A wet start-up method for hydrocracking
A hydrocracking and start-up oil technology, which is applied in the fields of hydrocarbon oil cracking and petroleum industry, can solve the problems of catalyst activity influence, inert gas passivation effect, and long start-up process, so as to accelerate the initial activity stabilization process and improve Catalyst activity, sufficient effect of sulfuration process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
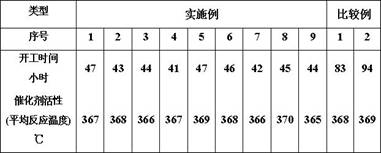
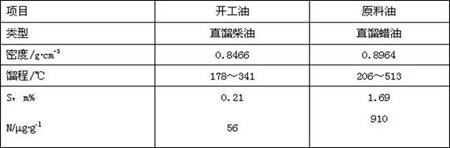
[0037] Firstly, low nitrogen start-up oil, hydrogen and vulcanizing agent are introduced into the hydrocracking unit, and then the hydrocracking catalyst is subjected to constant temperature vulcanization under the condition of 220°C. 4% of the theoretical dosage, after the hydrogen sulfide content in the circulating hydrogen reaches 4000ppm, reduce the adding rate of the sulfurizing agent to 1% of the theoretical dosage of the sulfurizing agent per hour and increase the bed temperature of the hydrocracking catalyst to 320°C, the time used is 15h, When the bed temperature of the hydrocracking catalyst reaches 320°C, increase the addition rate of the vulcanizing agent to 3% of the theoretical amount of vulcanizing agent per hour, continue the constant temperature vulcanization for 3 hours, then raise the temperature to 365°C and feed the raw material oil for reaction, wherein the The hydrocracking catalyst contains 3% nitrogen element, 5.5% nickel oxide, 18% molybdenum oxide and...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Firstly, low nitrogen start-up oil, hydrogen and vulcanizing agent are introduced into the hydrocracking unit, and then the hydrocracking catalyst is vulcanized at a constant temperature at 230°C. 5% of the theoretical dosage, after the hydrogen sulfide content in the circulating hydrogen reaches 5000ppm, reduce the adding rate of the sulfurizing agent to 1.5% of the theoretical dosage of the sulfurizing agent per hour and increase the bed temperature of the hydrocracking catalyst to 325°C, and the time used is 13h. When the bed temperature of the hydrocracking catalyst reaches 325°C, increase the addition rate of the vulcanizing agent to 4% of the theoretical amount of vulcanizing agent per hour, continue the constant temperature vulcanization for 2 hours, then raise the temperature to 365°C and feed the raw material oil for reaction, wherein the The hydrocracking catalyst contains 3% nitrogen element, 5.5% nickel oxide, 18% molybdenum oxide and 30% Y-type molecular sie...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Firstly, low-nitrogen start-up oil, hydrogen and vulcanizing agent are introduced into the hydrocracking unit, and then the hydrocracking catalyst is subjected to constant temperature vulcanization under the condition of 240°C. 3% of the theoretical amount, after the hydrogen sulfide content in the circulating hydrogen reaches 3000ppm, reduce the addition rate of the sulfide agent to 0.8% of the theoretical amount of the sulfide agent per hour and increase the bed temperature of the hydrocracking catalyst to 330°C, and the time used is 10h. When the bed temperature of the hydrocracking catalyst reaches 330°C, increase the addition rate of the vulcanizing agent to 3% of the theoretical amount of vulcanizing agent per hour, continue the constant temperature vulcanization for 4 hours, then raise the temperature to 360°C and feed the raw material oil for reaction, wherein the The hydrocracking catalyst contains 2.5% nitrogen element, 5.5% nickel oxide, 18% molybdenum oxide a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com