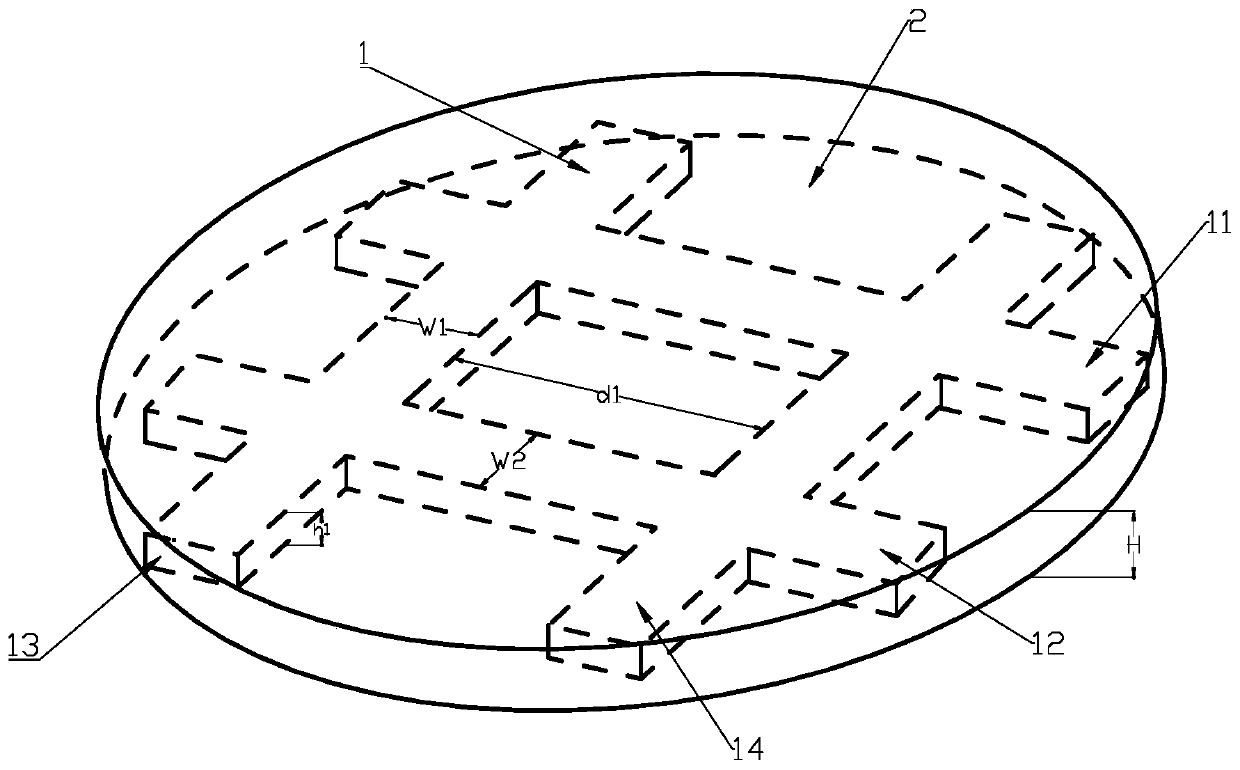
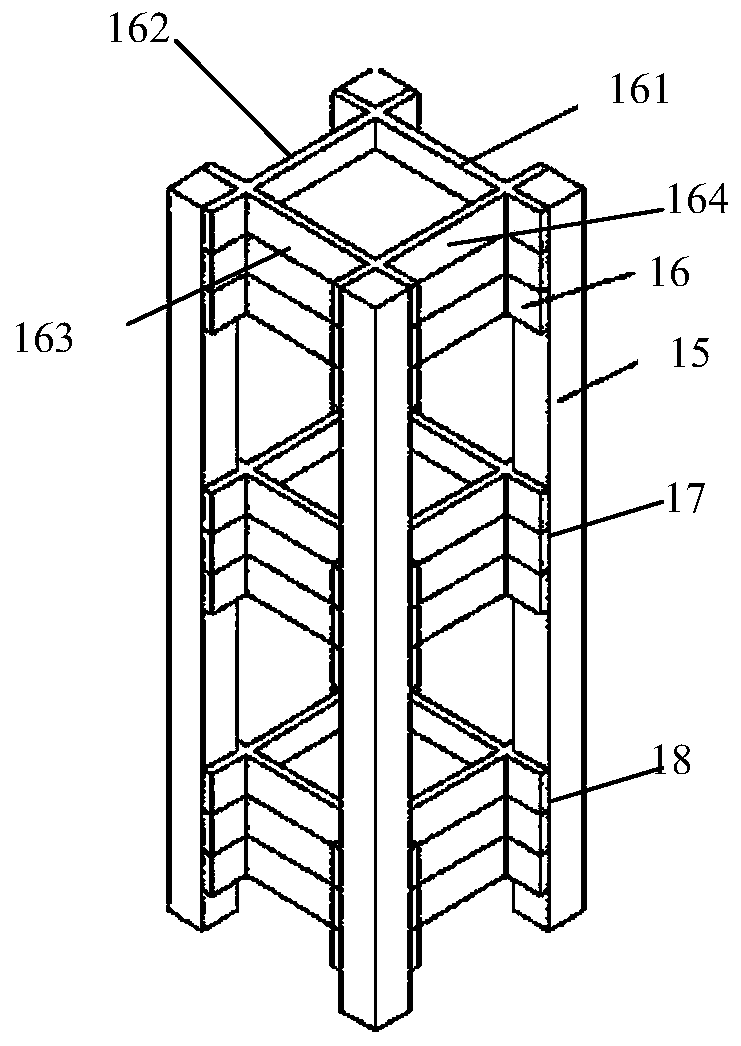
Multi-stage biomimetic mineralized collagen-based skull repair implant and preparation method thereof
A technology of biomimetic mineralization and mineralization of collagen, applied in bone implants, prostheses, skulls, etc., to enhance the ability of osseointegration, promote osteogenesis, and enhance osteoconductivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
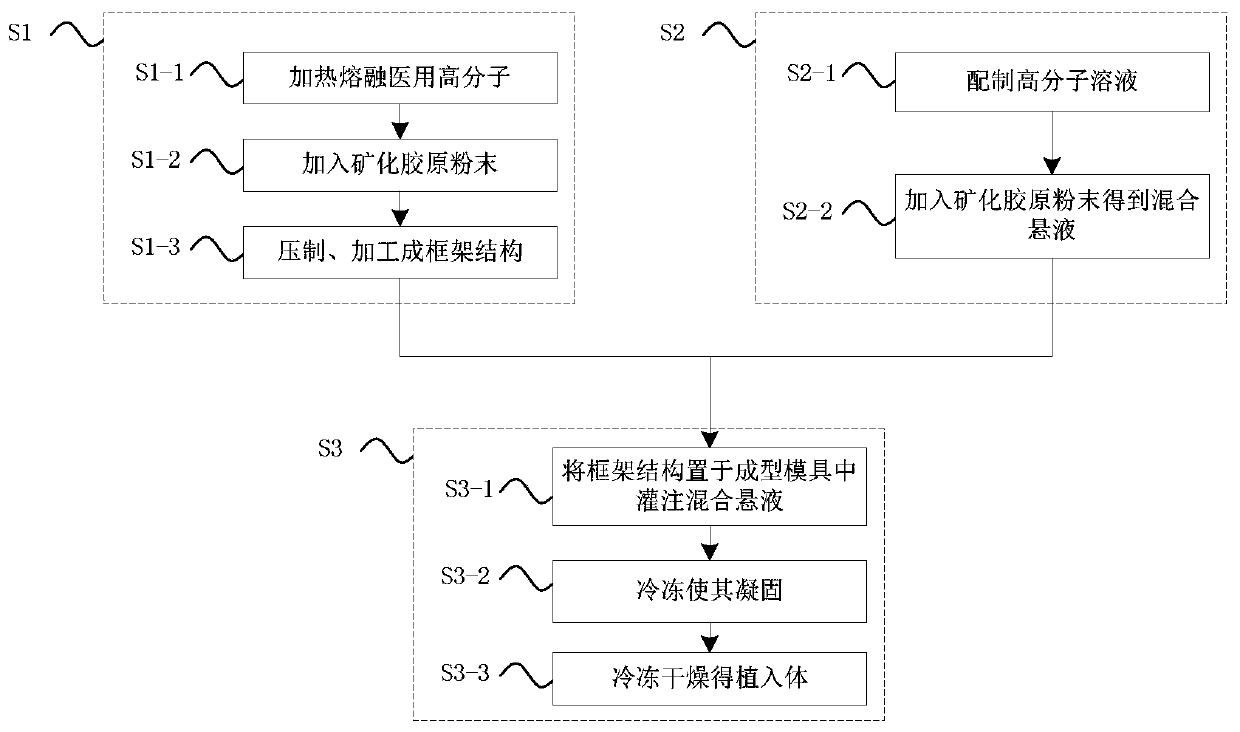
[0052] The specific preparation method of the above-mentioned multi-level biomimetic mineralized collagen-based skull repair implant will be described below. Correspondingly, the present invention also provides a preparation method of such a multi-level biomimetic mineralized collagen-based skull repair implant, the process of which is as follows image 3 shown, including the following steps:
[0053] Step S1, preparation of bionic dense bone, specifically includes:
[0054] Step S1-1, heating the medical polymer material with a viscosity average molecular weight of 50000-200000 to a molten state, the heating temperature is 60-180°C (eg 60, 80, 100, 120, 140, 160 or 180°C). The medical polymer material is one of polycaprolactone (polycaprolactone, PCL), polylactic acid (polylactic acid, PLA) and its copolymer (PCL-PLA).
[0055] Step S1-2, weighing the corresponding mass of mineralized collagen powder, the mass ratio of the mineralized collagen powder to the medical polymer ...
Embodiment 1
[0074] Step S1, preparation of bionic dense bone, specifically includes:
[0075] Step S1-1, placing 5 g of polycaprolactone (PCL) with a viscosity-average molecular weight of 100,000 on a constant-temperature heating plate for heating, and setting the heating temperature to 100° C. to transform the polycaprolactone into a molten state;
[0076] Step S1-2, weighing 5g of mineralized collagen powder, and adding it to the molten polycaprolactone obtained in step S1-1, and fully mixing the two substances by mechanical stirring to form a uniform phase;
[0077] Step S1-3, uniformly transfer the mixture obtained in step S1-2 into a "well"-shaped mold, place the mold on a heating plate to maintain the temperature to maintain the operability of the mixture, and adjust the fit of the mixture and the mold by external force degree, so that it finally reaches the shape of the mold, and then remove the system from the heating plate, let it cool to room temperature, and obtain a "well"-sha...
Embodiment 2~18
[0095] Except for the contents of Table 1 below, it was performed in the same manner as in Example 1.
[0096]
[0097]
[0098] "Mass ratio A" in the table is the mass ratio of mineralized collagen and medical polymer materials in bionic compact bone; "mass ratio B" is the mass ratio of mineralized collagen and medical polymer materials in bionic porous bone; PLA-PCL is Polylactic acid-caprolactone block polymer. Among them, the test results show that the ratio of mineralized collagen and medical polymer materials in Examples 9 and 10 directly affects the efficiency and effect of mineralized collagen repair, and an excessive ratio of mineralized collagen will make the overall mechanical properties of the scaffold material Significant decline, not enough to support the strength of skull repair, while the degradation time is greatly shortened, which does not match the regeneration rate, and the material is excessively degraded before the regeneration is completed, which c...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Pore size distribution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com