Carboxylesterase gene, recombinant plasmid, recombinant engineered bacterium, encoded protein and application
A technology of recombinant engineering bacteria and protein encoding, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of obtaining heterologous expression, rarely obtaining functional proteins, and unable to express proteins
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
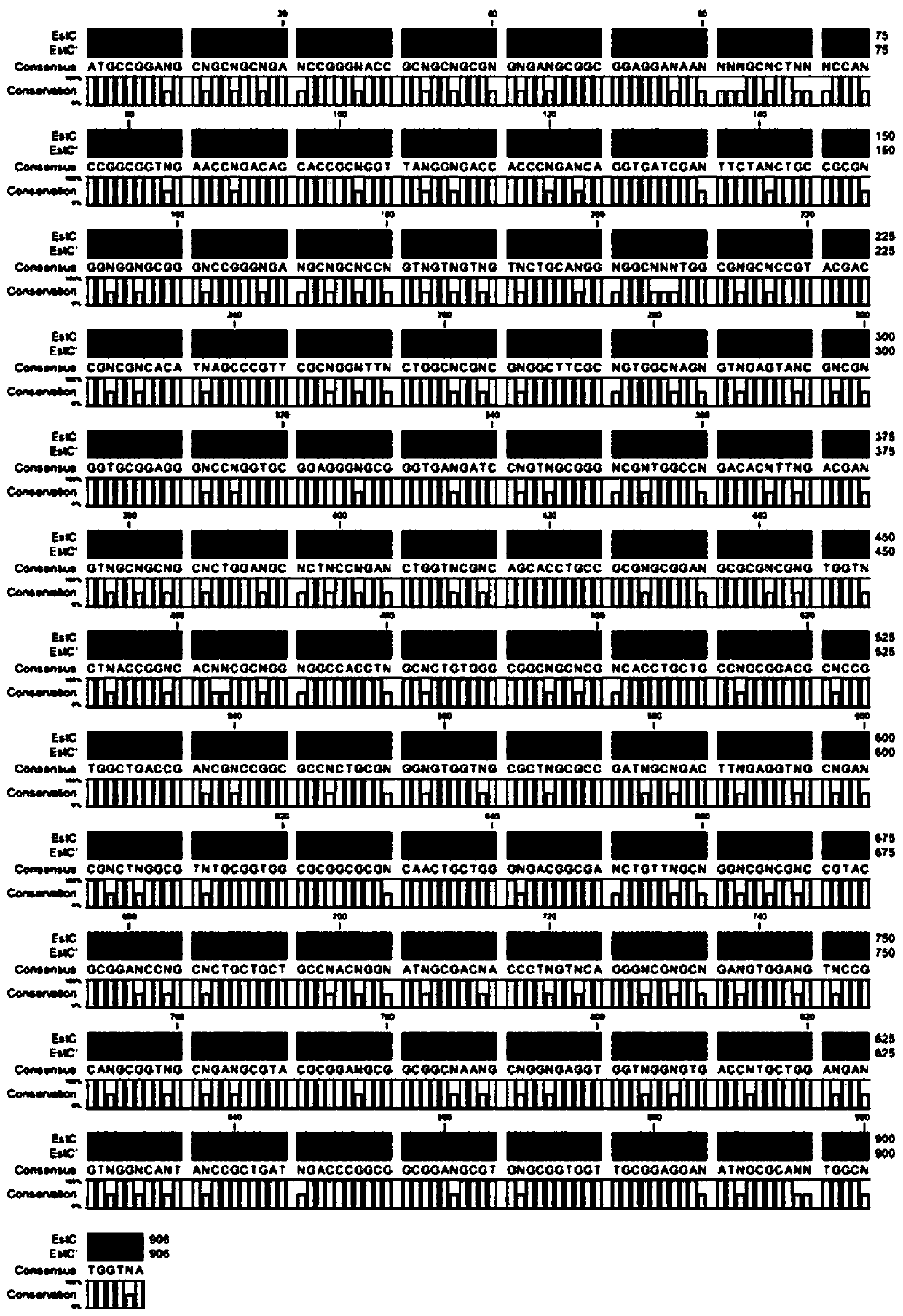
[0036] Optimization, Synthesis and Sequence Analysis of Carboxylesterase Gene estC
[0037]Streptomyces lividans TK24 locus (Locus tag) SLIV_RS20080 is the esterase gene estC, and the name of the protein encoded by this nucleotide sequence is α / β hydrolase (alpha / beta hydrolase), namely carboxylesterase, protein The product (Protein product) number (Accession) is WP_003975294, and the protein accession number in GenBank is AIJ14960. The nucleotide sequence of Streptomyces lividans TK24 esterase gene estC on the chromosome has a start point (Start) of 4442794, a stop point (Stop) of 4443699, a length of 906 bp, and 96 A bases, accounting for 10.6%; T bases are 109, accounting for 12%; C bases are 338, accounting for 37.3%; G bases are 363, accounting for 40.1%; GC content is relatively high, accounting for 77.4%. Due to the high GC content of the esterase gene estC and the complex protein post-translational modification process of Streptomyces, the heterologous expression of t...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Construction of recombinant plasmids and recombinant engineering bacteria
[0041] The artificially synthesized optimized carboxylesterase gene estC' was connected with the plasmid expression vector pET28b carrying the Kan resistance gene to obtain the recombinant plasmid pET28b-est C'. The connection condition is to react overnight at 16°C, and the connection system is:
[0042]
[0043] Mix 10 μL of the above ligation reaction solution with 100 μL of LE.coli Rosetta (DE3) competent cells, ice-bath for 30 minutes, heat shock at 42°C for 90 seconds, then immediately ice-bath for 5 minutes, add 500 μL LB medium to resume culture for 1 hour, and construct recombinant engineered bacteria Rosetta(DE3)pLysS / pET28b-estC', the engineered strain has Kan and Cam resistance, and can be screened by LB medium with Kan and Cam resistance.
Embodiment 3
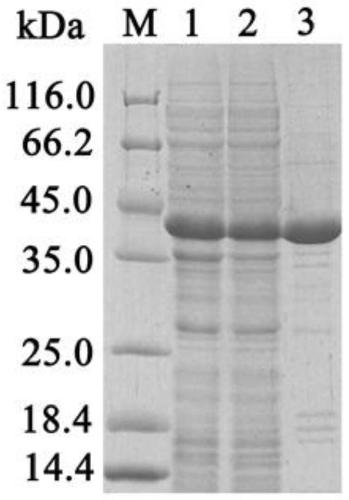
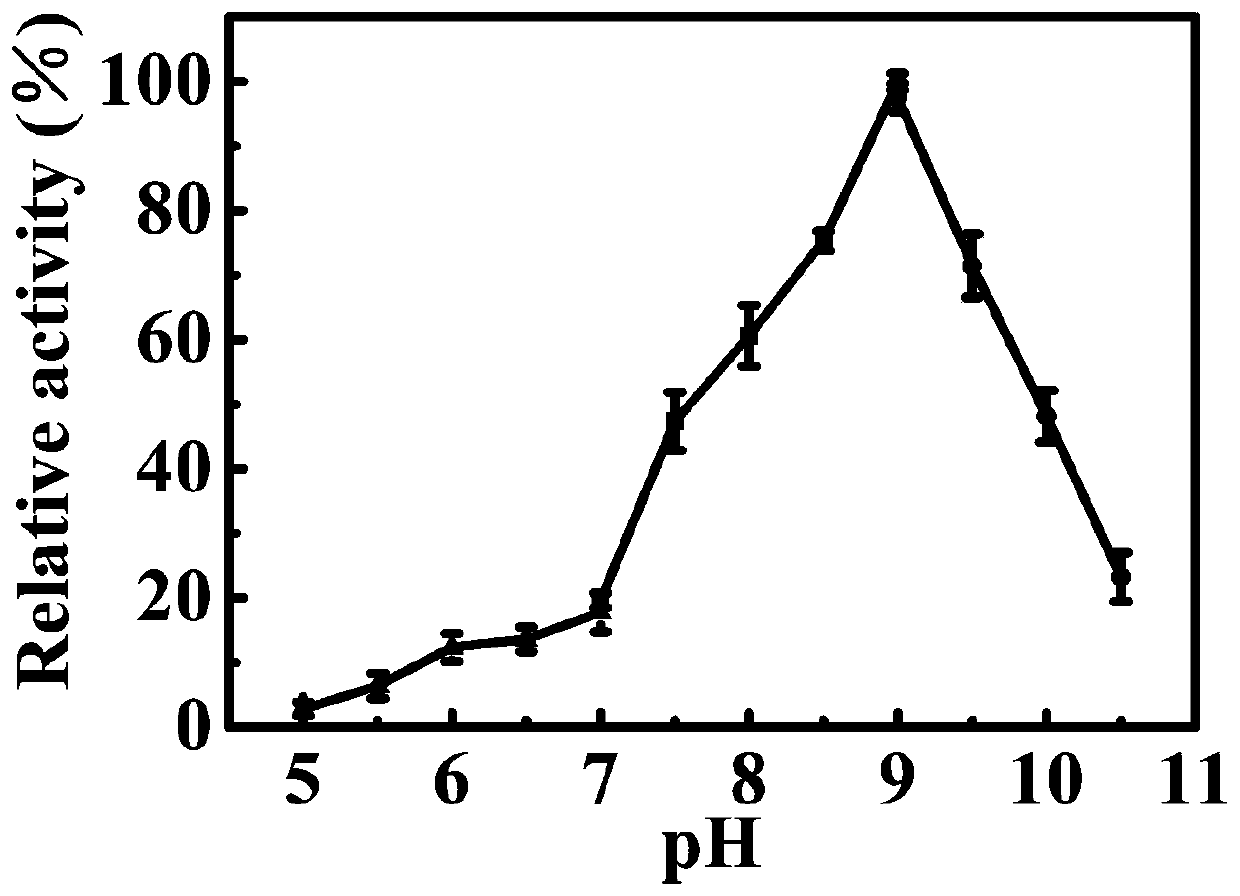
[0045] Expression of carboxylesterase EstC
[0046] Pick the recombinant engineered bacteria from the above-mentioned transformed plates, then inoculate them in a test tube containing 5mL LB liquid medium, shake and cultivate overnight at 37°C, 225rpm; Shaped flask, 37 ° C, 225 rpm shaking culture. Observe the growth of the bacteria during the period, and cultivate to OD 600 When the concentration is 0.4-0.6, add IPTG with a final concentration of 0.01-0.5mM, 180rpm, shake at 16°C-25°C at low temperature, and induce expression for 20-24h. Thereafter, the cells were collected by centrifugation at 5000 rpm for 5 min at 4°C, and ultrasonically disrupted to obtain carboxylesterase EstC.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com