Antifelting treatment method for machine washable wool fabric
An anti-felting and wool-washing technology, applied in the field of textile fabrics, can solve the problems of strong fabric damage, failure to meet the machine washable standard, and potential threats, so as to reduce the amount of use, improve the strong damage of wool fibers, and improve the original effect of style
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
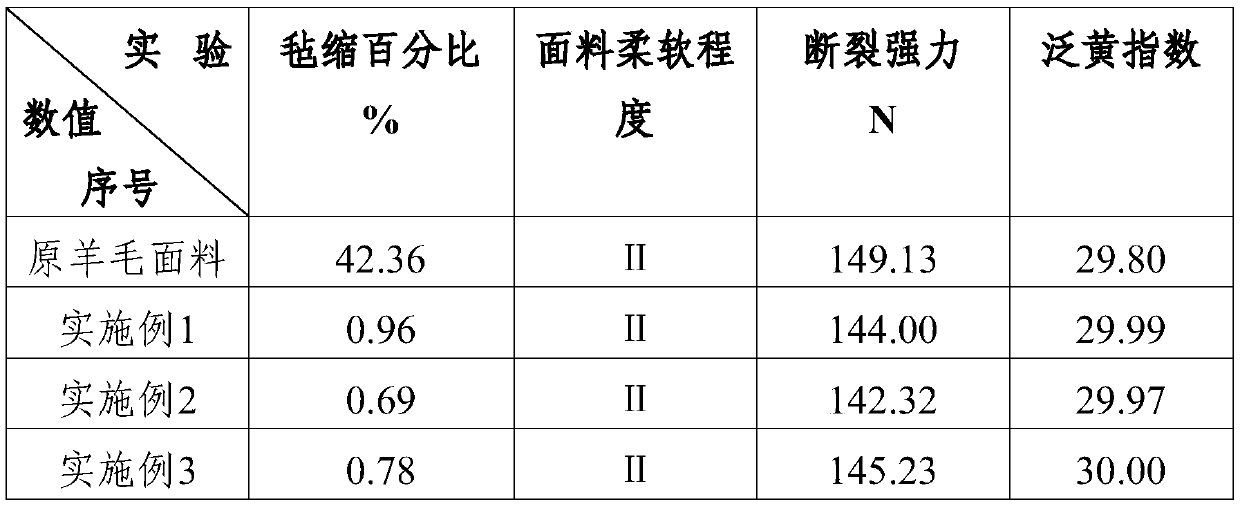
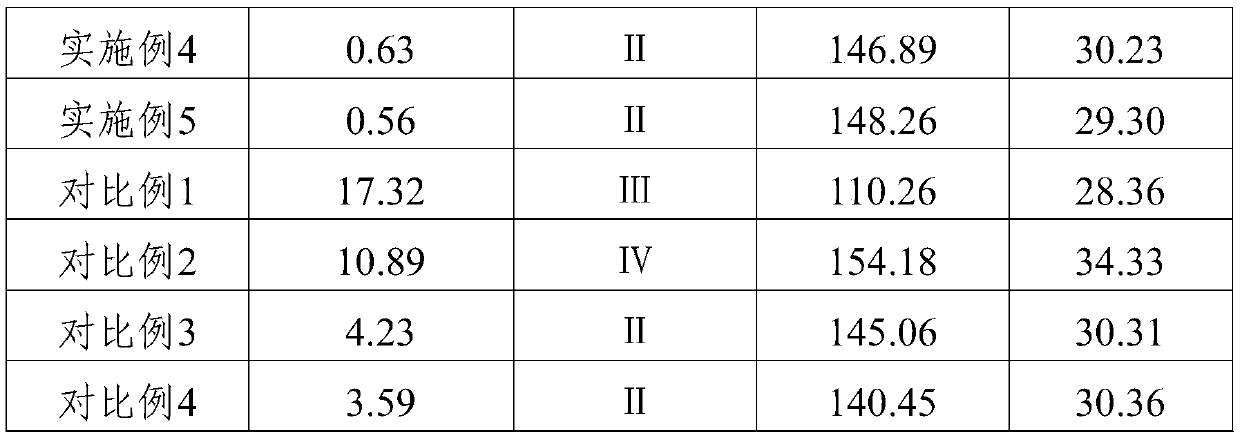
Embodiment 1
[0026] The felting finishing method of the wool fabric of embodiment 1 comprises the steps:
[0027] S1: Configure the pretreatment solution, add the active agent 2-mercaptoethanol and subtilisin into the pretreatment pool filled with a certain quality of water, wherein the concentration of 2-mercaptoethanol is 0.5g / L, and the amount of subtilisin added is 3% of the weight of the fabric, add sodium carbonate to adjust the pH to 10, control the temperature at 50-60°C, and stir for 20 minutes to obtain the pretreatment solution;
[0028]S2: Pretreatment, put the dry wool fabric to be finished in the pretreatment solution, the bath ratio is 1:30, pretreat for 20 minutes at 50-60°C and ultrasonic conditions, heat up to 75-85°C to extinguish the fire with enzyme, put Take out the wool fabric, rinse it with distilled water, and dry it at a low temperature of 60-80°C;
[0029] S3: Prepare a silicone emulsion, add silicone to the emulsifier at room temperature and at a speed of 1500-...
Embodiment 2
[0034] The difference between embodiment 2 and embodiment 1 is that the concentration of active agent 2-mercaptoethanol is 5g / L in step S1, the protease is SAV protease, and the addition amount of SAV protease is 2% of the weight of the woolen fabric, and sodium bicarbonate is added to adjust the pH Be 8; Bath ratio is 1: 60 in the step S2; The emulsifier add-on is 7% of the woolen fabric weight in the step S3, and the organosilicon add-on is 7% of the woolen fabric weight; Add sodium bicarbonate to regulate PH in the step S4 8. Among them, the Japanese Shinko vacuum silicone oil HIVAC-F5 is added in an amount of 7% of the weight of the wool fabric.
Embodiment 3
[0036] The difference between Example 3 and Example 1 is that the protease added in step S1 is Maxacal L protease, sodium phosphate is added to adjust the pH to 9, and the amount of soft and slippery block copolymerized silicone oil K-780 for cotton in step S3 is the weight of wool fabric 5%, the emulsifier is a compound of sorbitan fatty acid ester and sorbitan monooleate polyoxyethylene ether, and the mass ratio of the two is 1:3; the ultrasonic frequency in steps S2 and S5 is 30kHz, power 100W; the concentration of water-based polyurethane in the anti-felting finishing solution is 60g / L.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com