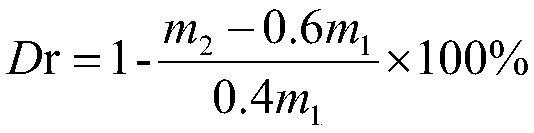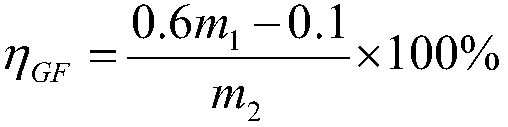Method for wet oxidation separation of glass fiber and epoxy resin in WPCB non-metallic powder
A technology of glass fiber and non-metal powder, which is applied in the field of wet oxidation separation of glass fiber and epoxy resin in WPCB non-metal powder, which can solve the problems of polluting the environment, destroying the structure of crosslinking agent, and difficult to handle non-metal powder, and achieves The reaction is easy to operate, realizes resource utilization, and is suitable for batch processing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
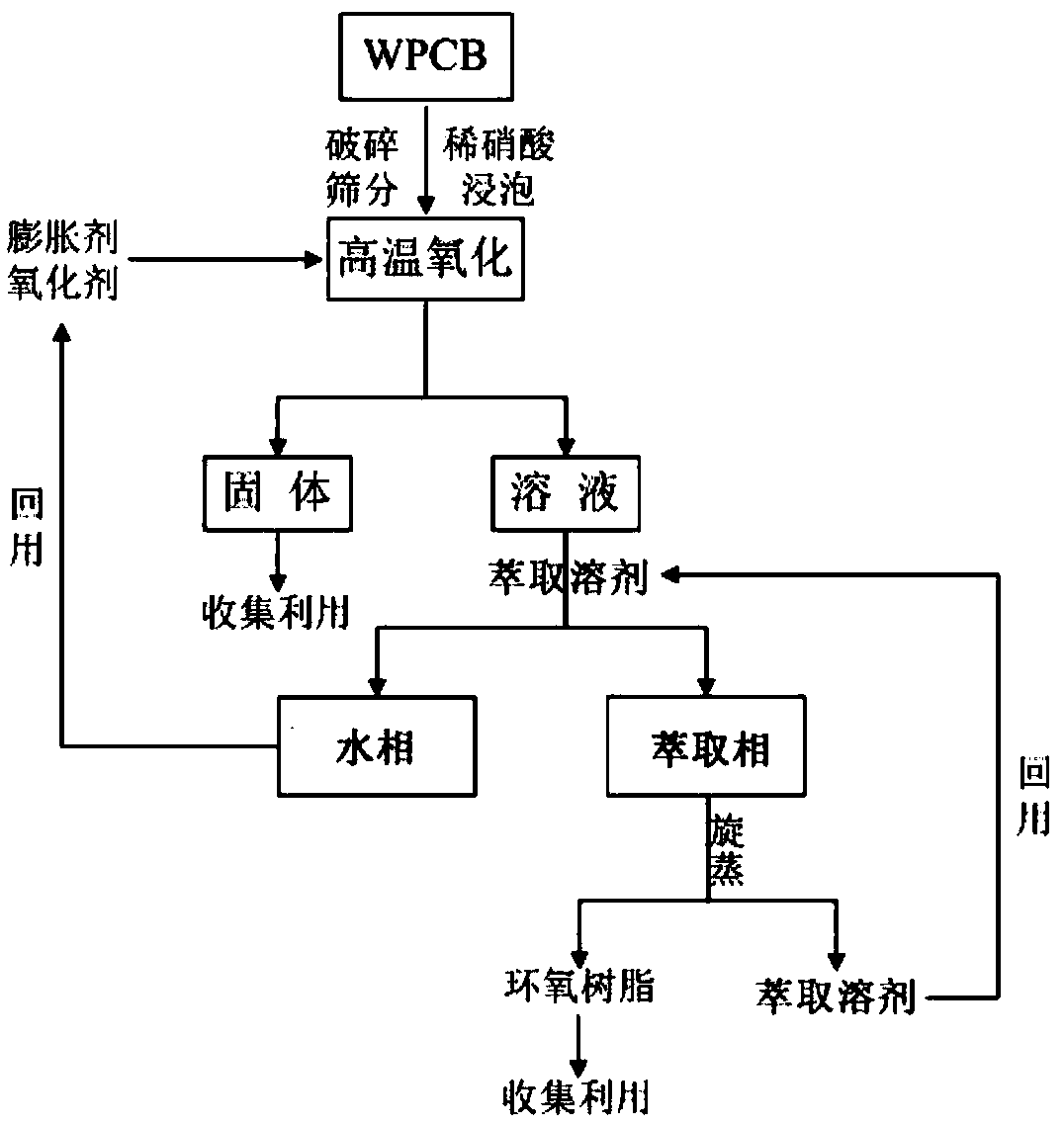
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Sieve WPCB non-metallic powder to obtain WPCB non-metallic particles with a particle size between 1 and 4mm, soak in 10% dilute nitric acid solution in a water bath at 70°C for 6 hours, then filter, and vacuum-dry the filter residue in an oven at 105°C 4h. Weigh the mass after drying as m 1 (2g) non-metallic powder, 48g acetic acid (expanding agent), 19.2g ZnCl 2 (Oxidant) mixed, placed in a 100ml hydrothermal kettle lining, put into an oven for reaction, the oven temperature was set at 190°C, and the reaction time was 20h. After the reaction is finished, the product is successively filtered with ethyl acetate and water to obtain the gray-brown non-metallic powder residue mass m 2 (1.2474g); The filtrate is extracted by ethyl acetate, and the extract is concentrated under reduced pressure by a rotary evaporator to obtain a brown epoxy resin solid mass m 3 (0.5526g), the epoxy resin that reclaims obtains is through Fourier transform infrared analyzer (potassium bromid...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Sieve WPCB non-metallic powder to obtain WPCB non-metallic particles with a particle size between 1 and 4mm, soak in 10% dilute nitric acid solution in a water bath at 70°C for 6 hours, then filter, and vacuum-dry the filter residue in an oven at 105°C 4h. Weigh the mass after drying as m 1 (2g) of non-metallic powder, 48g ethanol (swelling agent) and 19.2g ZnCl 2 (Oxidant) mixed, placed in a 100ml hydrothermal kettle lining, put into an oven for reaction, the oven temperature was set at 190°C, and the reaction time was 20h. After the reaction is finished, the product is successively filtered with ethyl acetate and water to obtain the gray-brown non-metallic powder residue mass m 2 (1.2730g); The filtrate is extracted by dichloromethane, and the extract is concentrated under reduced pressure by a rotary evaporator to obtain a brown epoxy resin solid mass m 3 (0.5270g), the epoxy resin that reclaims obtains is through Fourier transform infrared analyzer (potassium bro...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Sieve WPCB non-metallic powder to obtain WPCB non-metallic particles with a particle size between 1 and 4mm, soak in 10% dilute nitric acid solution in a water bath at 70°C for 6 hours, then filter, and vacuum-dry the filter residue in an oven at 105°C 4h. Weigh the mass after drying as m 1 (2g) of non-metallic powder, 40g acetic acid (expanding agent) and 8g CuCl 2 (Oxidant) mixed, placed in a 100ml hydrothermal kettle lining, put into an oven for reaction, the oven temperature is set at 220°C, and the reaction time is 20h. After the reaction is finished, the product is successively filtered with ethyl acetate and water to obtain the gray-brown non-metallic powder residue mass m 2 (1.3262g); The filtrate is extracted by ethyl acetate, and the extract is concentrated under reduced pressure by a rotary evaporator to obtain a brown epoxy resin solid mass m 3 (0.4378g), the epoxy resin that reclaims obtains is through Fourier transform infrared analyzer (potassium bromi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com