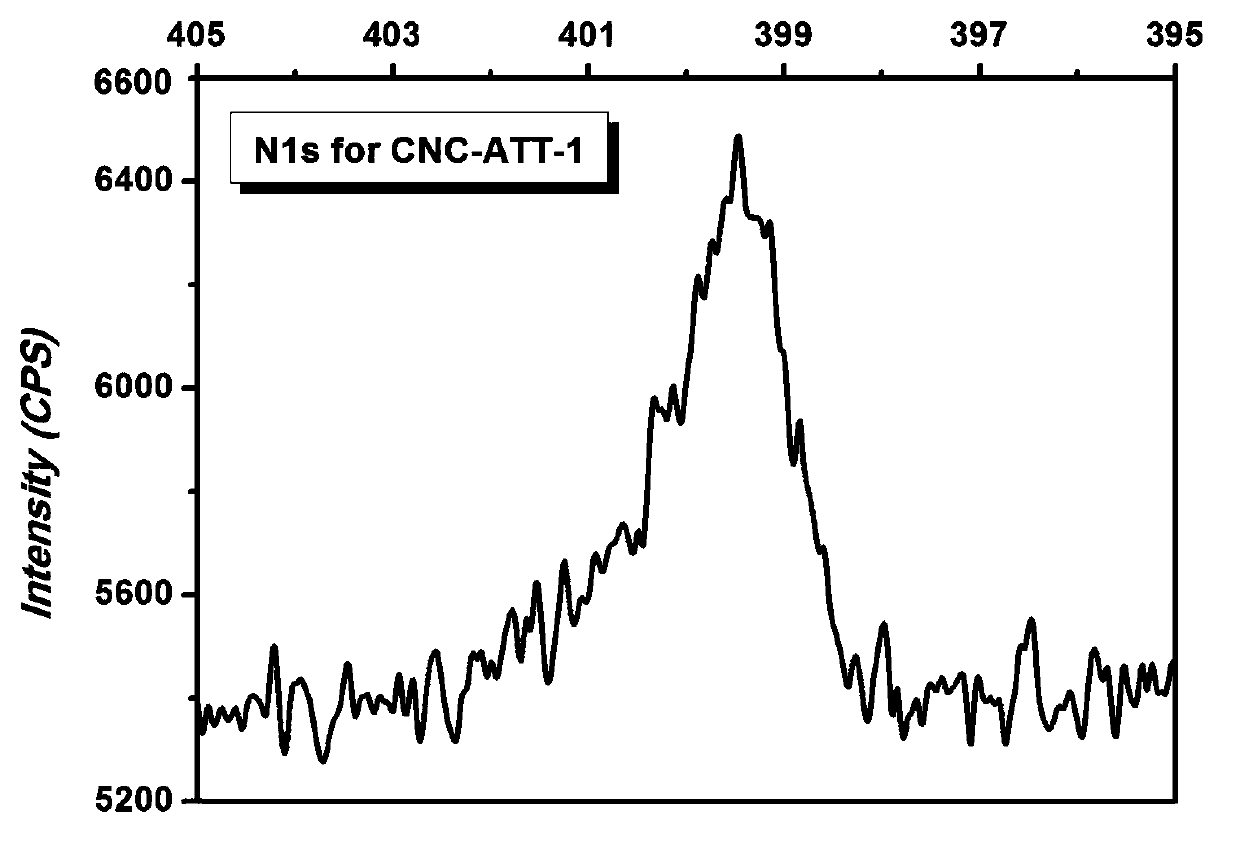
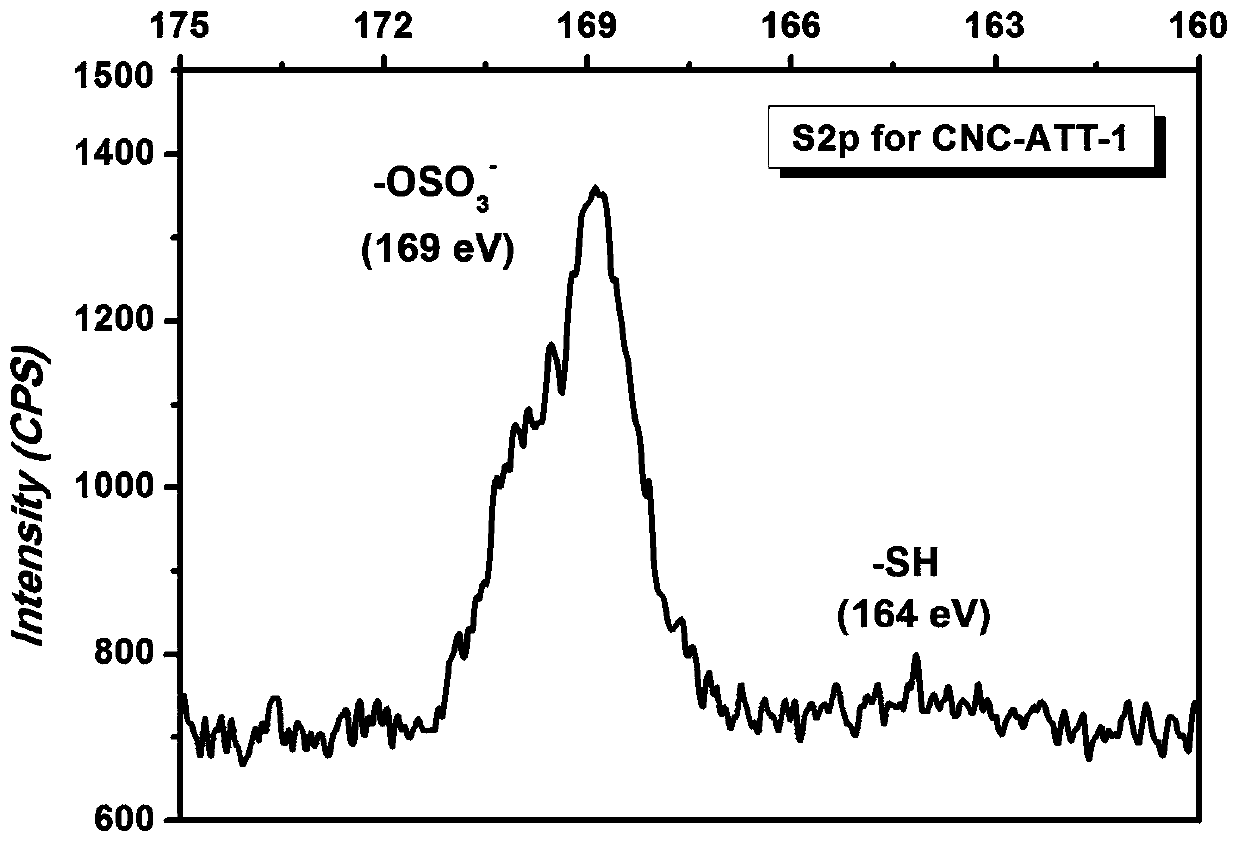
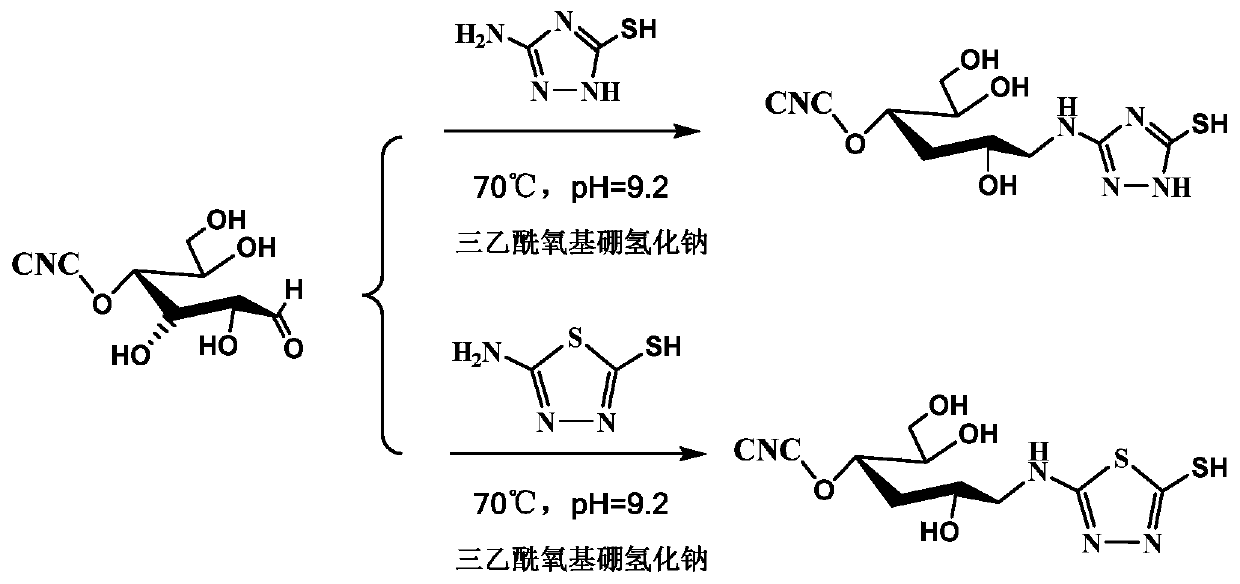
Terminal modification method for improving redispersibility and suspension stability of cellulose nanocrystals
A terminal modification and redispersibility technology, applied in the field of cellulose materials, can solve the problems of unfavorable modification and application, consumption of active hydroxyl groups, etc., and achieve the effects of improving redispersibility and stability, low cost, and mild reaction conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] The prepared cellulose nanocrystal suspension was adjusted to a mass fraction of 1%, and a 0.1 mol / L sodium carbonate solution was prepared. 2.64 mL of sodium carbonate solution was added dropwise to 100 mL of cellulose nanocrystal suspension until the pH of the suspension was 9.2. Under the protection of nitrogen, the suspension was heated to 70°C, and a total of 0.116 g of 3-amino-5-mercapto-1,2,4-triazole and a total of 3.179 g of triacetoxy Sodium borohydride (that is, add 1 / 3 each time), react for 72 hours, and then add 20 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid solution with a concentration of 3 mol / L to terminate the reaction. The obtained suspension was dialyzed in distilled water for 3 days, then potassium chloride solution was added dropwise thereto to adjust the ionic strength of the suspension to 1 mol / L, and finally dialyzed again in distilled water for 3 days to obtain a terminally modified cellulose nanocrystal suspension.
Embodiment 2
[0028] This example is basically the same as Example 1, except that the terminal modification agent is changed from 3-amino-5-mercapto-1,2,4-triazole to thiadiazole molecule 2-amino-5-mercapto- 1,3,4-Thiadiazole.
Embodiment 3
[0030] This example is basically the same as Example 1, except that the pH of the cellulose nanocrystal aqueous suspension is adjusted to 7 before the reaction.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com