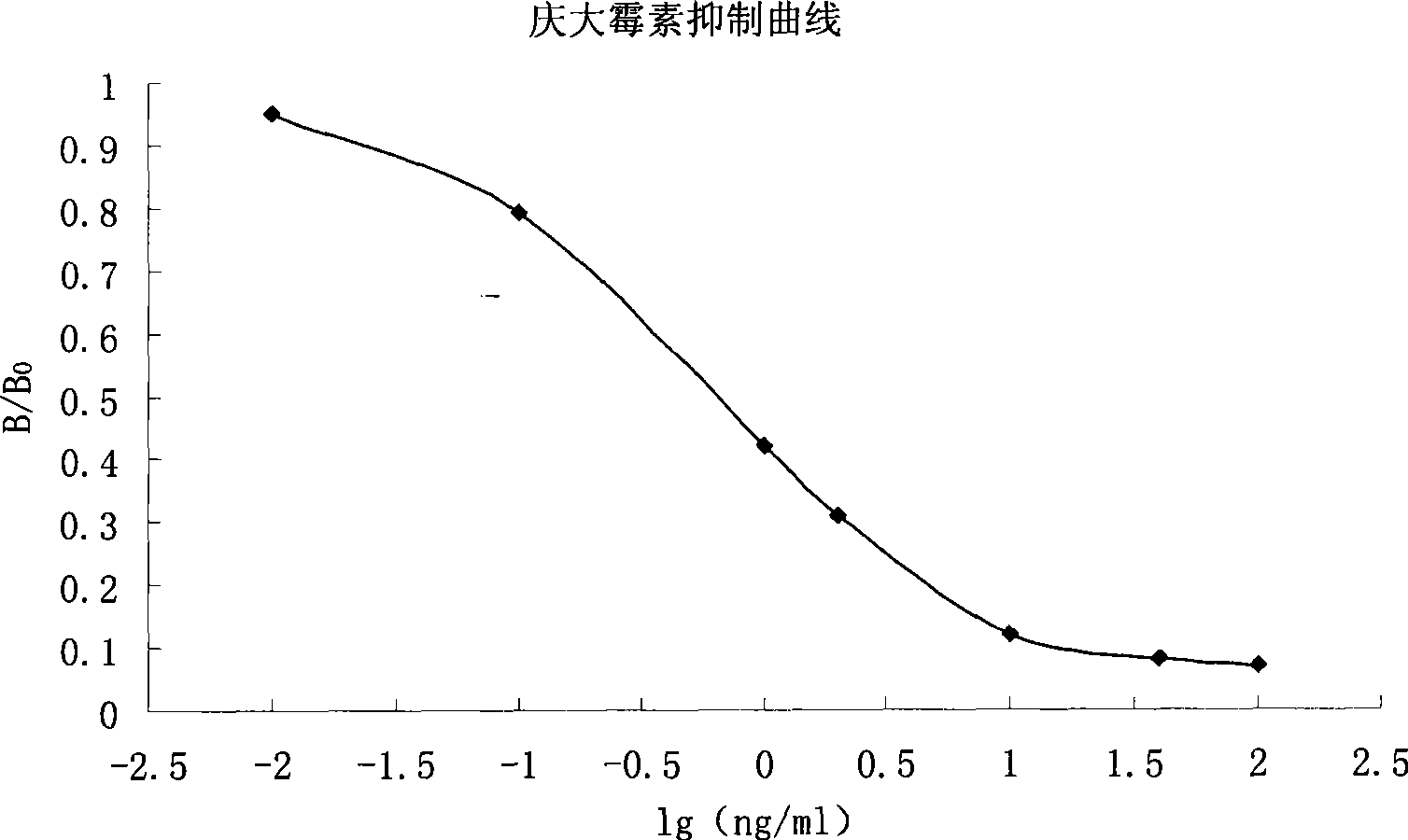
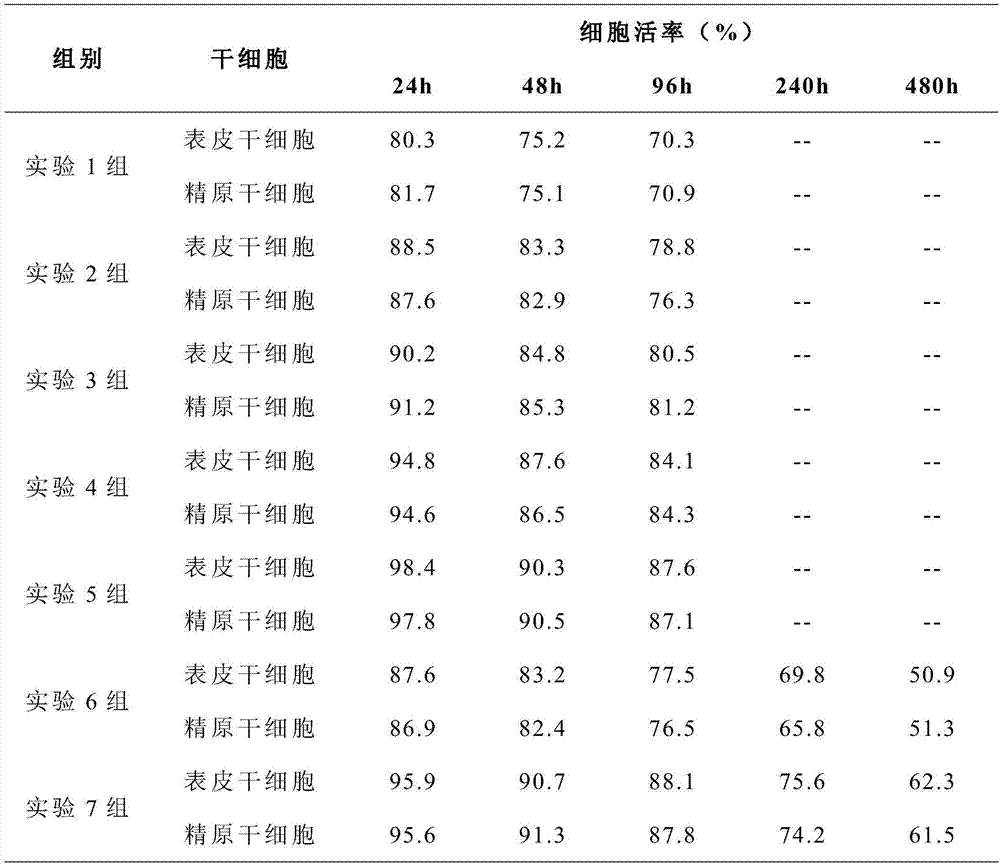
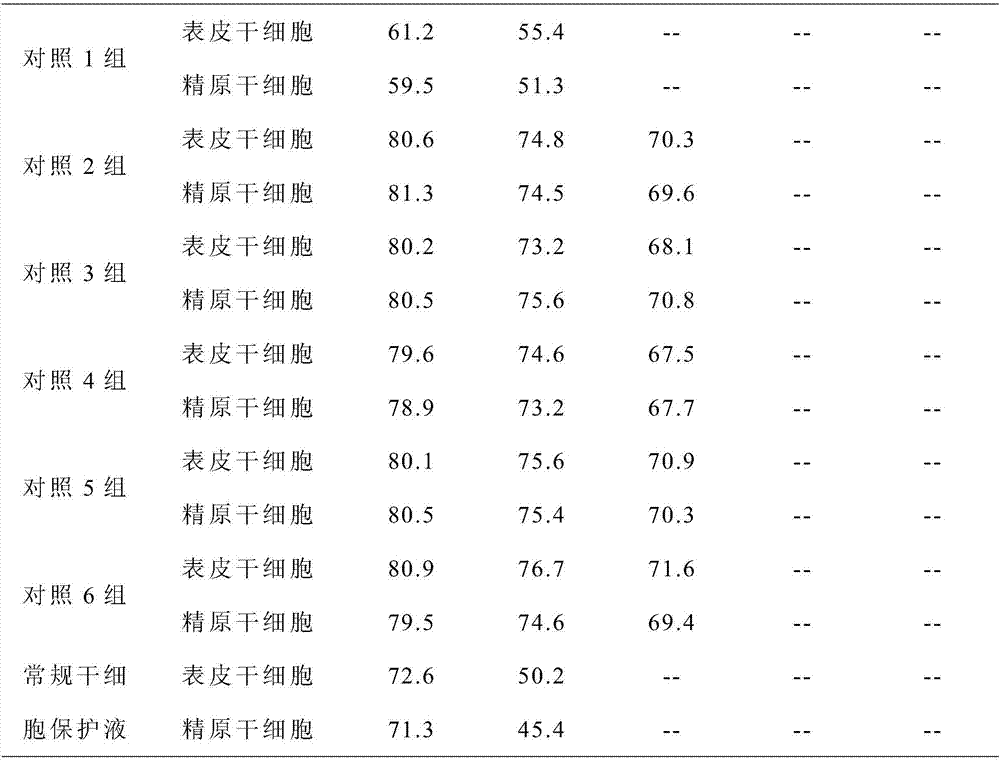
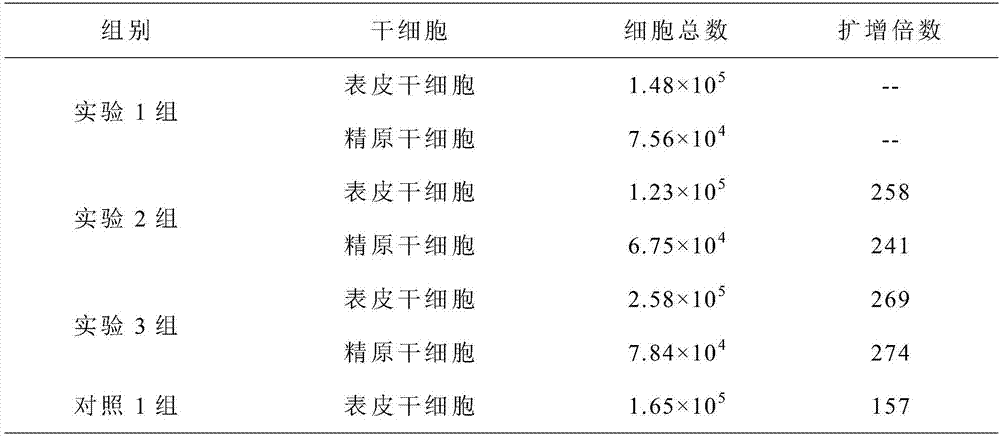
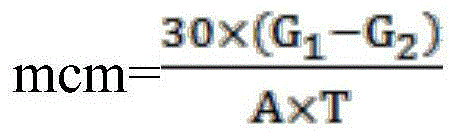Patents
Literature
165 results about "Aminoglycosides antibiotics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Aminoglycoside any of a group of bacterial antibiotics derived from various species of Streptomyces that interfere with the function of bacterial ribosomes. The aminoglycosides include gentamicin, streptomycin, tobramycin, amikacin, kanamycin and neomycin.
Methods and unit dose formulations for the inhalation administration of tobramycin
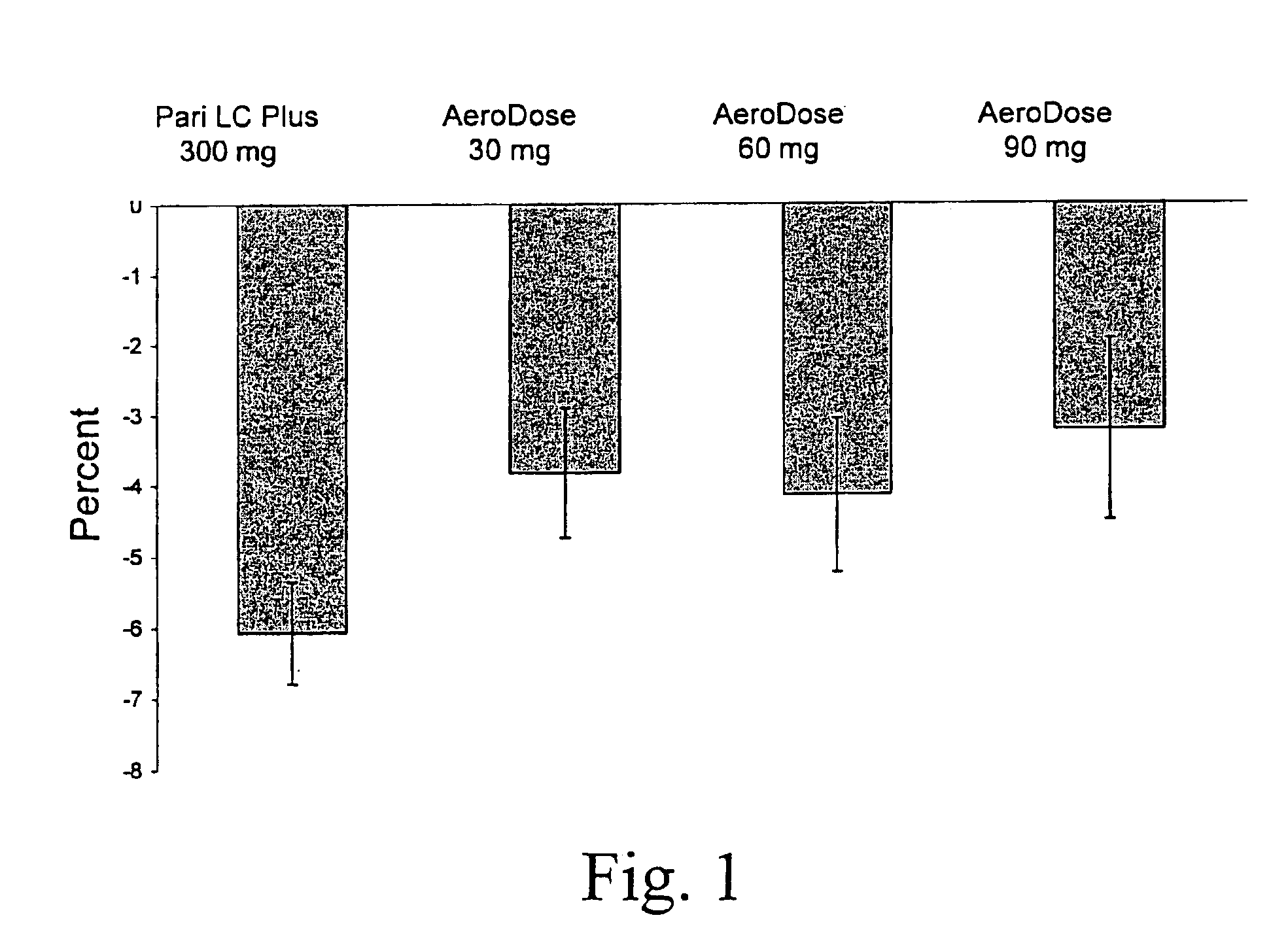
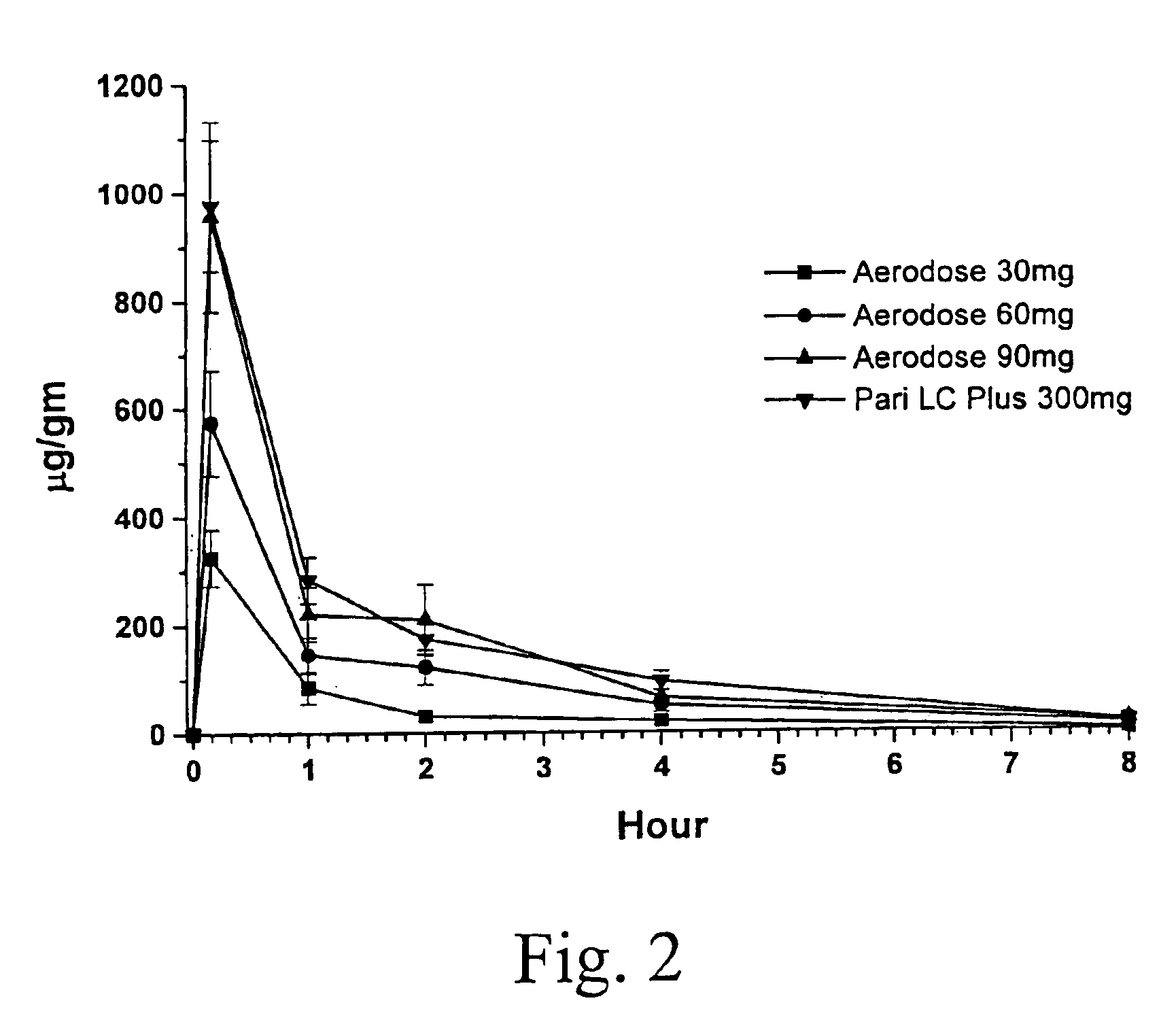
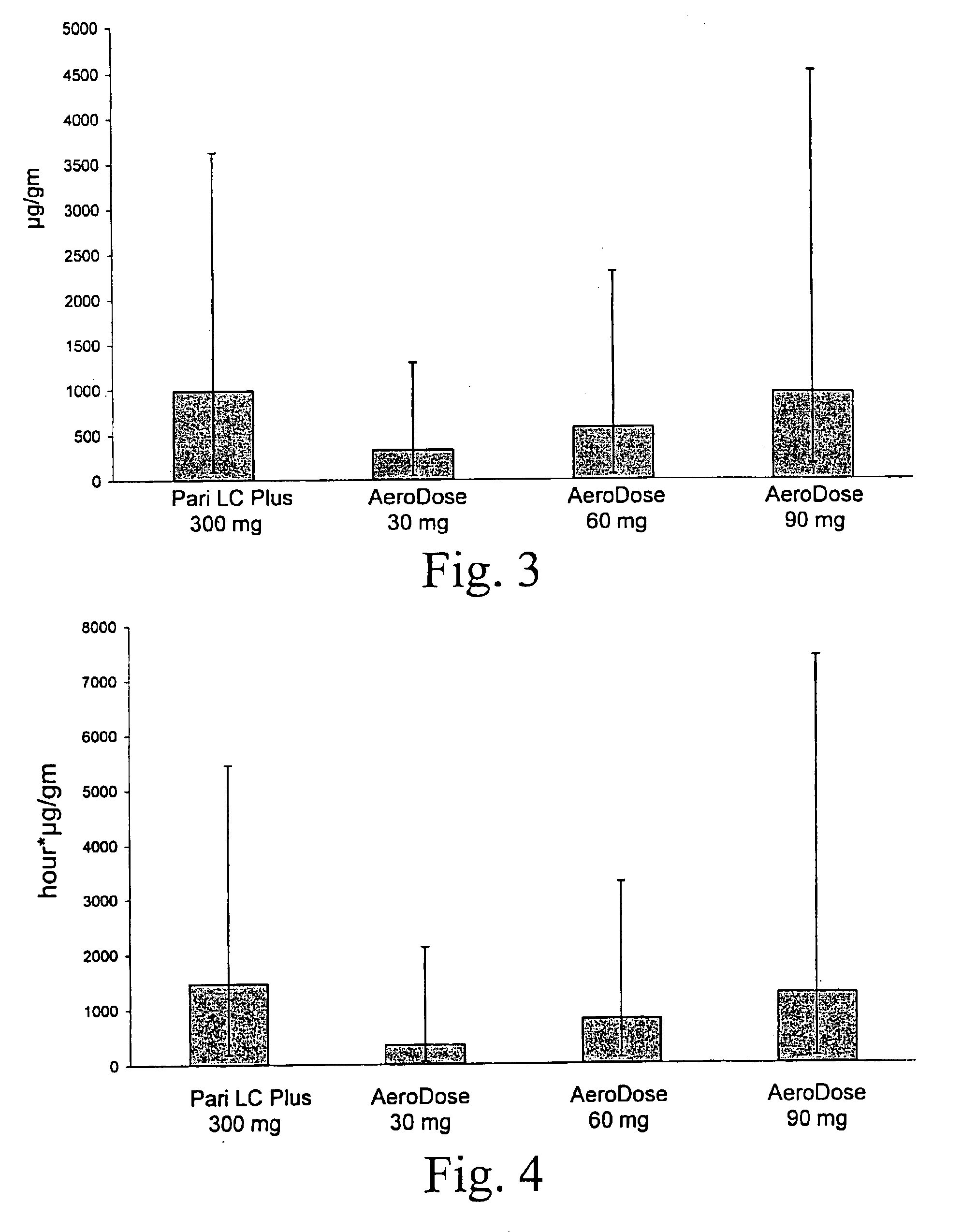
A patient suffering from an endobronchial infection is treated by administering to the patient for inhalation a dose of less than about 4.0 ml of a nebulized aerosol formulation comprising from about 60 to about 200 mg / ml of an aminoglycoside antibiotic, such as tobramycin, in a physiologically acceptable carrier in a time period of less than about 10 minutes. Unit dose devices for storage and delivery of the aminoglycoside antibiotic formulations are also provided.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
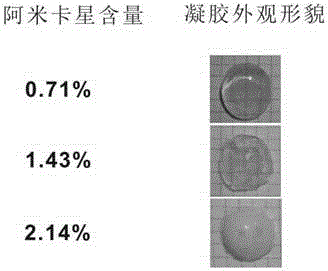
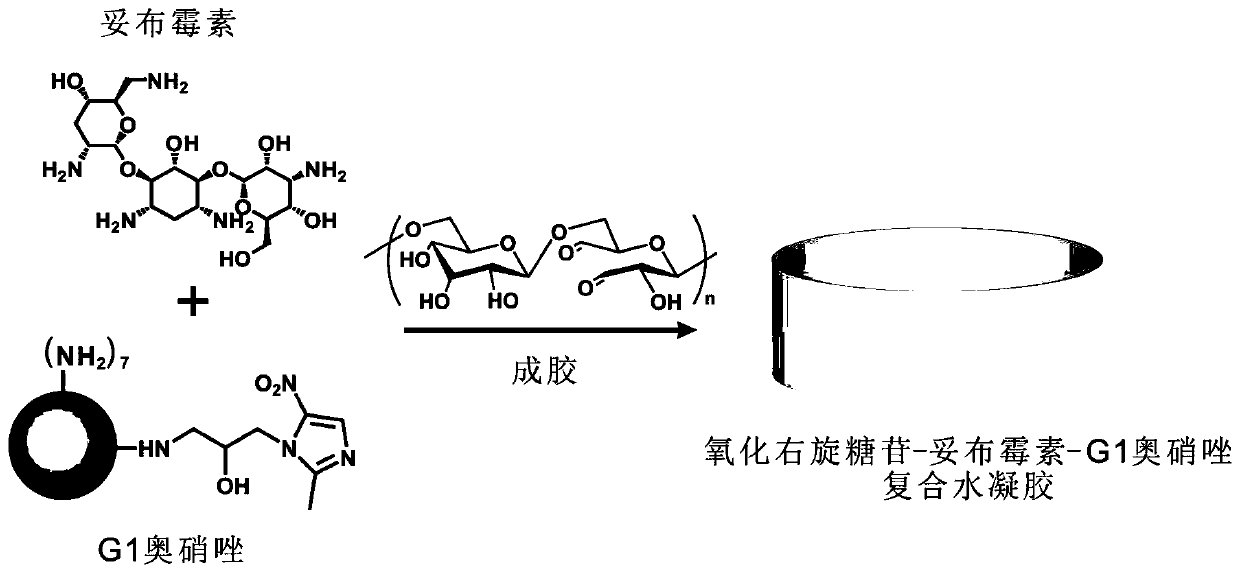
Release-controllable antibiotic hydrogel and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106822911AAvoid drug burstEasy to synthesizeAntibacterial agentsAerosol deliveryChemistryAminoglycoside
The invention relates to a release-controllable antibiotic hydrogel and a preparation method and application thereof. The release-controllable antibiotic hydrogel based on aminoglycoside antibiotics is formed by crosslinking the oxidized polysaccharide macromolecules and the aminoglycoside antibiotics through acid-sensitive schiff base groups; the schiff base bonds are broken under the acid environment produced by bacteria infection, so that the gel is degraded, and the antibiotics is released according to requirements. The invention also provides antibacterial application of the oxidized polysaccharide-aminoglycoside antibiotics hydrogel in vitro and in vivo. The release-controllable antibiotic hydrogel has the advantages that the preparation is simple, and the cost is low; the strength, shape and degrading of the gel, the medicine release rate and the like can be controlled according to the content of antibiotics, the broad-spectrum high-efficiency antibacterial property is realized, and the antibacterial effect is better than the antibacterial effect of multiple types of commercial antibacterial gels on market; the hydrogel may be prepared into creams, implants and medical apparatus coatings, so as to resist the infection by gram-negative bacterium, gram-positive bacterium and the like.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
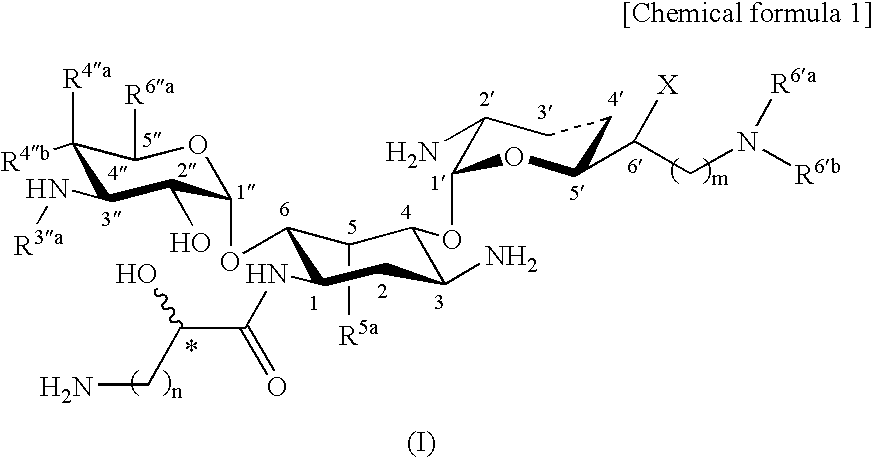
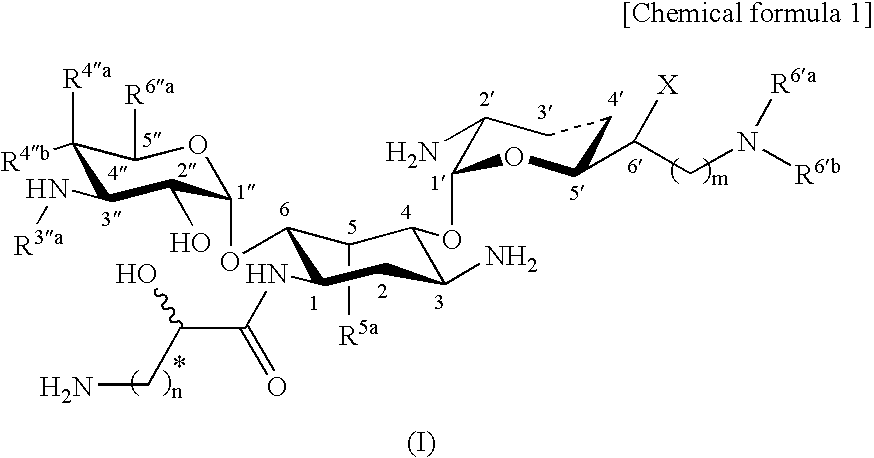
Novel aminoglycoside antibiotics effective against methicillin resistant staphylococcus auerus (mrsas)
InactiveUS20070161581A1Great anti-microbial activitySignificant antimicrobial activityAntibacterial agentsBiocideMethicillin resistant StaphylococcusGlycoside
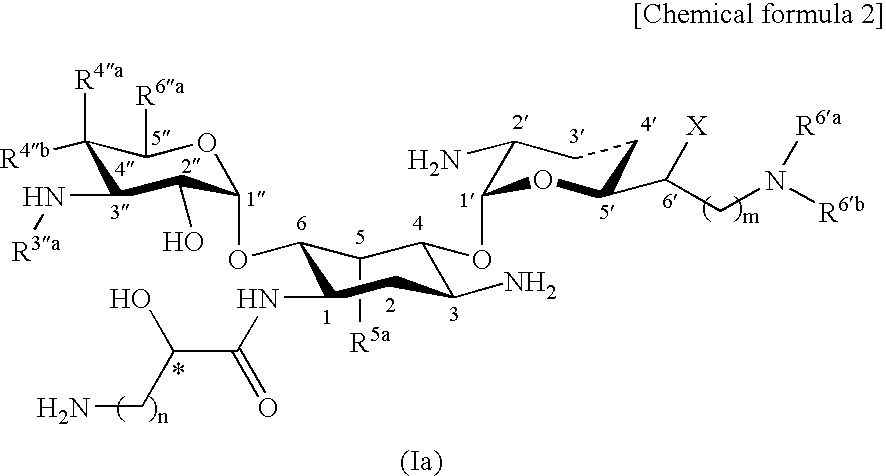
Disclosed are compounds represented by general formula (I) or pharmacologically acceptable salts or solvates thereof having excellent antimicrobial activity against bacteria causative of severe infections such as pneumonia and septicemia, particularly against MRSA, and also antimicrobial agents comprising these compounds, and pharmaceutical compositions comprising these compounds as an active component.
Owner:MEIJI SEIKA KAISHA LTD +1
Stable pharmaceutical composition comprising beta-lactam antibiotic and buffer
InactiveUS20090156518A1Prevent first-time-treatment failureEffective treatment regimenAntibacterial agentsBiocideMedicineAntibiotic Y
A pharmaceutical composition, comprising: at least one β-lactam antibiotic and at least one buffer component; wherein when the pharmaceutical composition is used as an anti-microbial drug, it optionally comprises further at least one aminoglycoside antibiotic mixed with the β-lactam antibiotic and the buffer component.
Owner:ZHANG HESHENG
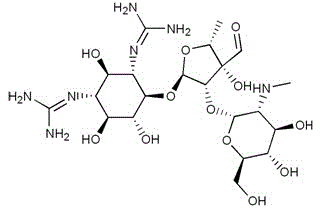
Derivative of micronomycine and its preparing process and medical application
A series of novel derivatives of micronomycin, its preparing process and the medicines containing them as active component are disclosed. The said derivatives are prepared through alkylating and acylating C1-NH2 of microromycin and chemical reactions. Its advantage is high antibacterial activity.
Owner:四川抗菌素工业研究所有限公司
Microfluidic chip electrophoretic-electrochemical detecting device with adjustable pH after separation and use thereof
InactiveCN102788831AChange pHDoes not affect electrophoretic separationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLaboratory glasswaresElectrode placementAntibiotic Y
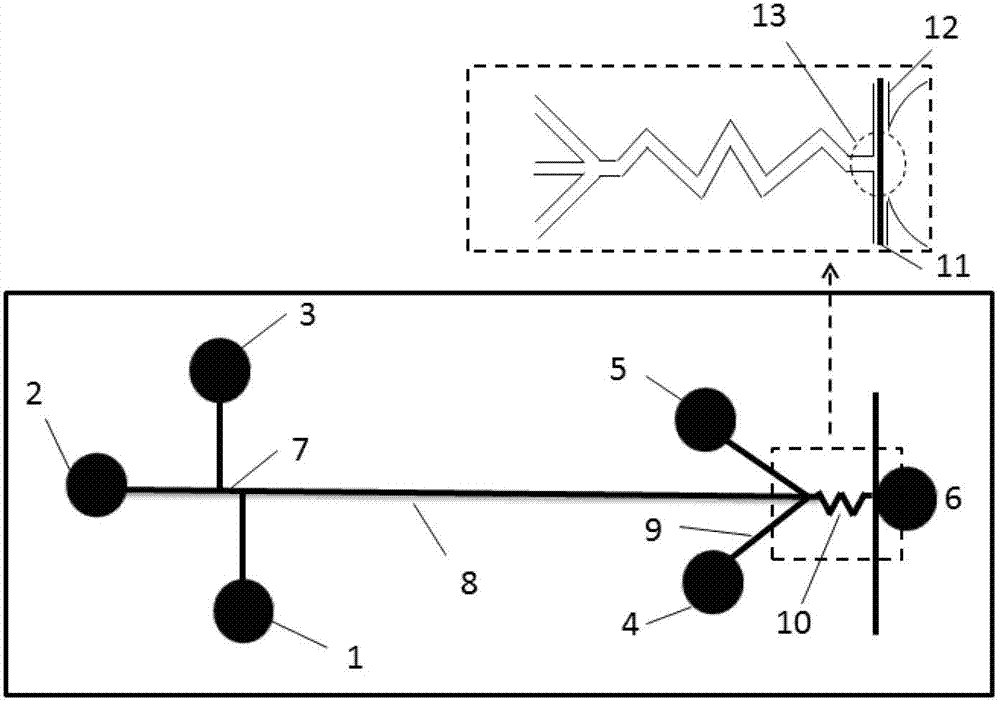
The invention discloses a microfluidic chip electrophoretic-electrochemical detecting device with adjustable pH after separation and use of the device in aminoglycoside antibiotics analysis. The analysis device comprises a double-T shaped sampling channel, a separating channel, two auxiliary channels, a W-shaped channel and an electrode placement channel. Through adding the two auxiliary channels and the W-shaped channel at the tail end of the separating channel in a microfluidic chip, an alkaline solution is added through the auxiliary channels after being electrophoretically separated, and the solution from the separating channel and the auxiliary channels is mixed evenly through the W-shaped channel, a pH value of the solution in a working electrode determining region is improved, so that the solution meets a strong alkaline condition needed by the detection of carbohydrates, simultaneously, electrophoretic separation under an acidic separation buffer solution is not influenced. By the device disclosed by the invention, a transition metal nano material is decorated on the surface of the electrode by using an electrodeposition method and by means of the relatively large specific surface area and the special catalytic property of the metal nano material, so that the working electrode with high performance is obtained, and aminoglycoside antibiotics are determined through the amperometry.
Owner:GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI GSCAS +1
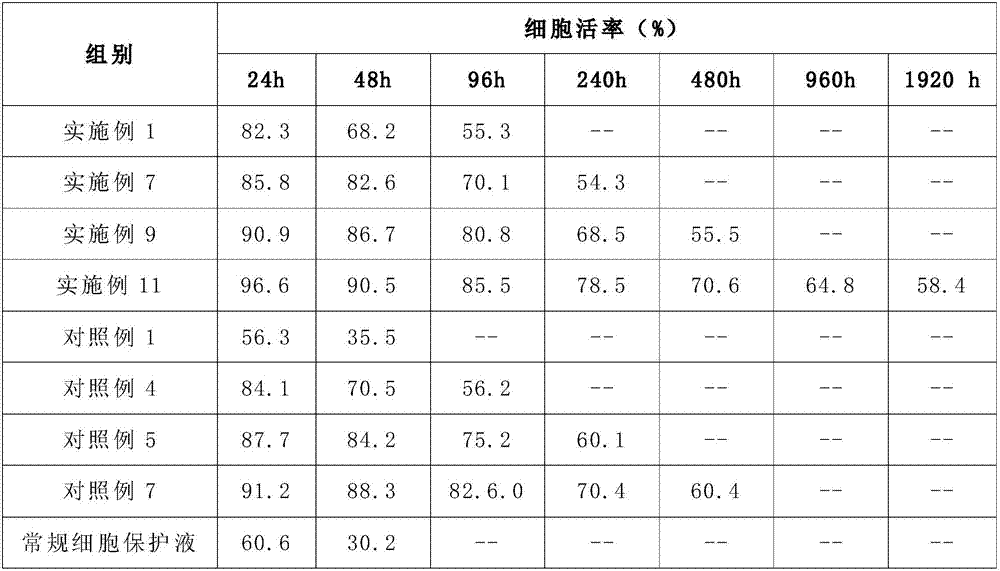
Bone marrow stem cell protection solution and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107668024AEffective protectionExpand the scope of clinical applicationDead animal preservationCell activityInosamycins
The present invention provides a bone marrow stem cell protection solution, which is mainly prepared by dissolving a hypoxic protection agent, heparin sodium and an aminoglycoside antibiotic in a DMEM / F12 culture medium aqueous solution, wherein per mL of the DMEM / F12 culture medium aqueous solution can respectively dissolve 5-10 mg of the hypoxic protection agent, 0.01-0.05 U of the heparin sodium and 50-200 U of the aminoglycoside antibiotic, and the concentration of the DMEM / F12 culture medium aqueous solution is 30-40 mg / ml. According to the present invention, the bone marrow stem cell protection solution has advantages of stable performance, safety and no toxicity, can effectively protect bone marrow stem cells, can make bone marrow stem cells be preserved for a long time and can maintain the cell activity in vitro, can maintain the original multidirectional differentiation ability, and can expand the clinical application of bone marrow stem cells, wherein the bone marrow stem cells can be transported to most domestic cities and neighboring countries by using the existing transportation tools.
Owner:CENTURY BIOSTRENGTH BEIJING PTY LTD
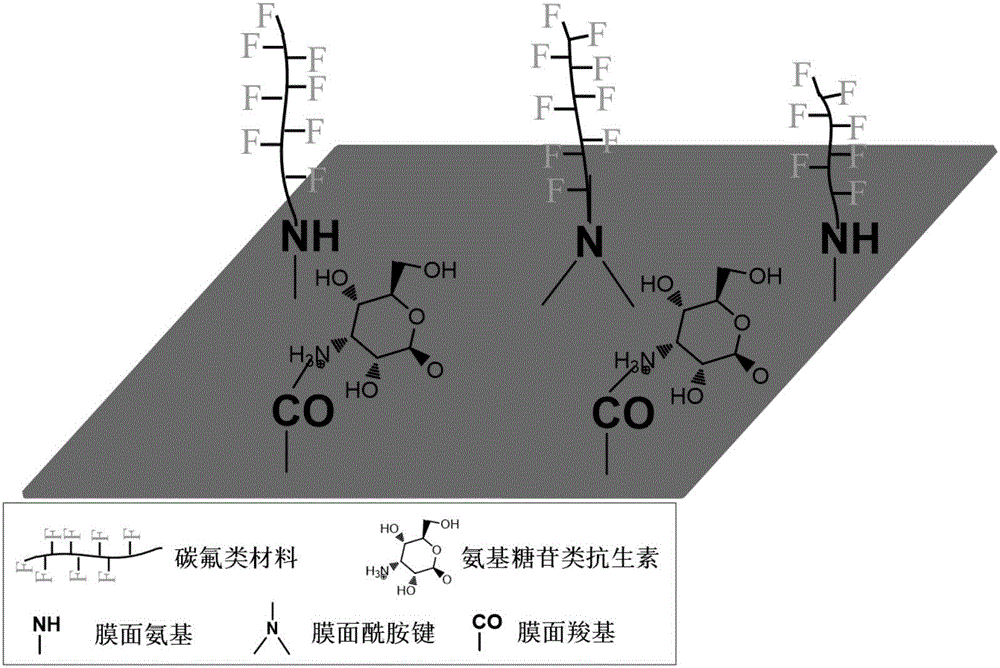
Aromatic polyamide composite RO (reverse osmosis) membrane grafted with fluorocarbon materials and aminoglycoside antibiotics as well as preparation method
ActiveCN106823865AMaintain permeation selectivityStrong anti-pollutionMembranesReverse osmosisEscherichia coliHigh flux
The invention relates to an aromatic polyamide composite RO (reverse osmosis) membrane grafted with fluorocarbon materials and aminoglycoside antibiotics as well as a preparation method. The method comprises the steps as follows: a solution containing fluorocarbon materials with the molar concentration being 0.05-0.2 mol / L and a bromo-3,4-dimethoxy acetophenone initiator with molar concentration being 0.001-0.1 mol / L is prepared; the surface of a primary RO membrane is immersed in the solution, the membrane is taken out, and grafting is initiated under an ultraviolet lamp; the surface of the RO membrane is immersed in an aminoglycoside antibiotic solution, finally, the membrane is dried, and the RO membrane is composited. The permeation selectivity of the unmodified aromatic polyamide composite RO membrane is kept; the aromatic polyamide composite RO membrane has the characteristics of low flux attenuation degree of a low-surface-energy material modified membrane and high flux recovery rate of a hydrophilic material modified membrane. The aromatic polyamide composite RO membrane grafted with the fluorocarbon materials and aminoglycoside antibiotics has excellent antibacterial performance and triple anti-fouling functions after being contacted with bacillus subtilis or Escherichia coli.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
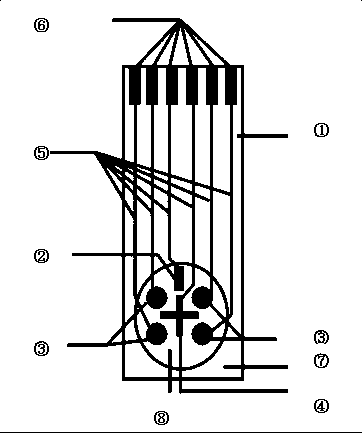
Preparation method and application of sensor for simultaneously detecting four aminoglycoside antibiotics
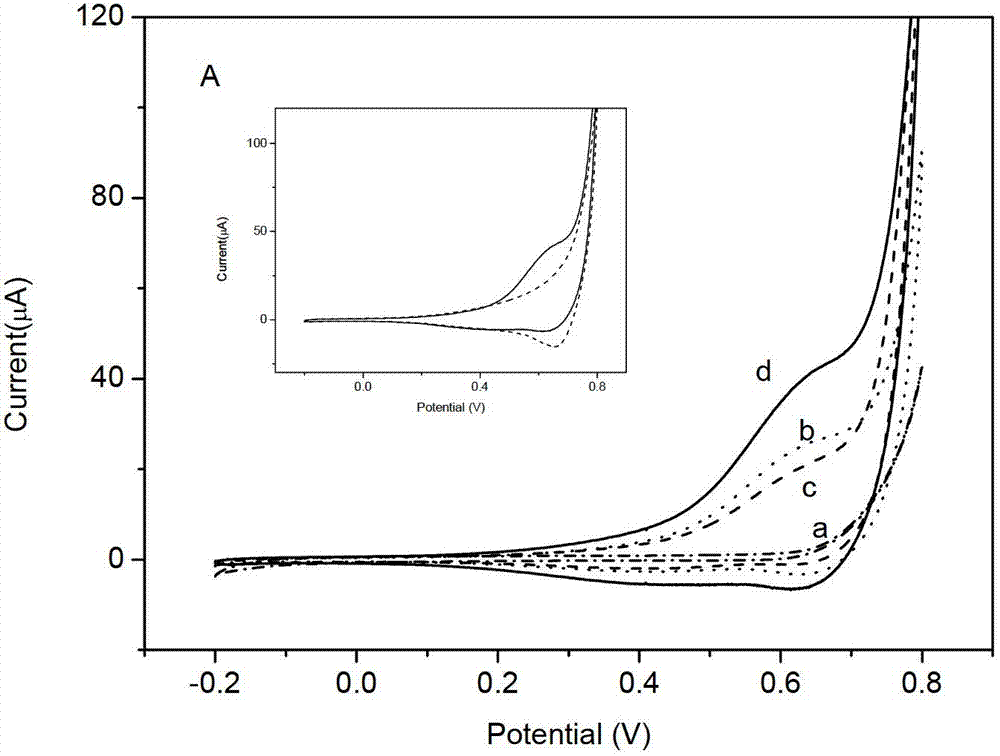
The invention discloses a preparation method and an application of a sensor for simultaneously detecting four aminoglycoside antibiotics and belongs to the technical field of novel function materials and biosensor analysis. According to the invention, a reference electrode is printed by the use of a silver paste and four working electrodes and a counter electrode are printed by the use of a conductive carbon paste on a rectangular substrate surface coated with a layer of a polyester film. Thus, a four-channel screen-printed electrode is prepared. The preparation method is characterized in that antibodies of four aminoglycoside antibiotics including streptomycin, gentamycin, kanamycins and spectinomycin are respectively fixed on surfaces of the four working electrodes by the use of a Pt nanoparticle-sulfated graphene-carboxymethyl chitosan conductive composite nano-material; and after the detection liquids are dripped, the four working electrodes are connected with a multichannel electrochemical workstation detection circuit so as to realize simultaneous detection of the four aminoglycoside antibiotics. The sensor provided by the invention is simple to prepare and convenient to process, requires low cost, and is convenient to carry. The detection method is simple and rapid and has high sensitivity and good specificity.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Branched chain amino acid-dependent aminotransferase inhibitors and their use in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases
The invention relates to BCAT inhibitors and the use thereof for treating or preventing neuronal loss associated with stroke, ischemia, CNS trauma, hypoglycemia and surgery, as well as treating neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Huntington's disease and Down's syndrome, treating or preventing the adverse consequences of the overstimulation of the excitatory amino acids, treating anxiety, psychosis, convulsions, aminoglycoside antibiotics-induced hearing loss, migraine headache, chronic pain, neuropathic pain, Parkinson's disease, diabetic retinopathy, glaucoma, CMV retinitis, urinary incontinence, opioid tolerance or withdrawal, and inducing anesthesia, as well as for enhancing cognition.
Owner:WARNER LAMBERT CO LLC
Aqueous solution preparation containing aminoglycoside antibiotic and bromfenac
Owner:SENJU PHARMA CO LTD
Antibiotic compound recipe comprising piperacillin
The invention involves antibiotic compound recipe containing piperacillin, sulbactam or clavulanic acid, ion chelator which can inhibit the formation of particles chelator, the recipe can be further added in buffering ingredient as stability system, the characteristics of the recipe is that it can be prepared to stable pharmaceutical solutions, and with aminoglycoside antibiotics in the same container are re-prepared to drugs used for complex anti-microbial infection.
Owner:ガンゾウ ヘメイ ファーマスーティカル カンパニー リミテッド
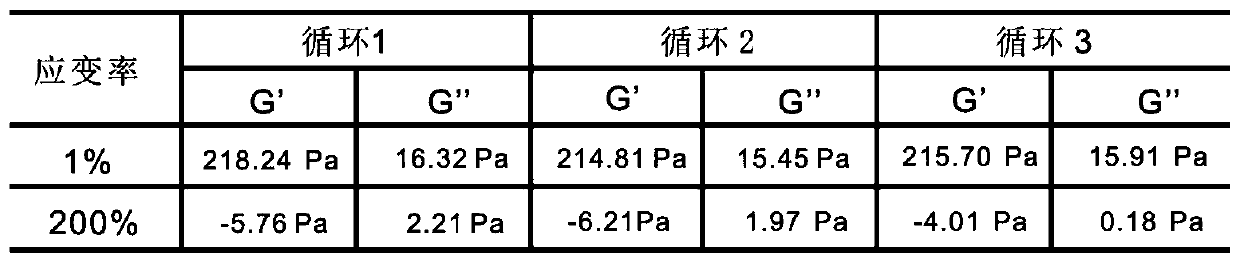
Preparation method and application of controlled-release antibiotic composite hydrogel
ActiveCN110314242AEasy to synthesizeHigh antibacterial efficiencyAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDendrimerAnaerobic bacteria
The invention provides composite antibiotic hydrogel based on controlled release of aminoglycoside antibiotics and ornidazole. The composite antibiotic hydrogel is obtained by crosslinking an oxidizednatural polysaccharide polymer, the aminoglycoside antibiotics and the ornidazole through an acid-sensitive Schiff base bond, wherein the ornidazole is modified by a first-generation polyamidoamine dendrimer with an amino terminal. The Schiff base bond is broken in an acidic environment caused by bacterial infection, so that gel degradation is caused, and the on-demand release of the antibioticsis realized. The composite antibiotic hydrogel is easy to prepare and low in cost. According to the prepared controlled-release composite antibiotic hydrogel, the strength, morphology and degradationof the gel, the release rate of drugs and the like can be controlled based on the content of antibiotics, the composite antibiotic hydrogel has broad-spectrum high-efficiency antibacterial properties,and the bacteriostatic effect is superior to that of various kinds of commercial antibacterial gel on the market. The hydrogel is expected to be prepared into external dressings, ointment preparations, implants, coatings on medical apparatuses and instruments and the like and used for resisting infection caused by Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-positive bacteria, anaerobic bacteria and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHANGZHENG HOSPITAL +1
Formulation to treat ear infection
InactiveUS20080139545A1Reducing bacterial biofilmsCleanse surgical or dental instrumentAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBacteroidesMammal
The present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition that includes: (a) at least one of a non-aminoglycoside antibiotic and an anti-inflammatory agent; and (b) a biofilm-dissolving agent. The present invention also provides for methods of killing or inhibiting the growth of a fungus by contacting the fungus with a composition of the present invention, methods of killing or inhibiting the growth of a virus by contacting the virus with a composition of the present invention, methods of killing or inhibiting the growth of a bacteria by contacting the bacteria with a composition of the present invention, methods of treating a disorder in a mammal by administering the composition of the present invention to the mammal, methods for preserving contact lens by contacting the contact lens with a composition of the present invention, methods for cleansing surgical or dental instrument by contacting the fungus with a composition of the present invention, and kits that include (a) a container that includes the pharmaceutical composition of the present invention, and (b) a drug delivery device.
Owner:CHOE WON TAEK +2
Streptomycin molecular engram solid phase extraction column and preparing process and application thereof
InactiveCN1632563AQuick purificationFast elutionComponent separationDispersed particle separationCross-linkCross linker
This invention discloses a streptomycin module trace solid extraction small column and its process method, which comprises the following: polymer material model module of streptomycin, function single methacrulic acid, and cross linker two methacrylic acid glycol ester combined. It is a cross linked polymers fixed with hole distribution function group, which has the memory function to the streptomycin module space structure and high selection isolation and concentration to the remaining analyzed liquid.
Owner:HUNAN TONGSEN TECH
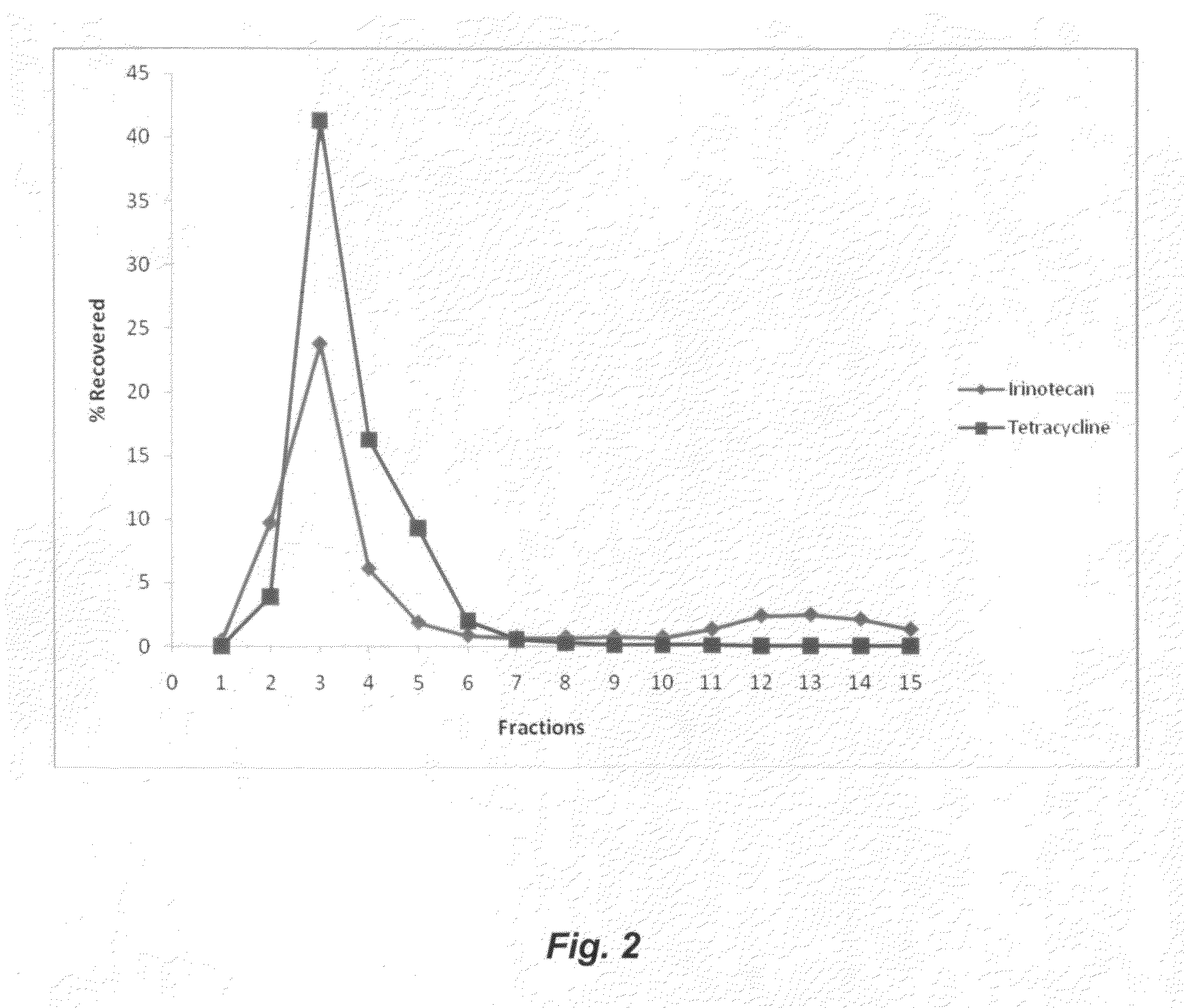
Methods for co-encapsulation of combination drugs and co-encapsulated combination drug product
ActiveUS20100247620A1Reduce processing stepsShorten the timeOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsAnticarcinogenPhospholipid
This invention is for an improved process to co-encapsulate hydrophobic drugs and hydrophilic drugs in phospholipid liposomes. Non-toxic supercritical or near-critical fluids with / without polar cosolvents are utilized to solubilize phospholipid materials and hydrophobic drugs, and form uniform liposomes to encapsulate hydrophobic drugs and hydrophilic drugs.DNA topoisomerase I (Top1) is the target of camptothecin, and novel Top1 inhibitors are in development as anticancer agents. Top1 inhibitors damage DNA by trapping covalent complexes between the Top1 catalytic tyrosine and the 3′-end of the broken DNA. Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase (Tdp1) can repair Top1-DNA covalent complexes by hydrolyzing the tyrosyl-DNA bond. Inhibiting Tdp1 has the potential to enhance the anticancer activity of Top1 inhibitors and to act as antiproliferative agents. It has been recently reported that neomycin inhibits Tdp1 more effectively than the related aminoglycosides paromomycin and lividomycin A. Inhibition of Tdp1 by neomycin is observed both with single- and double-stranded substrates but is slightly stronger with duplex DNA, which is different from aclarubicin, which only inhibits Tdp1 with the double-stranded substrate. Inhibition by neomycin can be overcome with excess Tdp1 and is greatest at low pH. Aminoglycoside antibiotics and the ribosome inhibitors thiostrepton, clindamycin-2-phosphate, and puromycin are the first reported pharmacological Tdp1 inhibitors. The development of Tdp1 inhibitors as anticancer agents can be envisioned as combinations of Tdp1 and Top1 inhibitors. Moreover, Tdp1 inhibitors might also be effective by themselves as anticancer agents. In addition, Tdp1 inhibitors might be valuable as anti-infectious agents.This invention can produce a co-encapsulated combination drug product consisting of a topoisomerase 1 inhibitor such as camptothecins including neat camptothecin and its derivatives irinotecan, topotecan and other derivatives, and a tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase (Tdp1) such as aminoglycoside antibiotics including neomycin and tetracycline, and the ribosome inhibitors thiostrepton, clindamycin-2-phosphate, and puromycin.
Owner:APHIOS
Preparation method of drug slow-release antibacterial dressing and drug slow-release antibacterial dressing prepared by means of preparation method
ActiveCN108721690AImprove water absorptionGood water vapor transmission rateBandagesBiocompatibility TestingAntibacterial activity
The invention discloses a preparation method of drug slow-release antibacterial dressing and drug slow-release antibacterial dressing prepared by means of the preparation method. The preparation method comprises the steps of (1) mixing carboxymethyl chitosan, macromolecular collagen, and aminoglycoside antibiotics; (2) pouring the mixture into a mold, allowing standing, and drying to obtain non-crosslinked sponge material; (3) soaking the non-crosslinked sponge material in anhydrous ethyl alcohol solution containing EDC / NHS (1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide / N-Hydroxysuccinimide),and crosslinking to obtain composite crosslinked sponge dressing that is antibacterial dressing. Amino groups of the antibiotics covalently bond with carboxyl groups of carboxymethyl chitosan and collagen to form amido bonds, and in this manner, the antibiotics are grafted to dressing matrix. Slow breaking of the amido bonds on a polymer framework allow the antibiotics of the dressing to release slowly; therefore, antibacterial dressing products having good biocompatibility, long-term antibacterial activity and wound healing promotion are prepared.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Compositions and methods for determining nephrotoxicity
InactiveUS20090220982A1Improve the level ofMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisNephrotoxicityAntibiotic Y
The present invention provides novel in vitro assays for determining the nephrotoxicity of a compound. These assays correlate well with in vivo nephrotoxicity and also provide high-throughput methods to screen multiple compounds for in vivo nephrotoxicity. In addition, the methods of the present invention may be adapted to screen for nephroprotectant compounds, including those that protect cells and animals from the nephrotoxic effects of aminoglycoside antibiotics.
Owner:ACHAOGEN
Placenta and umbilical cord cell protective solution
InactiveCN107114356AModerate activityInhibit apoptosisDead animal preservationAntibiotic YUmbilical cord
The invention provides a placenta and umbilical cord cell protective solution. The protective solution is mainly prepared by dissolving a mycoplasma inhibitor and aminoglycoside antibiotics with an aqueous solution of MEM-alpha medium. 1 mL of the aqueous solution of MEM-alpha medium is respectively used for dissolving 10-30 mg of the mycoplasma inhibitor and 180-240 U of the aminoglycoside antibiotics. Concentration of the aqueous solution of MEM-alpha medium is 10-15 mg / mL. The protective solution provided by the invention not only can effectively kill or inhibit formation of mycoplasma and prevent placenta cell or umbilical cord cell infection, but also can provide a stable osmotic pressure environment for placenta or umbilical cord cells through addition of protective components. Then, human environment can be effectively simulated, and cell survival rate is raised. Meanwhile, nutrients can be provided for storing and transporting cells within a short period of time; immune performance of cells is enhanced; cell infection is prevented; cell viability is effectively improved; and cell transport time is prolonged.
Owner:CENTURY BIOSTRENGTH BEIJING PTY LTD
Aminoglycosides molecular molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction column
InactiveCN102974327AImprove adsorption capacityReduce pollutionComponent separationOther chemical processesCross-linkFunctional monomer
The invention discloses an aminoglycosides molecular molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction column. Molecularly imprinted polymeric microspheres are filled in a columnar shell, and a preparation method for the molecularly imprinted polymeric microspheres comprises the steps of: taking 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane or phenyltriethoxysilane as functional monomers, taking tetraethyl orthosilicate as a cross-linking agent and taking aminoglycoside antibiotics as template molecules, performing hydrolytic condensation by adopting a sol-gel method, forming a rigid network structure of an Si-O-Si bond on the surface of activated silica gel to form the polymeric microspheres; and eluting.by using template molecules, so as to obtain the molecularly imprinted polymeric microspheres. The extraction column is used for separating and concentrating target objects before sample pretreatment is performed on residue of veterinary drugs of the aminoglycoside antibiotics, and selectively adsorbing the target objects, and has the advantages of being simple and fast in separation, purification and concentration, little in organic solvent consumption and high in repeatedly used times, and the like.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV +1
Branched chain amino acid-dependent aminotransferase inhibitors and their use in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases
The invention relates to BCAT inhibitors and the use thereof for treating or preventing neuronal loss associated with stroke, ischemia, CNS trauma, hypoglycemia and surgery, as well as treating neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Huntington's disease and Down's syndrome, treating or preventing the adverse consequences of the overstimulation of the excitatory amino acids, treating anxiety, psychosis, convulsions, aminoglycoside antibiotics-induced hearing loss, migraine headache, chronic pain, neuropathic pain, Parkinson's disease, diabetic retinopathy, glaucoma, CMV retinitis, urinary incontinence, opioid tolerance or withdrawal, and inducing anesthesia, as well as for enhancing cognition.
Owner:WARNER-LAMBERT CO
Corynebacterium glutamicum and application thereof
ActiveCN103374540AIncrease productionImprove synthesis abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismNeomycin
The invention relates to the microbial field, and discloses corynebacterium glutamicum strains and application thereof. A corynebacterium glutamicum MHZ-0510 strain has a preservation number CGMCC No.7939; a corynebacterium glutamicum MHZ-0511 strain has a preservation number CGMCC No.7940; the two strains have significantly improved ability of fermentation for generating L-glutamine, compared with that of the original strain of wild type of corynebacterium glutamicum B498, and can be widely applied to fermentation production of L-glutamine. The corynebacterium glutamicum strains involved in the invention are obtained by screening aminoglycoside antibiotics, such as streptomycin and neomycin, have resistance to the aminoglycoside antibiotics including streptomycin and neomycin, and have improved ability to synthesis of L-glutamine, thus increasing the yield of L-glutamine. Therefore, aminoglycoside antibiotics can be widely applied to screen of L-glutamine.
Owner:MEIHUA BIOTECH LANGFANG CO LTD
Aminoside antibiotics ELISA detection method in Animal derived food
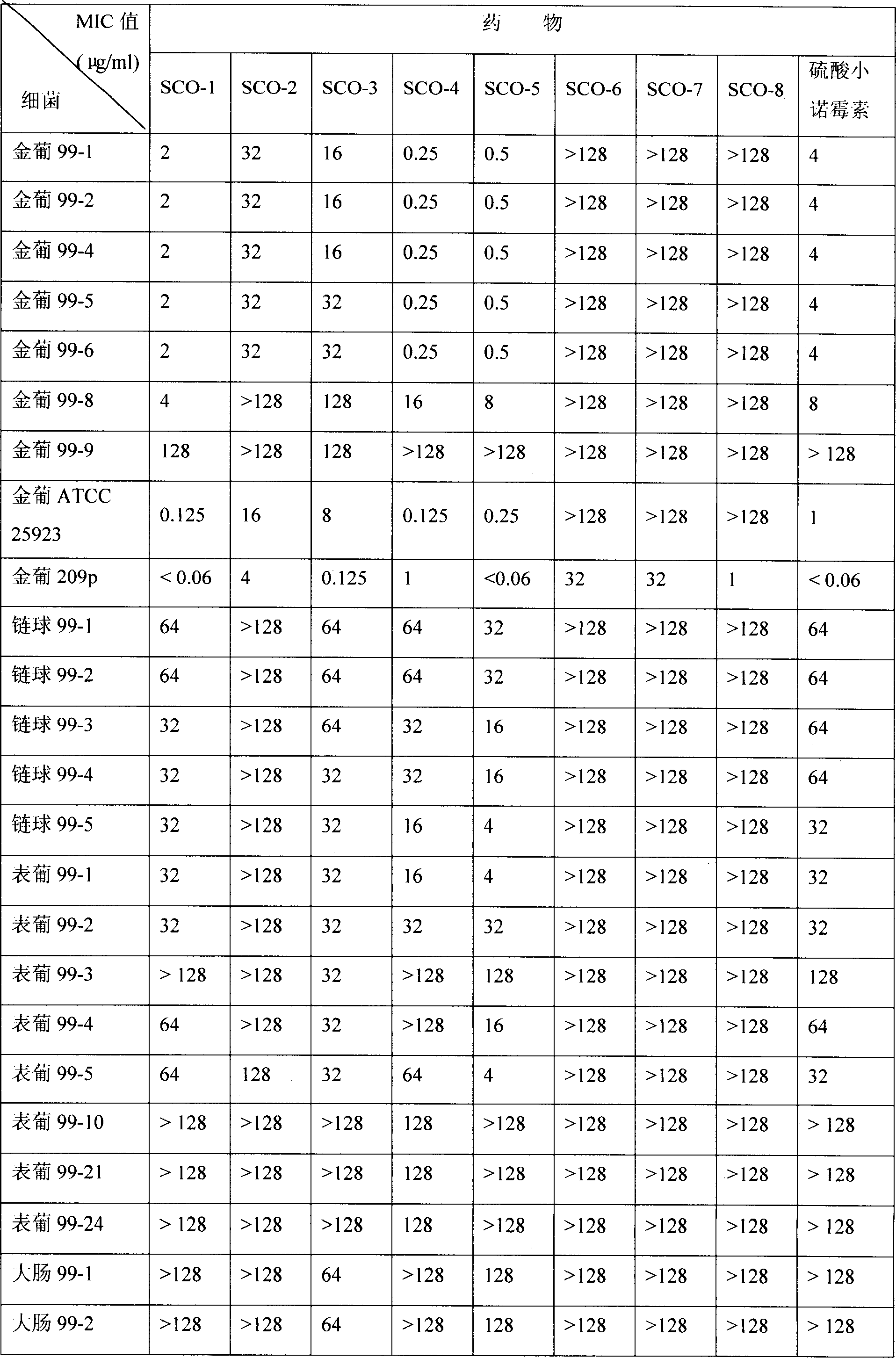
InactiveCN101398427AHigh precisionEnables multi-residue detectionMaterial analysisKanamycinAntibiotic Y
The invention relates to an enzyme-linked immunodetection method of aminoglycoside antibiotics in animal-derived foods, belonging to the immnunoassay field. The invention utilizes a carbodiimide method to synthesize immunogen (NM)L-(KM)m-(GM)n-(SM)k-BSA with multiple antigen determinants, such as aminoglycoside antibiotics, by four steps, utilizes a glutaric dialdehyde method to synthesize the envelope antigen of the aminoglycoside antibiotics and establish the enzyme-linked immunodetection method of the aminoglycoside antibiotics in the animal-derived foods; a polyclonal antibody with the specificity of aminoglycoside cluster is adopted as a detection reagent; gentamicin, neomycin, kanamycin or streptomycin is adopted as a standard substance, the four antibiotics and OVA conjugate are adopted as the envelope antigens, and the establishment of an ELISA method for detecting multi-residue of the aminoglycoside antibiotics provides a detecting means with high speed and high efficiency for the multi-residue detection of the aminoglycoside antibiotics in the animal-derived foods. The invention has the advantages of simple pre-processing, high sensitivity, high precision and the like.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Skin spermatogonium protection liquid and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107125240ASuitable for preservationHave a bactericidal effectDead animal preservationSpermatogoniumAntibiotic Y
The invention provides skin spermatogonium protection liquid and a preparation method thereof. The protection liquid is mainly formed by dissolving aminoglycoside antibiotics in DMEM (Dulbecco's modified eagle medium) culture medium water solution, 80-120U of the aminoglycoside antibiotics are dissolved in every mL of the DMEM culture medium water solution, and the concentration of the DMEM culture medium water solution is 13-25mg / mL. The skin spermatogonial stem cell protection liquid sufficiently simulates a human internal environment and is more suitable for survival of skin stem cells and spermatogonial stem cells and stable in property, the survival rate of the skin stem cells and the spermatogonial stem cells can be remarkably improved, and cultivation of the skin stem cells and the spermatogonial stem cells can be further enlarged while the skin stem cells and the spermatogonial stem cells are preserved.
Owner:CENTURY BIOSTRENGTH BEIJING PTY LTD
Medicinal composition for treating canker sore and local infection of body surface and reducing inflammation, product and application thereof
InactiveCN101703775ARelieve painReduce congestionAntisepticsDigestive systemGlucocorticoidAntibiotic Y
The invention relates to a medicinal composition for treating canker sore and local infection of body surface and reducing inflammation, a product and application thereof. The medicinal composition comprises aminoglycoside antibiotics, local anaesthetics and glucocorticoids in weight ratio of (0.1-10):(1-10):(0.01-10). Compared with the prior art, the medicinal composition has the advantages that local anaesthetics can alleviate pains of patients in time; antibiotics has the antibiotic effect of treating infection caused by bacteria; and the glucocorticoids has the anti-inflammatory effect of reducing focus hyperemia, reducing permeability of capillary and inhibiting inflammatory cells from transferring to the inflammatory part; and the synergistic action of the three medicaments promotes the healing of canker sore so as to achieve good treatment effect.
Owner:金日制药(中国)有限公司
Preparation method and application for aminoglycoside-antibiotic molecularly imprinted polymers
InactiveCN103224589AHighly selective enrichmentHigh extraction recoveryOther chemical processesCross-linkFunctional monomer
The invention discloses a preparation method and application for aminoglycoside-antibiotic molecularly imprinted polymers. The target molecularly imprinted polymers with the fixed hole sizes and the fixed shapes are made with streptomycin as template molecules, methacrylic acid as functional monomers and ethylene glycol dimethacrylate as cross-linking agents in a thermal initiation polymerization mode, and are used as solid phase extraction column packing. High-selectivity enrichment of aminoglycoside antibiotics can be conducted by a produced solid phase extraction column. The aminoglycoside-antibiotic molecularly imprinted polymers are high in antibiotic extraction recovery rate, and can be used for sample pretreatment of detection of aminoglycoside antibiotics in animal derived food.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
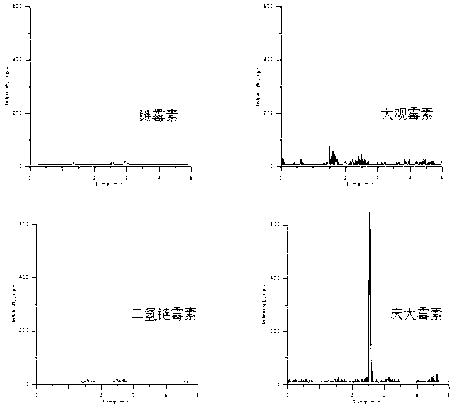
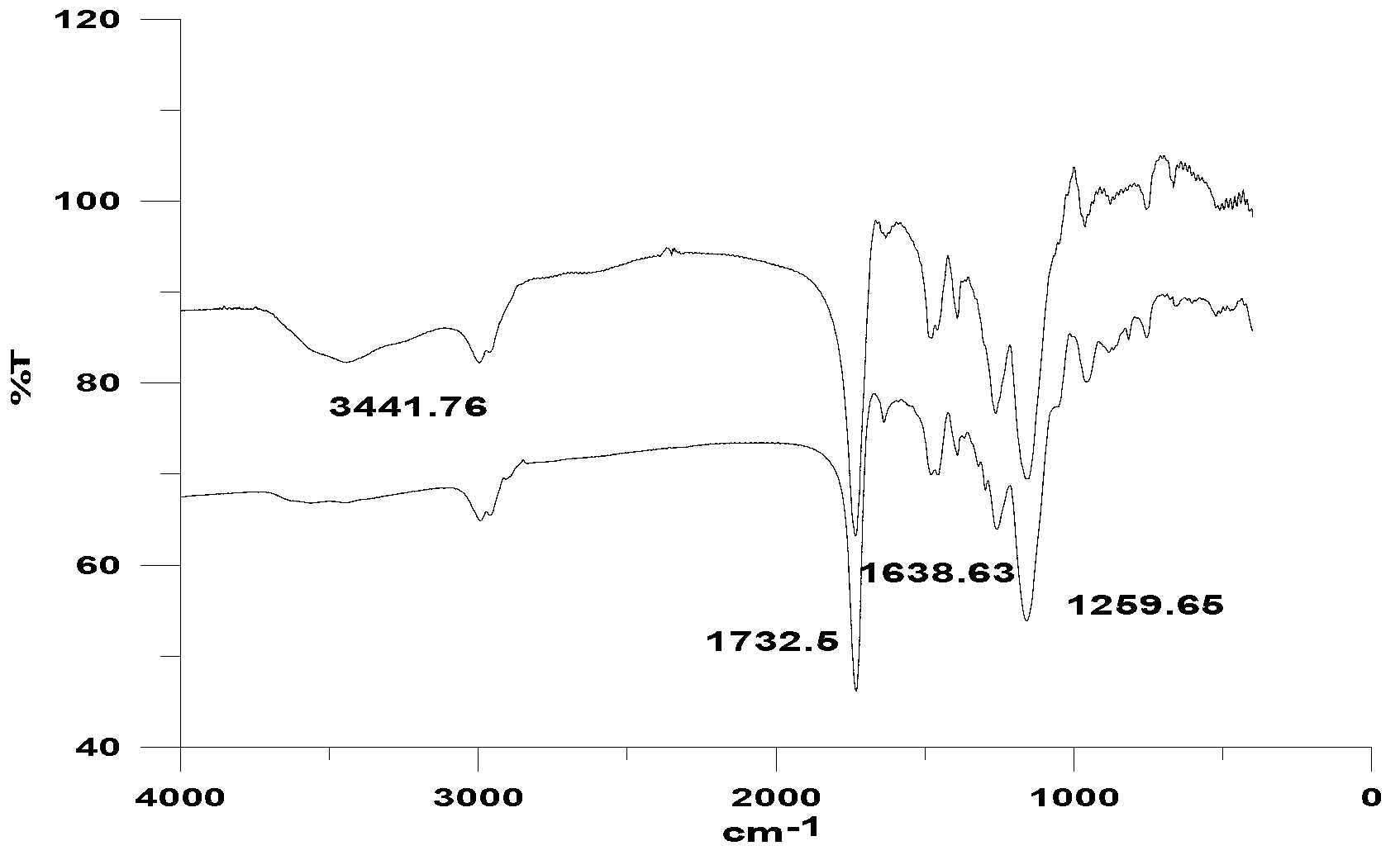
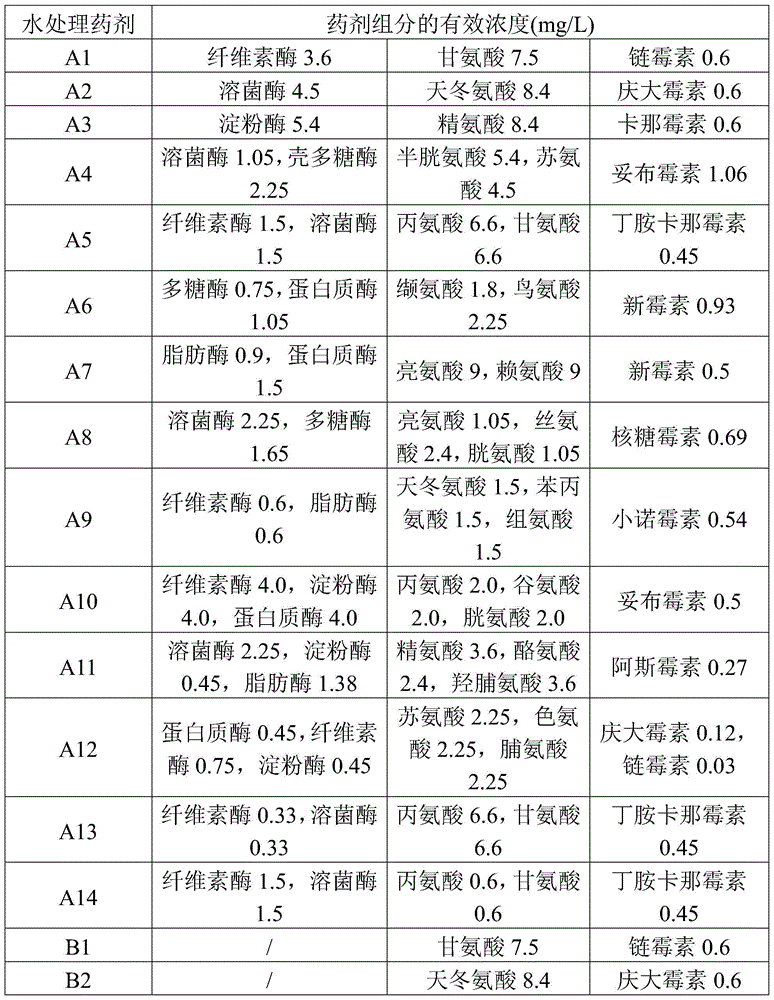
Water treatment medicament composition and application thereof
ActiveCN104556429AImprove the bactericidal effectGood corrosion inhibitionScale removal and water softeningBiological water/sewage treatmentAntibiotic YAmino acid
The invention discloses a water treatment medicament composition. The water treatment medicament composition contains amino acid, aminoglycoside antibiotics and enzyme, wherein amino acid has effects of scale inhibition and corrosion inhibition, the aminoglycoside antibiotics have a bactericidal effect, and enzyme is cooperative with amino acid and antibiotics and has a synergistic effect. The invention also discloses application of the water treatment medicament composition in water treatment. A performance evaluation result of the water treatment medicament composition shows that the scale inhibiting ratio of calcium carbonate inhibition performance is more than 99%, the corrosion rate of a dynamic simulation experiment is 0.025mm / a, and the number of heterotrophic bacteria in 72h at least can reach 2.1*10<2> per ml. The water treatment medicament composition does not contain phosphorus and is low in dosage, strong in scale inhibition performance, good in corrosion inhibition performance, excellent in sterilizing effect and long in time of duration.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Process for detecting PRPsc using an antibiotic from the family of aminoglycosides
A process of concentration by precipitation of PrPsc for detecting or diagnosing PrPsc, wherein a tissue or biological fluid stemming from or obtained from an animal or human organism is brought together with an antibiotic from the family of aminoglycosides, preferably streptomycin or one of its derivatives. The use of such an antibiotic for eliminating PrPsc from a tissue or biological fluid and a kit for diagnosing pathologies associated with the presence of PrPsc is also disclosed.
Owner:AGENCE FRE DE SECURITE SANITAIRE DES ALIMENT +3
Antibiotic compound containing aminoglycoside antibiotic
The invention discloses an antibiotic compound, which comprises the following parts: at least one aminoglycoside antibiotics, at least one ion chelant to inhibit the generation of particle or at least one buffer component or at least one ion chelant and at least one buffer component. The compound can build with at least one beta-lactam antibiotics in the same container to form the solvent to as the drug to control microbe infection or build with at least one beta-lactam antibiotics and at least one beta-lactamase inhibitor in the same container to form the solvent to as the drug to control microbe infection.
Owner:ガンゾウ ヘメイ ファーマスーティカル カンパニー リミテッド
Method for preparing organic fertilizer by use of aminoglycoside antibiotic mushroom dregs
InactiveCN107337497ASimple preparation processEasy to operateAmmonium salt fertilisersOrganic fertilisersHigh concentrationTreatment effect
The invention discloses a method for preparing organic fertilizer by use of aminoglycoside antibiotic mushroom dregs, relates to a harmless treatment and resourceful utilization method of the aminoglycoside antibiotic mushroom dregs and aims to solve the problems that a technology for effectively treating aminoglycoside antibiotic mushroom dregs is still absent at present, the treatment effect is poor, the high-concentration aminoglycoside antibiotic mushroom dregs cannot be treated, the treatment cost is high, environmental risks still exist after treatment, treated mushroom dregs cannot be effectively utilized and the like. The mushroom dregs with the residual quantity of aminoglycoside antibiotics being 1,000-2,000 mg / kg are jointly treated by use of persulfate and hydrogen peroxide in cooperation with ultraviolet radiation, and the organic fertilizer is prepared from the treated mushroom dregs. The removal efficiency of aminoglycoside antibiotics is up to 99.6%, the sterilization capability is high, the treatment cycle is short, and treatment cannot completed within 1 hour.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com