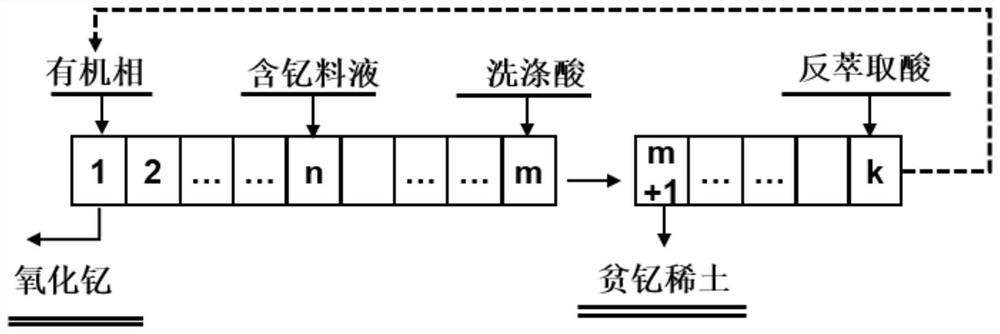
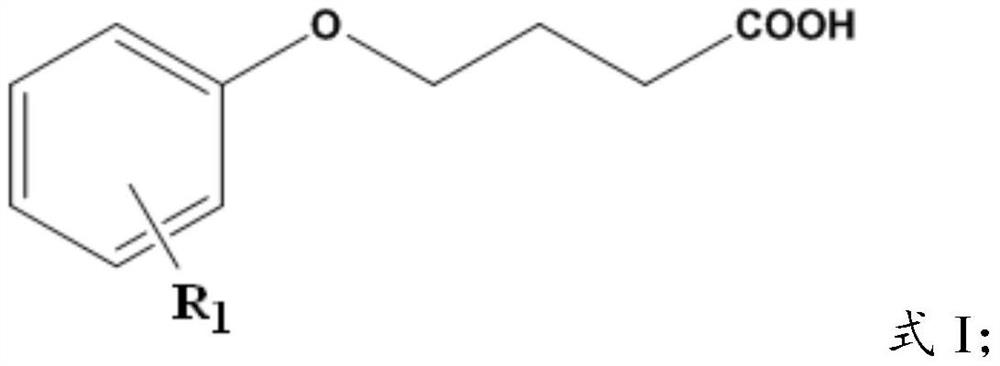
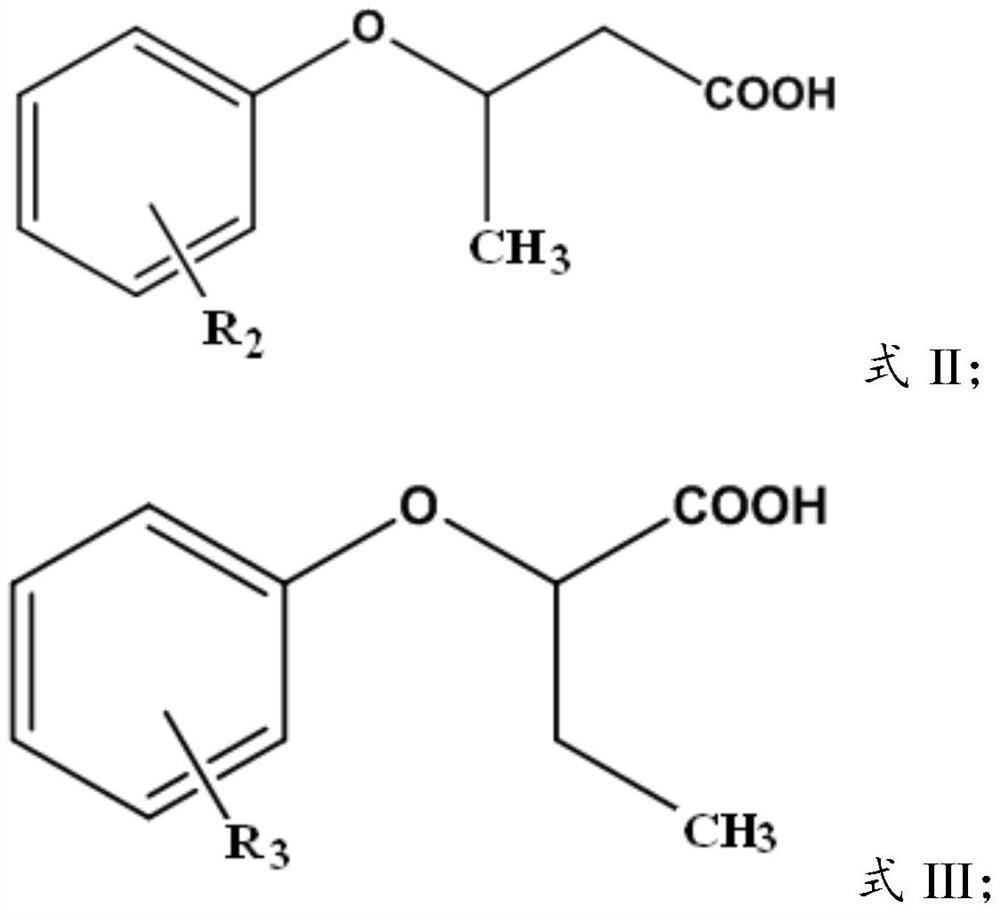
A kind of rare earth extraction agent and the method for separating rare earth yttrium
An extractant and rare earth technology, applied in the field of rare earth extraction and separation, can solve the problems of decreased extraction capacity, increased economic cost, low separation coefficient, etc., and achieves the effects of reducing the number of extraction stages, eliminating pollution, and achieving good selectivity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Example 1 Preparation of 2,6-dimethylheptylphenoxy n-butyric acid
[0041] Add 50 grams of absolute ethanol and 48.4 grams of sodium 2,6-dimethylheptylphenolate into the reaction vessel, start stirring and heating, raise the temperature to 110°C, and slowly add 37.8 grams of sodium bromide-n-butyrate into the reaction vessel . After reacting for 1 hour, cool to room temperature, distill the solvent of the obtained reaction product under reduced pressure, then add 6mol / L hydrochloric acid solution for acidification, wash the acidified product three times with water, and distill under reduced pressure at 160°C to obtain 2,6- Dimethylheptylphenoxy n-butyric acid.
[0042] The 2,6-dimethylheptylphenoxy-n-butyric acid prepared in Example 1 of the present invention has been subjected to acid-base titration and NMR detection, and the purity is greater than 95%. It has the structure of formula I, and R in formula I 1 Take 2,6-dimethylheptyl.
Embodiment 2
[0043] Example 2 Preparation of 2,6-dimethylheptylphenoxyisobutyric acid
[0044] Add 100 grams of absolute ethanol and 48.4 grams of sodium 2,6-dimethylheptylphenolate into the reaction vessel, start stirring and heating, raise the temperature to 100°C, and slowly add 37.8 grams of sodium bromoisobutyrate into the reaction vessel . After reacting for 1.5 hours, cool to room temperature, distill the solvent of the obtained reaction product under reduced pressure, then add 6mol / L hydrochloric acid solution for acidification, wash the acidified product three times, and distill under reduced pressure at 160°C to obtain 2,6- Dimethylheptylphenoxyisobutyric acid.
[0045] The 2,6-dimethylheptylphenoxyisobutyric acid prepared in Example 2 of the present invention is subjected to acid-base titration and NMR detection, and the purity is greater than 97%, and has the structure of formula II. In formula II, R 2 Take 2,6-dimethylheptyl.
Embodiment 3
[0046] Example 3 Preparation of 2,6-dimethylheptylphenoxy sec-butyric acid
[0047] Add 150 grams of absolute ethanol and 48.4 grams of sodium 2,6-dimethylheptylphenolate into the reaction vessel, start stirring and heating, raise the temperature to 90°C, and slowly add 37.8 grams of sodium bromide sec-butyrate into the reaction vessel . After reacting for 2 hours, cool to room temperature, distill the solvent of the obtained reaction product under reduced pressure, then add 6mol / L hydrochloric acid solution for acidification, wash the acidified product three times with water, and distill under reduced pressure at 160°C to obtain 2,6- Dimethylheptylphenoxy-sec-butyric acid.
[0048] The 2,6-dimethylheptylphenoxy-sec-butyric acid prepared in Example 3 of the present invention has been subjected to acid-base titration and NMR detection, and the purity is greater than 98%. It has the structure of formula III. In formula III, R 3 Take 2,6-dimethylheptyl.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com