Release-controllable antibiotic hydrogel and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of antibiotics and hydrogels, applied in the fields of polymer chemistry and biomaterials, can solve the problems of inability to precisely control drug release, and achieve the effects of avoiding drug burst release, good tissue adhesion performance, and good antibacterial effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] Example 1: Oxidation of polysaccharide macromolecules
[0060] Dissolve 1 g of dextran (Mw: 45-60 kDa) in 12.5 mL of deionized water, add 8 mL of sodium periodate solution (0.5 M, 107 mg / mL) dropwise, and stir for 4 h in the dark, then add 1 mL of ethylene glycol and stir for 1 h After the reaction was terminated, impurities were removed from the reactant by dialysis (molecular weight cut-off: 3500Da). After 2 days of dialysis, the sample was freeze-dried and prepared into an aldylated dextran solution (80 mg / mL), which was refrigerated for use. , the synthetic route of oxidized dextran is as figure 1 shown.
[0061] Dissolve 1 g of sodium carboxymethylcellulose (Mw: 100 kDa) in 70 mL of deionized water, add 18 mL of sodium periodate solution (0.5 M, 107 mg / mL) dropwise, and stir for 4 h in the dark, then add 2 mL of ethylene glycol, Stir for 1 h to terminate the reaction, then remove impurities from the reactant by dialysis (molecular weight cut-off: 3500 Da), lyophi...
Embodiment 2
[0066] Embodiment 2: the preparation of antibacterial hydrogel
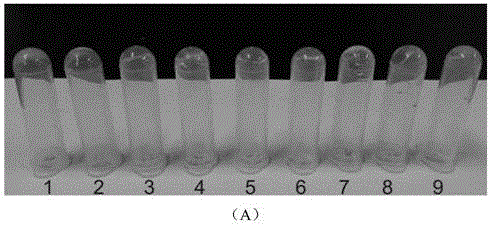
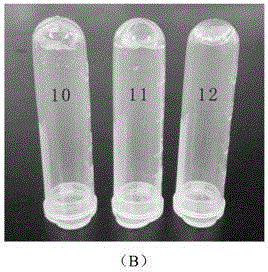
[0067] This embodiment (1)~(9) mainly uses oxidized dextran as the representative of polysaccharide macromolecule, and observes its cross-linking reaction with various aminoglycoside antibiotic drugs, such as image 3 Shown in A; (10)~(12) are respectively the cross-linking reaction of oxidized carboxymethyl cellulose, oxidized sodium alginate, oxidized chondroitin sulfate and amikacin; as image 3 Shown in B; Combined image 3 A and image 3 B can be obtained, oxidized natural polysaccharide macromolecule and aminoglycoside antibiotic drugs can form transparent and uniform hydrogel. In contrast, oxidized sodium alginate took longer to form hydrogels with drugs, which may be due to its lower water solubility and higher viscosity.
[0068] (1) Mix 150 μL of oxidized dextran solution (50 mg / mL) and 50 μL of netilmicin solution (50 mg / mL), and form a gel at room temperature for about 2 minutes.
[0069] (2) Mix ...
Embodiment 3
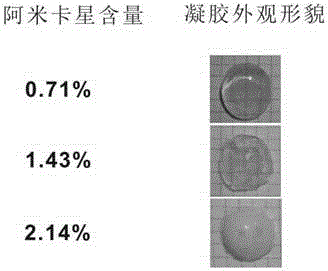
[0083] Embodiment 3: Determination of gel time and mechanical properties of 0.71% amikacin hydrogel (0.71% is the drug content of amikacin (accounting for the percentage of total hydrogel mass))
[0084] Preparation of oxidized dextran-amikacin hydrogel with amikacin content of 0.71%: Mix 170 μL of oxidized dextran solution (50 mg / mL, 48% degree of oxidation) with 30 μL of amikacin solution (50 mg / mL), About 90s to form a gel.
[0085] Test of mechanical properties: A multifunctional rheometer was used to test the mechanical properties of the hydrogel with an amikacin content of 0.71%. The specific method is: 850 μL oxidized dextran solution (50 mg / mL, 48% oxidation degree) was mixed with 150 μL amikacin solution (50 mg / mL), and then immediately transferred to a rheometer plate at 37 ° C for time-dependent simulation. Quantitative measurement (the rheometer model is ARES-G2, TA Instrument Company, the strain rate is 1%, and the frequency is 1 Hz). Such as Figure 5 As shown...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Storage modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Storage modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Storage modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com