Regenerated cellulose fiber
A technology of regenerated cellulose and fiber, which is applied in the manufacture of cellulose/protein conjugated artificial filaments, conjugated synthetic polymer artificial filaments, and fire-resistant and flame-retardant filaments. It can solve the problem of different dyes and low flame retardancy , can not be processed and produced, etc., to achieve the effect of being friendly to humans and the environment, strong heat resistance, and high water absorption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
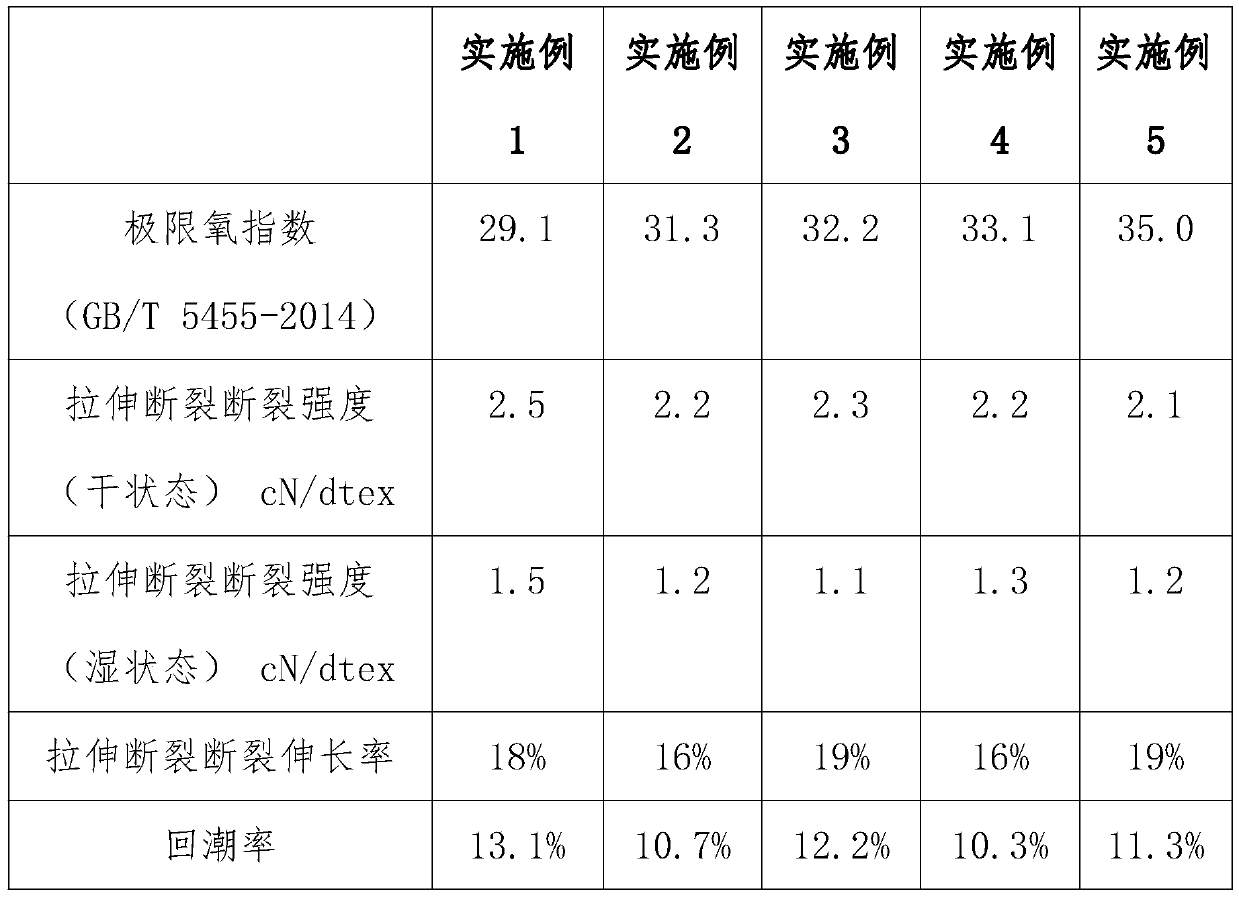
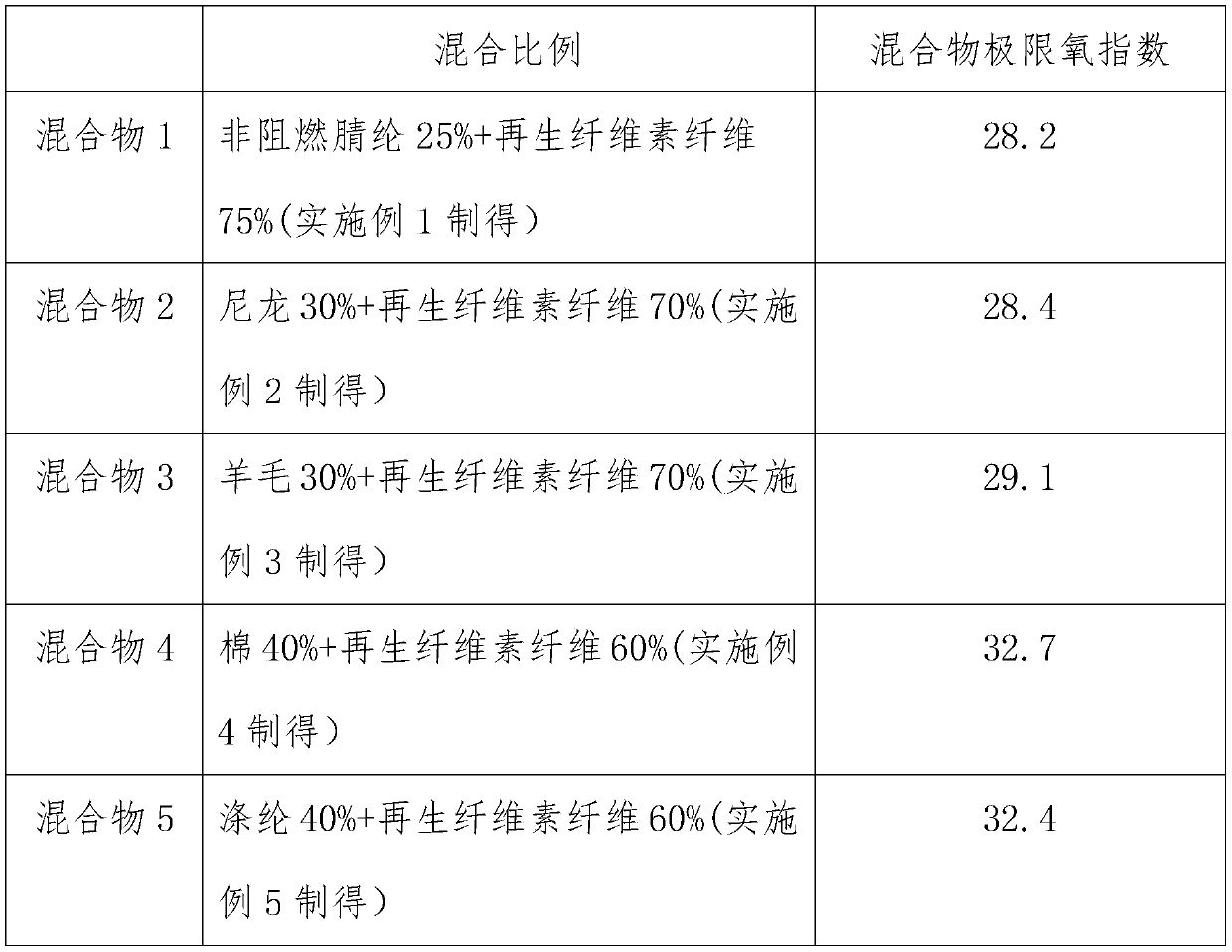
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] A regenerated cellulose fiber proposed by the present invention comprises the following components: regenerated cellulose, component A and component B;
[0040] Component A is one or more of polyvinyl chloride, polyvinylidene chloride and polyvinyl bromide; component B is antimony oxide or a mixture of antimony oxide and organic phosphorus flame retardant; antimony oxide Including antimony trioxide, antimony pentoxide and antimony tetraoxide;
[0041] Component A is polyvinyl chloride; Component B is antimony trioxide; by weight, regenerated cellulose, component A and component B are respectively: 100Kg, 80Kg and 1.6Kg.
[0042] In an optional embodiment, the preparation method of regenerated cellulose fibers, the specific steps are:
[0043] S1. Weigh the regenerated cellulose corresponding to the dry weight in parts by weight and put it into the beating equipment for beating to obtain cellulose pulp C;
[0044] S2, take component A by weight to obtain raw material D; ...
Embodiment 2
[0056] A regenerated cellulose fiber proposed by the present invention comprises the following components: regenerated cellulose, component A and component B;
[0057] Component A is one or more of polyvinyl chloride, polyvinylidene chloride and polyvinyl bromide; component B is antimony oxide or a mixture of antimony oxide and organic phosphorus flame retardant; antimony oxide Including antimony trioxide, antimony pentoxide and antimony tetraoxide;
[0058] Component A is polyvinyl chloride; Component B is antimony trioxide, and by weight, regenerated cellulose, component A and component B are 100Kg, 10Kg and 7Kg respectively.
[0059] In an optional embodiment, the preparation method of regenerated cellulose fibers, the specific steps are:
[0060] S1. Weigh the regenerated cellulose corresponding to the dry weight in parts by weight and put it into the beating equipment for beating to obtain cellulose pulp C;
[0061] S2, take component A by weight to obtain raw material ...
Embodiment 3
[0073] A regenerated cellulose fiber proposed by the present invention comprises the following components: regenerated cellulose, component A and component B;
[0074] Component A is one or more of polyvinyl chloride, polyvinylidene chloride and polyvinyl bromide; component B is antimony oxide or a mixture of antimony oxide and organic phosphorus flame retardant; antimony oxide Including antimony trioxide, antimony pentoxide and antimony tetraoxide;
[0075] Component A is polyvinyl chloride; Component B is antimony trioxide; by weight, regenerated cellulose, component A and component B are 100Kg, 50Kg and 35Kg respectively.
[0076] In an optional embodiment, the preparation method of regenerated cellulose fibers, the specific steps are:
[0077] S1. Weigh the regenerated cellulose corresponding to the dry weight in parts by weight and put it into the beating equipment for beating to obtain cellulose pulp C;
[0078] S2, take component A by weight to obtain raw material D; ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| limiting oxygen index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elongation at break | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com