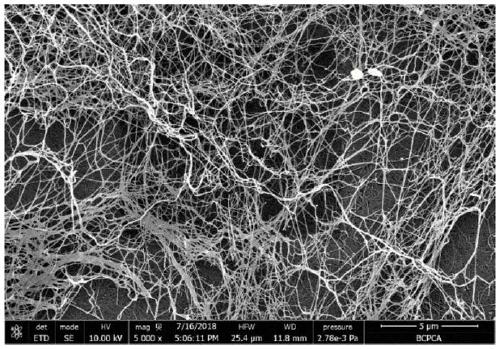
Biological surgery patch and preparation method thereof
A surgical and biological technology, applied in medical science, coatings, non-woven fabrics, etc., can solve problems such as long solid fermentation time, insignificant improvement of mechanical properties of membrane materials, unfavorable cell and tissue proliferation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0025] The invention provides a method for preparing a biosurgical patch. The preparation base material is a bacterial cellulose film obtained through biological fermentation; the bacterial cellulose film obtained through biological fermentation is purified, oxidized, and freeze-thawed. , Composite process treatment, electrospinning treatment, freeze-drying treatment and film pressing treatment to obtain biosurgical patch;
[0026] The preparation method of described biosurgical patch comprises the following steps:
[0027] 1) Fermenting and culturing the strains to obtain bacterial cellulose membranes; adding biopolymer materials during the fermentation and culturing; the biopolymer materials include polylactic acid, polyamide, polyester, glycerin, polylactide, poly One or more of caprolactone, polyvinyl chloride, polyethylene;
[0028] 2) Soaking the bacterial cellulose membrane obtained in step 1) in the inorganic alkali solution and the acid solution successively to obtai...
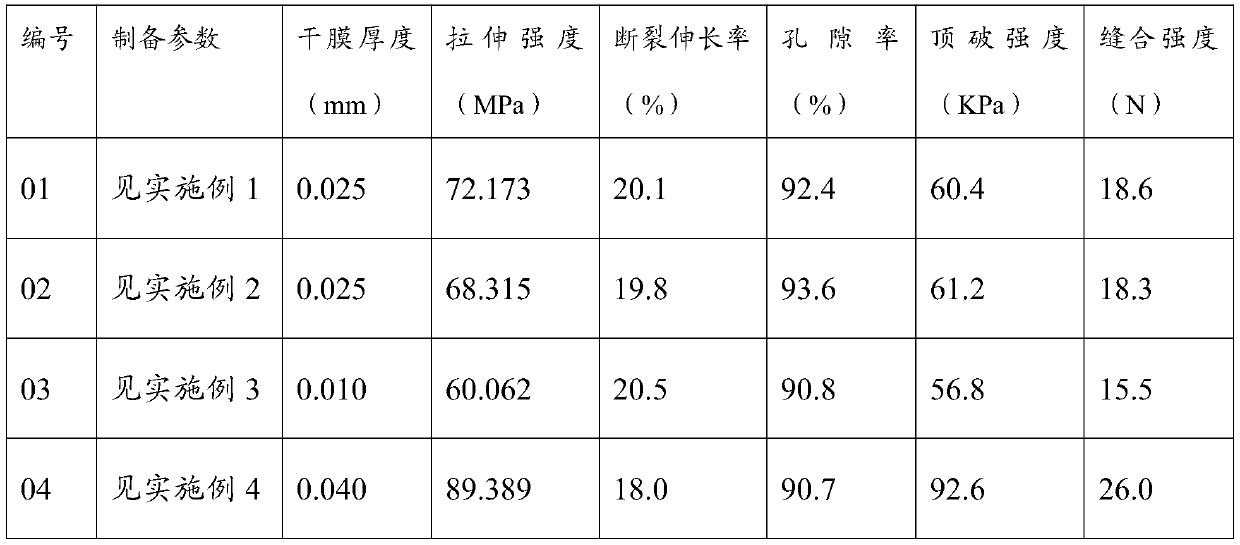
Embodiment 1
[0044] Step 1) Preparation of culture medium: Weigh 20g of mannitol, 15g of polyethylene glycol, 25g of sucrose, 20g of glucose, 0.5mg of niacin, 5g of yeast powder, 10g of corn steep liquor powder, 5g of beef extract, 10g of peptone, KH2 PO 4 2g, MgSO 4 2g, 8g of absolute ethanol, 0.5g of ammonium sulfate, 0.5g of citric acid, 0.5g of sodium carboxymethylcellulose, 10g of gluconic acid, and 40g of sodium gluconate were added to 1000mL of purified water.
[0045] Step 2) Fermentation: Activate the microbial strains that produce cellulose film to obtain activated strains, transfer the activated strains to stainless steel trays for expanded cultivation, obtain seed liquid, and cultivate them in a constant temperature incubator at 37°C for 10 days. On the first day and the third day, 2% mannitol and 5% polyethylene glycol were added respectively, and the pH of the system was maintained at 6.8 during the whole fermentation process, and the oxygen flow rate was 0.4L / min. One layer...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Step 1) Preparation of culture medium: Weigh 25g of mannitol, 10g of polyethylene glycol, 30g of sucrose, 15g of glucose, 0.8mg of niacin, 6g of yeast powder, 15g of corn steep liquor powder, 10g of beef extract, 5g of peptone, KH 2 PO 4 1.5g, MgSO 4 2.5g, 10g of absolute ethanol, 0.8g of ammonium sulfate, 0.6g of citric acid, 0.6g of sodium carboxymethylcellulose, 10g of gluconic acid, and 50g of sodium gluconate were added to 1000mL of purified water.
[0056] Step 2) Fermentation: Activate the microbial strains that produce cellulose film to obtain activated strains, transfer the activated strains to stainless steel trays for expanded cultivation, obtain seed liquid, and cultivate them in a constant temperature incubator at 40°C for 6 days. On the first day and the third day, 2% mannitol and 5% polyethylene glycol were added respectively, and the pH of the system was maintained at 3.8 during the whole fermentation process, and the oxygen flow rate was 3.5L / min. One...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com