Novel artificial blood vessel
An artificial blood vessel, a new type of technology, applied in medical science, prosthesis, etc., can solve problems such as appropriate repopulation of unfavorable host cells, processing technology and clinical outcome limitations, to enhance specific migration and selective adhesion, and the method is simple. , high biocompatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0019] Below in conjunction with implementing regulation this patent is described further.
[0020] 1) Manufacturing method of double-layer artificial blood vessel
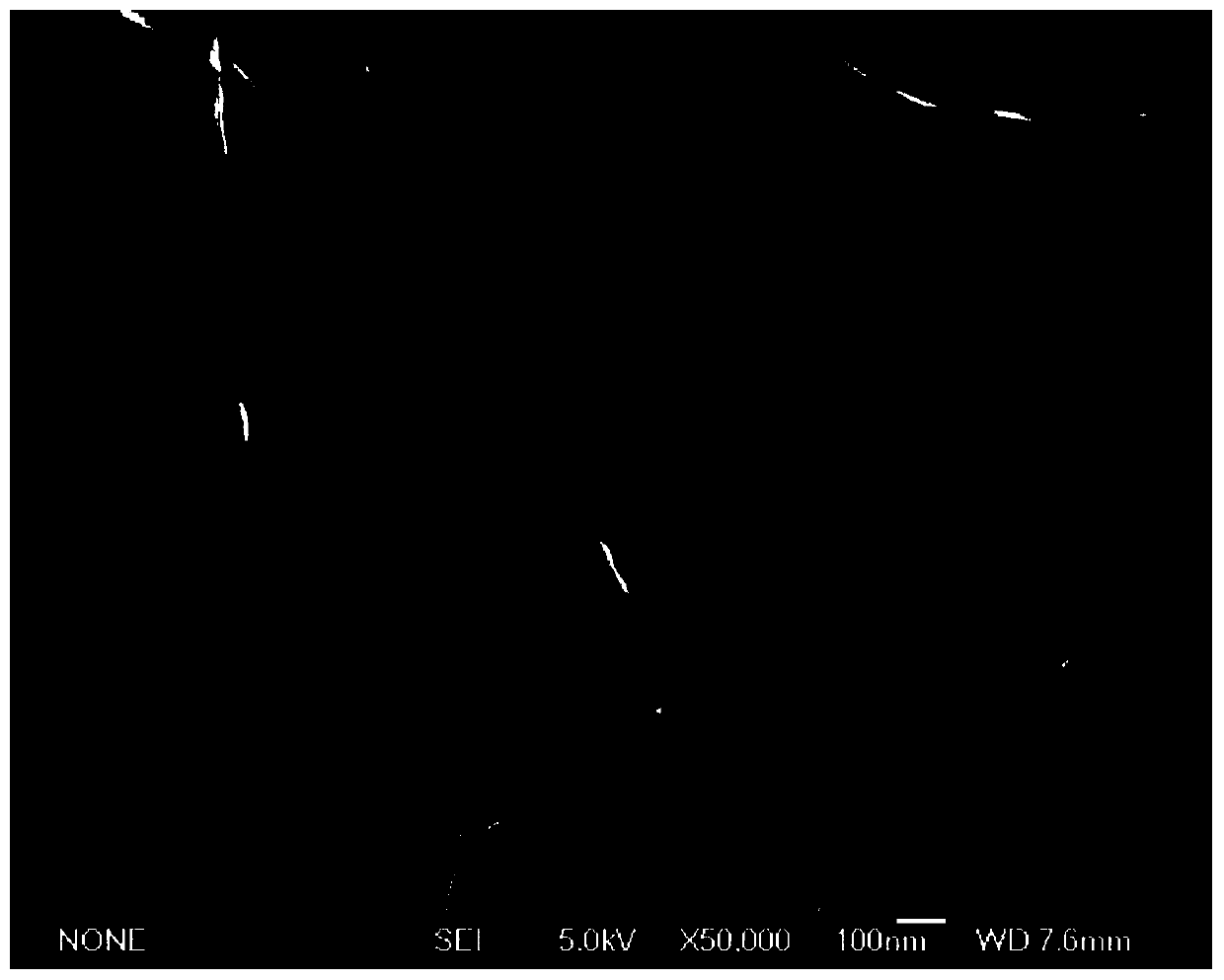
[0021] Outer layer: bacterial cellulose. Obtained by culturing Acetobacter xylinum in acetic acid bacteria medium (#350). The bacterial cellulose membrane is firstly rinsed with clean water, then boiled with 1% NaOH until the solution is clear, and finally soaked in ultrapure water until weakly alkaline or neutral. Soak in 75% medical alcohol for 10 minutes, and irradiate with ultraviolet light for 1 hour to sterilize.
[0022] Inner layer: ordered fiber filaments. A 7% (v / v) polycaprolactone (PCL) printing solution was prepared, and polycaprolactone ordered fibers were obtained by rapid prototyping means such as 3D printing. Soak in 75% medical alcohol for 10 minutes, and irradiate with ultraviolet light for 1 hour to sterilize.
[0023] 2) In vitro cell culture
[0024] The prepared ordered fibers and bact...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com