Fluorescence probe used for pulmonary fibrosis dyeing
A pulmonary fibrosis and fluorescent probe technology, applied in the field of fluorescent probes for pulmonary fibrosis staining, can solve the problems of many reagents, cumbersome dyeing process, long time-consuming, etc., and achieves reduction of experimental errors, simple dyeing process and good sensitivity Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0016] Example 1 Application of Formula I Molecules in Primary Alveolar Macrophage Staining
[0017] The 6-8 week C57BL / 6J mice were divided into three groups according to body weight: negative control group, model group and positive drug group. The model group and the positive drug cloth group were injected with 3 mg / kg bleomycin into the trachea to simulate human idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, while the negative control group was given the same volume of normal saline as a negative control. The mice in the positive drug group were given the positive drug nintedanib 30mg / kg by oral gavage on the second day after the model was established for drug interference treatment, and the other two groups were given the corresponding solvent as a control. After 21 days of the entire model cycle, the mice were treated with Euthanasia.
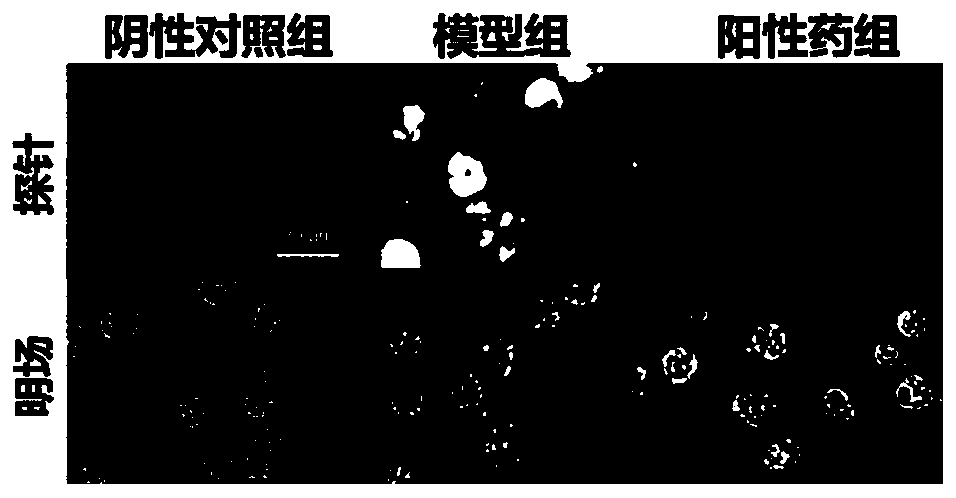
[0018] The primary alveolar macrophages were isolated from the three groups of mice. After the culture was stable, the cells were transferred to a 96-we...
Embodiment 2
[0019] Application of embodiment 2 formula I molecule in lung tissue section staining
[0020] The mouse model is the same as described in Example 1. After the mouse is euthanized, the lungs of the mouse are taken out and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 24 hours, and then the tissue is subjected to a series of dehydration, transparency, wax immersion, embedding, sectioning, and patching 1. Baking the slices to make paraffin sections, and then incubating the slices with 10 μM molecular probe of formula Ⅰ for 30 minutes, washing off with PBS, staining the nuclei with Hoechst reagent, washing off the PBS again, and collecting images with a fluorescence microscope. see results figure 2 , the tissue of the model group showed bright staining results, followed by the positive drug group, and the staining results of the negative control group were weaker, indicating that the probe shown in formula I can detect tissue damage caused by bleomycin modeling.
Embodiment 3
[0021] Example 3 Application of Molecules of Formula I in Live Mouse Imaging of Pulmonary Fibrosis.
[0022] The mouse model is the same as that described in Example 1. On the 21st day, after the mouse is shaved, the molecular probe of formula I with a concentration of 10 mg / kg is injected into the tail vein, anesthetized with isoflurane gas 1.5 hours later, and placed in a small Images were acquired with an In Vivo Imaging System (IVIS), and mice were euthanized at the end. see results image 3 , after bleomycin modeling, the mouse lung tissue showed a more obvious staining effect of probe I, indicating that the probe shown in formula I can detect pulmonary fibrosis caused by bleomycin modeling.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com