Quantitative screening method for halohydrin dehalogenase library and related microfluid system
A technology of halohydrin dehalogenase and microfluidic system is applied in the field of enzyme engineering to achieve the effects of simple detection process, low price and easy acquisition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] System settings and reagent selection of the microfluidic platform;
[0052] Step A: Selection of carrier;
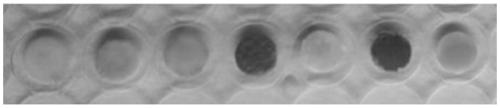
[0053] The specific steps include: screening 7 different types of cellulose and glass fiber membrane paper on the market as the preferred carrier material. In this embodiment, the neutral carrier is selected. The material is simple and low in cost, making it an ideal carrier material.
[0054] Step B: indicator / buffer system
[0055] The choice of indicator depends on the optimal pH of enzyme activity. The optimal pH of halohydrin dehalogenase is 8-9, and the p Ka value of indicator and buffer should be similar. Therefore, phenol red (pKa = 8.0) and HEPES (pKa = 8.2) were selected as indicators and buffers in the catalytic reaction, respectively; an equal amount of HEPES buffer dissolved in 8 μl of phenol red solution was added dropwise to 7 discs (from From left to right are marked as A to G). Use a 6mm punching machine to punch the above seven filter paper carriers, a...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Screening mutation libraries
[0064] Step A: Protein expression and collection
[0065] The wild-type halohydrin dehalogenase and the heterologous expression mutant in recombinant E. coli were selected, cultured at 120 rpm at 37°C for 18 hours and suspended in 10 mM HEPES, and the cells were lysed by ultrasonic treatment. After centrifugation, the supernatant was collected as a crude enzyme extract. The Bradford method was used to determine the protein concentration, and the halide release method was used to measure the activity; for whole cell screening, the cells were suspended in HEPES buffer, washed twice, and used for library screening; The components of the medium used include 10g / L peptone, 5g / L yeast extract, 5g, 10g / L sodium chloride, ampicillin as an antibiotic, and arabinose as an inducer;
[0066] Step B: Library screening of cell-free and whole-cell enzymes
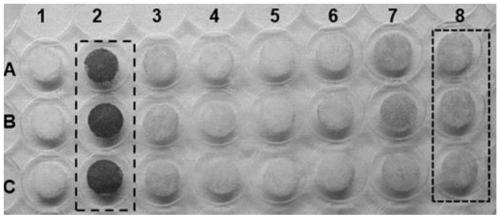
[0067] In order to prove the utility of the present invention for library screening, 5mM 1,3-DCP was used...
Embodiment 3
[0069] Activity analysis of halohydrin dehalogenase mutants
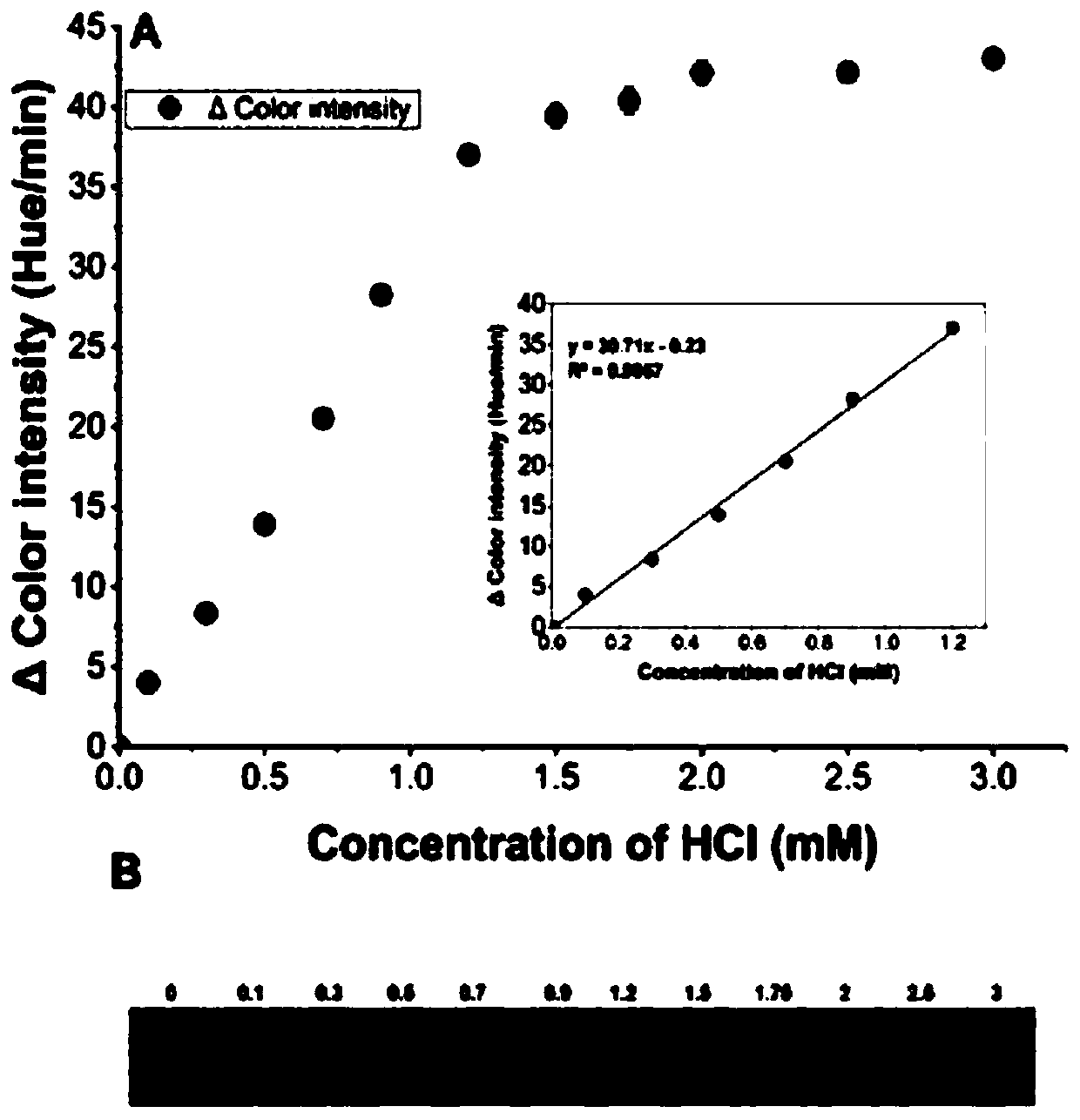
[0070] Four substrates of 1,3-DBP, 2,3-DBP, 1,3-DCP and 2,3-DCP were used to determine the enzyme activity of the HheC mutant; first use a 6mm puncher to punch out 5 paper discs and place them Into a petri dish, two of the paper discs are used as negative controls (without transferring the halohydrin dehalogenase genome) and blank (without enzyme), and the other three paper discs are added with the same enzyme, the same substrate and the color reagent . Fix the camera on a tripod to capture images, and take images every 30 seconds for 10 minutes. With the increase of the reaction product concentration, the color of the filter paper changes continuously, and the steepest part of the fitting curve is used to determine the initial rate; the reaction difference of different substrates is studied by changing the type of substrate in the paper tray, and the result is Figure 4 As shown, the results indicate that the HheC mu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com