A calcium ion exchange porous starch hemostatic material and its preparation method and application
A technology of porous starch and hemostatic material, applied in application, pharmaceutical formulation, surgery, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient particle uniformity, harsh reaction conditions, and large equipment dependence, and achieve the ability to increase the ability to adsorb water molecules, rich sources, The effect of promoting rapid degradation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
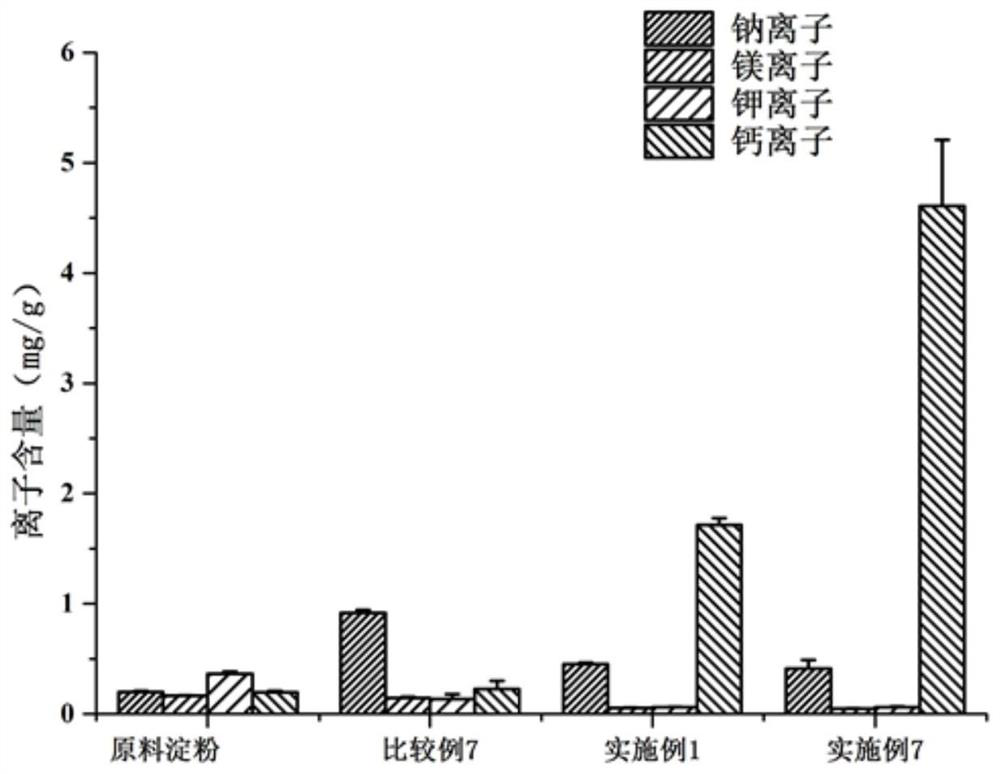
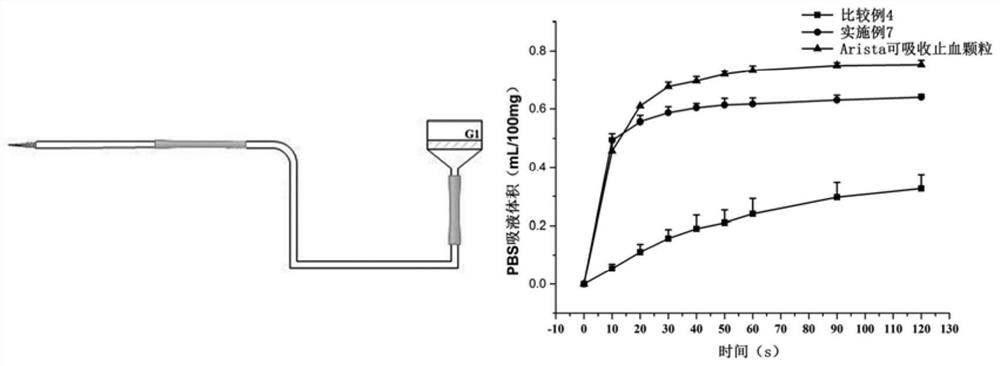
[0045] The preparation method of the present invention is screened out through a large number of experiments. In the process of preparing the porous starch hemostatic material, the ethanol alkali method, the reverse microemulsion method and the cross-linking reaction are combined for the first time, and the ethanol alkali method is used to prepare a rough surface. For the porous starch hemostatic material, use the inverse microemulsion method to control the particle size and particle size distribution range of the starch hemostatic material; secondly, when the present invention selects ethanol as the porogen, its addition is very important, adding Too little particle surface porous structure, low roughness, small specific surface area, only when within the scope of the present invention, the surface roughness of the obtained starch granules reaches a peak, and the liquid absorption rate also reaches a peak; finally, the present invention firstly uses calcium ions Exchanged into...
Embodiment 1
[0050] 1) Gelatinization: Take 10 g of corn starch and add it to 500 g of water to obtain a starch aqueous solution with a concentration of 2 wt%, mechanically stir at 50 rpm, heat at 45° C. for 1 min, cool to 20° C., add NaOH solution to adjust the pH of the starch aqueous solution to 9.0, A gelatinized starch solution is obtained.
[0051] 2) Emulsification, pore formation and crosslinking: Take 3g of emulsifier Span80 (Span 80) and add it to 250ml of liquid paraffin, stir for 10min until the two are evenly mixed, heat to 45°C, and then slowly add 500mL of the product obtained in step 1) The gelatinized starch solution is emulsified at a speed of 500rpm. After the gelatinized starch solution and the emulsifier solution are emulsified, add 10ml of absolute ethanol, stir mechanically at a speed of 500rpm for 15min, add 0.5mL of epichlorohydrin, and stir for 2h to generate crosslinking reaction.
[0052] 3) Calcium ion exchange: After the cross-linking reaction, under mechanic...
Embodiment 2
[0055] 1) Gelatinization: Get 2g of potato starch and add it into 100g of water to obtain a starch aqueous solution with a concentration of 2wt%. Mechanically stir at 100rpm, heat at 65°C for 5min, cool to 30°C, add NaOH solution to adjust the pH of the starch aqueous solution to 9.0, A gelatinized starch solution is obtained.
[0056] 2) Emulsification, pore formation and crosslinking: Take 1.6g of emulsifier Span60 (Span 60) and add it to 200ml of soybean oil, stir for 5 minutes until the two are evenly mixed, heat to 50°C, and then slowly add 100mL of step 1) to get The gelatinized starch solution was emulsified at a speed of 1000rpm. After the gelatinized starch solution and the emulsifier solution were emulsified, 50ml of polyethylene glycol was added, and after mechanical stirring at a speed of 1000rpm for 20min, 0.5mL of epichlorohydrin was added and stirred. 4h cross-linking reaction occurred.
[0057] 3) Calcium ion exchange: After the cross-linking reaction, under m...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com