Method and application for improving fermentation enzyme production of bacillus licheniformis by knocking out spoIIQ and pcf genes
A Bacillus licheniformis and gene technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of increased viscosity of fermentation broth, liquid escape, disadvantage, etc., and achieve the effects of stable bacterial growth, improved fermentation performance and less foam output
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] Example 1 Construction of Recombinant Bacillus licheniformis (B.licheniformis) DL-1ΔspoⅡQ
[0065] Using the Bacillus licheniformis genome as a template, PCR amplification was performed on the upper and lower homology arms spoIIQF, spoIIQR and the fusion fragment spoIIQF-spoIIQR of the spoIIQ gene. The nucleotide sequences of the primers were as follows:
[0066] spo II QF1: CATCGCCAGTCACTAGGATCCACGCCGAGGACGTAGCCT
[0067] spoⅡQR1: TTACCGTGCTTGGCATTATCCCTCGCTGAACATGTCCCGCTTT
[0068] spoⅡQF2:AAAGCGGGACATGTTCAGCGAGGGATAATGCCAAGCACGGTAA
[0069] spoⅡQR2:CAGTATTGACTGCAGGCGGCCGCAAGCTTGAACGGCTGCCTATT
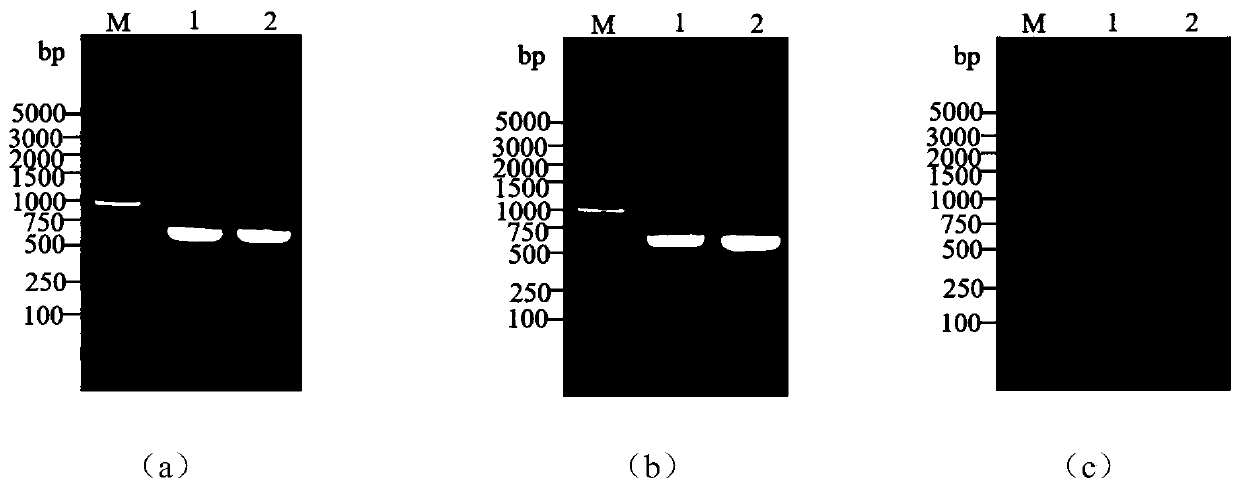
[0070] The amplified product was detected by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis, and specific bands appeared at about 600bp and 1200bp, the results are shown in figure 1 (a), (b), (c).
[0071] The knockout pTOPO-Cmr was double digested with BamHI and NotI, purified according to the steps provided in the purification kit, and the fusion fragment was connected to the vector by ...
Embodiment 2
[0074] Embodiment 2 Construction of recombinant bacteria Bacillus licheniformis (B.licheniformis) DL-1ΔspoⅡQΔpcf, Bacillus licheniformis (B.licheniformis) DL-1Δpcf
[0075] Since the construction process and method of the recombinant B. licheniformis DL-1Δpcf and the recombinant B. licheniformis DL-1ΔspoⅡQΔpcf are the same, only the recombinant B. licheniformis DL-1ΔspoⅡQΔpcf is used as example to illustrate;
[0076] Using Bacillus licheniformis genomic DNA and pHT01 plasmid as templates, PCR amplified pcf and Cm r and the recombinant fragment pcf-Cm r , the nucleotide sequences of the primers used are as follows:
[0077] pcfF CGCGGATCCTGTATAAGCCCTATCAAGATG
[0078] pcfR TTACCGTGCTTGGCATTATCCCTCGCTGAACATGTCCCGCTTT
[0079] cm r F CTACTGTTCAAACCAATGTGAAACTTTTGCTGGCCTTTTGCTCAC
[0080] cm r R CGCGGATCCTAGTGACTGGCGATGCTGTCGG
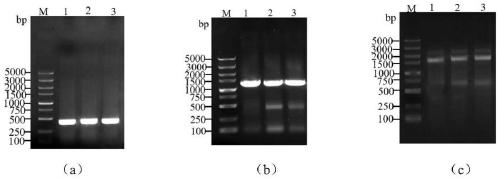
[0081] The amplified products were detected by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis, and specific bands appeared at around 600bp, 1200bp, and 1600bp, r...
Embodiment 3
[0083] Example 3 Determination of spore formation rate and enzyme activity of the starting bacterium and the recombinant bacterium (B.licheniformis) DL-1ΔspoⅡQ
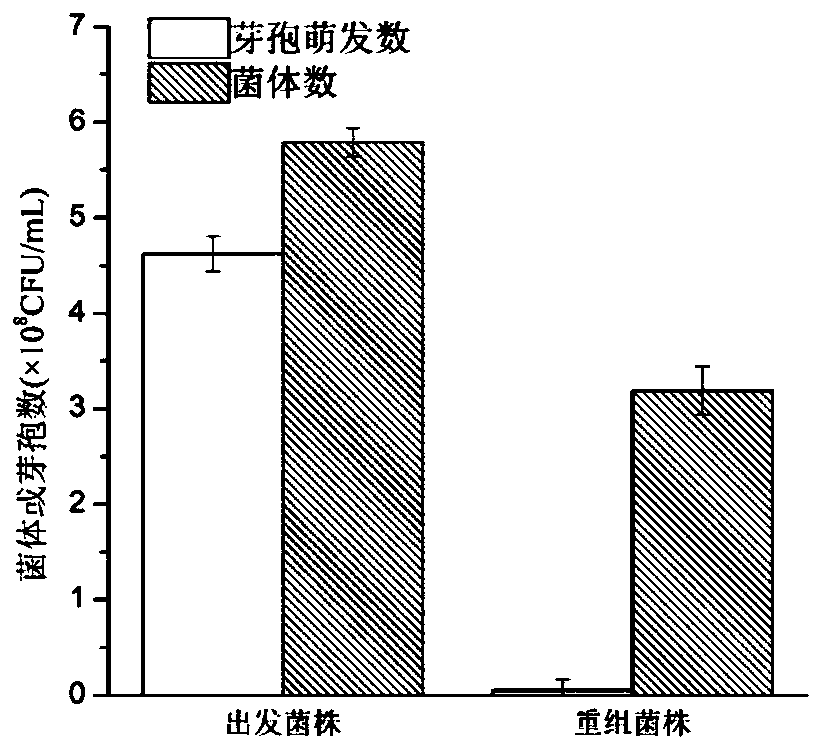
[0084] Take out the bacterial solution of Bacillus licheniformis (B.licheniformis) DL-1 and recombinant bacteria (B.licheniformis) DL-1ΔspoⅡQ from the inoculation loop glycerol tube and streak on the LB plate, culture at 37°C for 24 hours, pick the plate The single colony above was inoculated into 50mL liquid LB medium, cultured at 37°C and 200rpm for 20h and subcultured twice; take the second-generation activated bacterial solution and transfer the starting strain and recombinant bacteria to 100mL liquid LB culture at an inoculation amount of 2%. base, 37°C, 200rpm shake flask culture for 36h, take out 2mL of bacteria and recombinant bacteria, heat treatment in 80°C water bath for 15min, apply LB solid medium after gradient dilution, culture at 37°C for 20h, plate colony count, according to The formula spore formatio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com