Micro-fluidic chip for quickly capturing or detecting cells and method
A microfluidic chip and microfluidic technology, applied in cell dissociation methods, animal cells, tumors/cancer cells, etc., can solve the problems of cell morphology and activity, limited capture efficiency, and difficulty in cell separation, etc. Capture and in vitro proliferation efficiency, improved sensitivity and specificity, the effect of high specificity capture
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
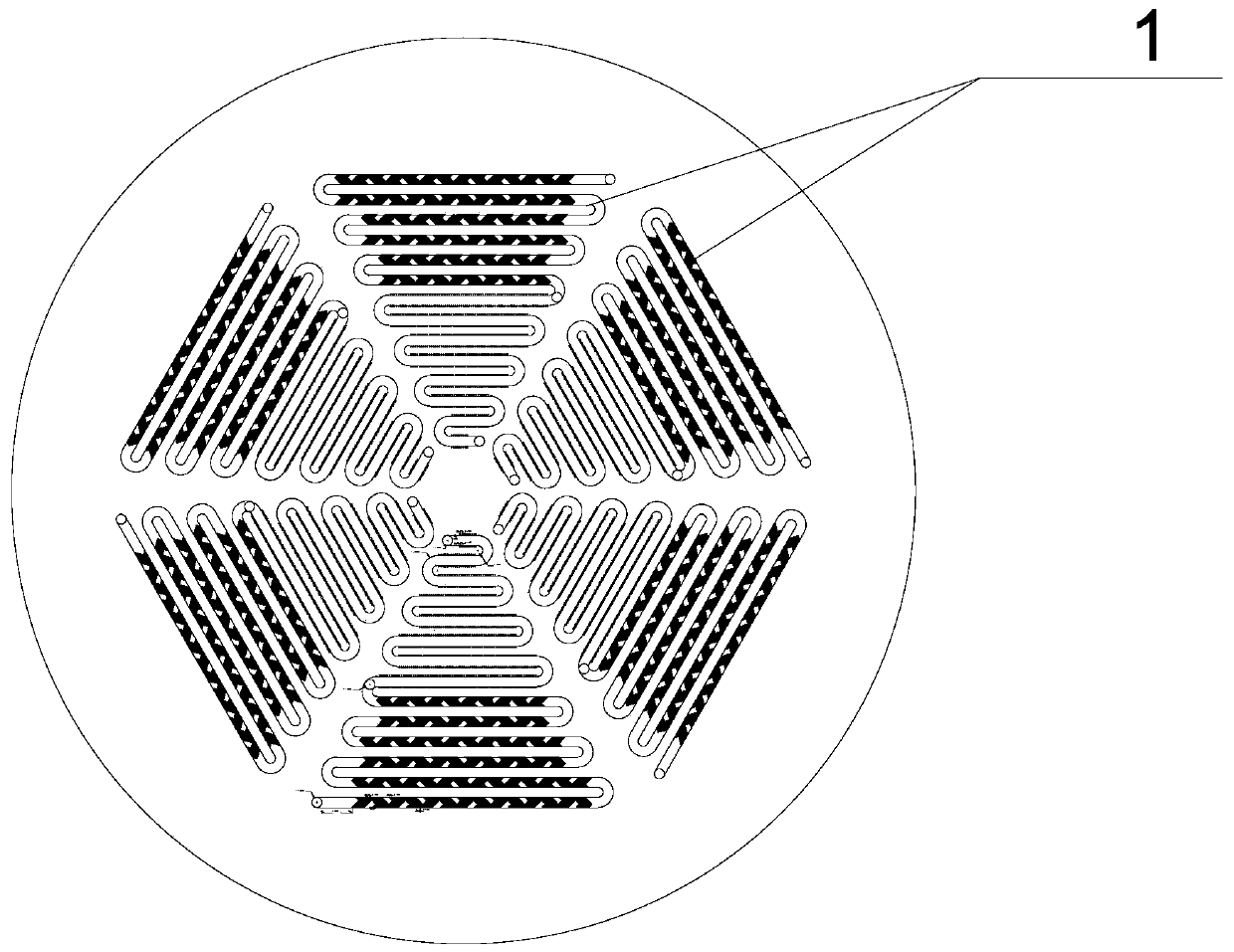
[0065] like figure 1 As shown, 6 groups of identical microfluidic units are distributed on the microfluidic chip, arranged in a circular array.
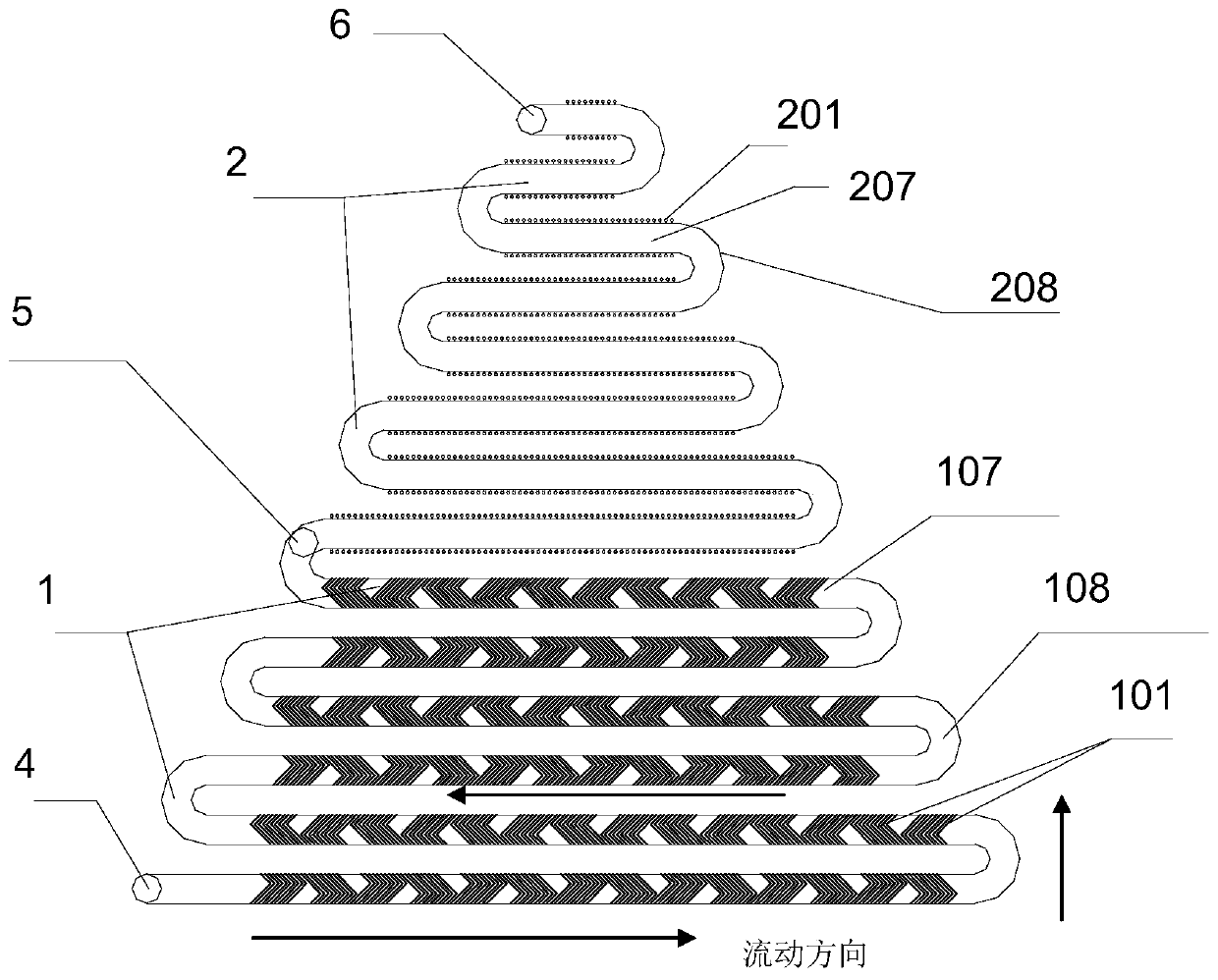
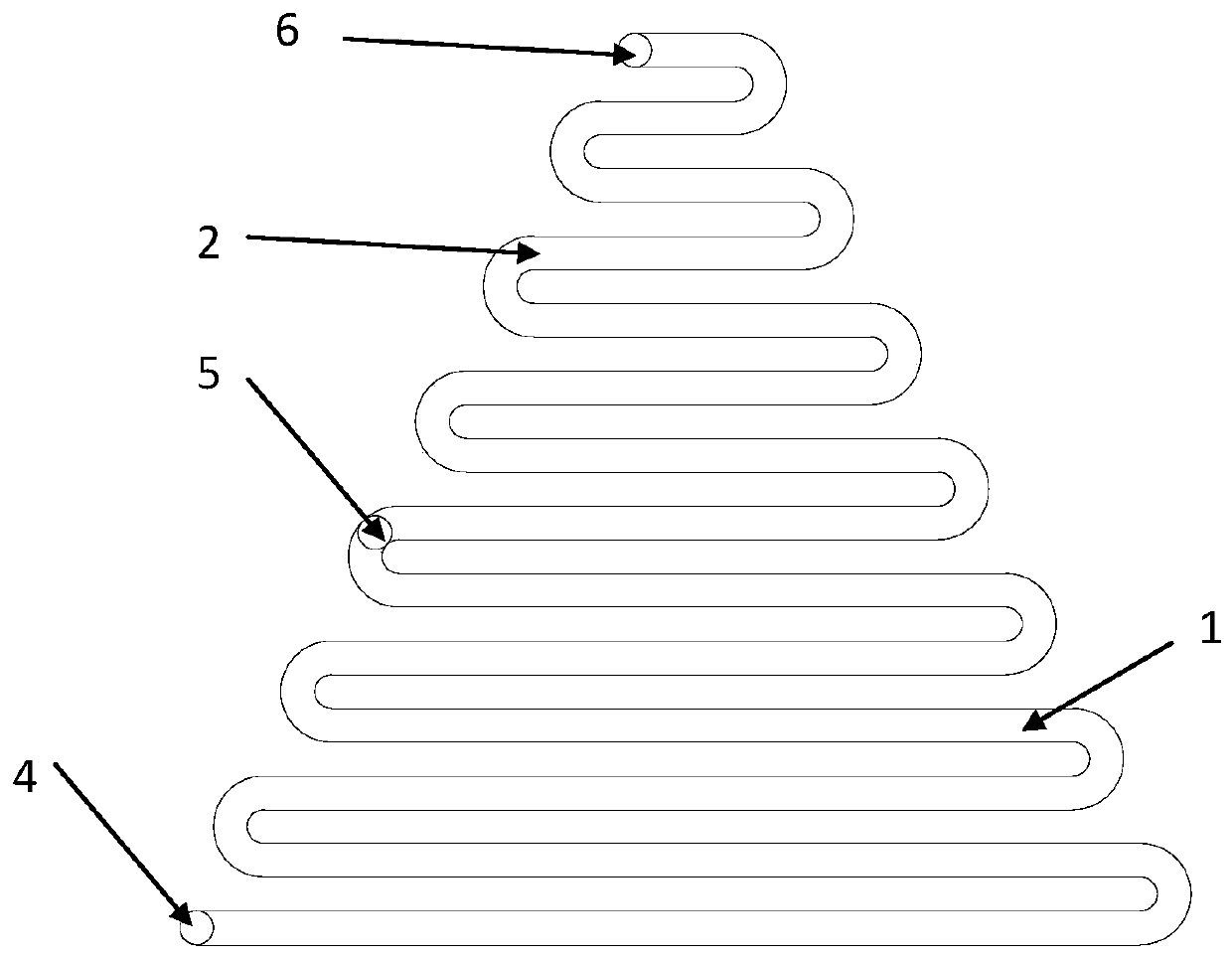
[0066] The design diagram of the microfluidic unit is shown in figure 2 As shown, the structure includes interconnected channel A and channel B, channel A and channel B are serpentine channels with a rectangular cross-section; the serpentine channel without fishbone structural units and cylindrical microcavity structures is shown as image 3 shown.
[0067] Both channel A and channel B are serpentine, including straight channels and arc channels; and the straight channels of the two are arranged parallel to each other; the length of each straight channel is different, and from the center of the microfluidic chip to the outside, the straight channel The length gradually increases; the length of the straight channel of channel B is smaller than that of channel A. The linear channels of channel A are parallel to each other, and the ...
Embodiment 2
[0077] In the channel A between the injection port I and the injection port II of each microfluidic unit of the microfluidic chip in Example 1, first use 3-methoxymercaptopropylsilane to modify the surface with mercapto groups, and construct a total length of 100bp The DNA tetrahedron structure, and acrylamide is modified on three vertices, and the DNA tetrahedron is fixed on the inner surface of the channel through the Michael addition reaction of acrylamide and the sulfhydryl group in channel A. The other vertex of the DNA tetrahedron is decorated with biotin.
Embodiment 3
[0079] Select the aptamer sequence that can specifically recognize Escherichia coli O157:H7 cells, and realize the construction of DNA tetrahedron-avidin-aptamer structure through avidin-biotin, and connect the aptamer sequence that can capture Escherichia coli O157:H7 cells Fixed to the inner surface of channel A. The aptamer sequence contains an EcoRI restriction site.
[0080] Take Escherichia coli O157:H7 cells for fluorescent staining, resuspend in phosphate buffer solution with pH=7.4, and prepare 10 7 、10 6 、10 5 、10 4 、10 3 、10 2 CFU / mL mixture.
[0081] Open the inlet II and give a negative pressure of -0.06Mpa vacuum, and slowly pass 100 μL of the cell suspension containing E. coli O157:H7 cells from the inlet I into the microfluidic chip to realize sample injection and aspiration of waste liquid , target cells are recognized and captured by the aptamer sequence within lane A.
[0082] After the target cells are captured, under the negative pressure condition...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com