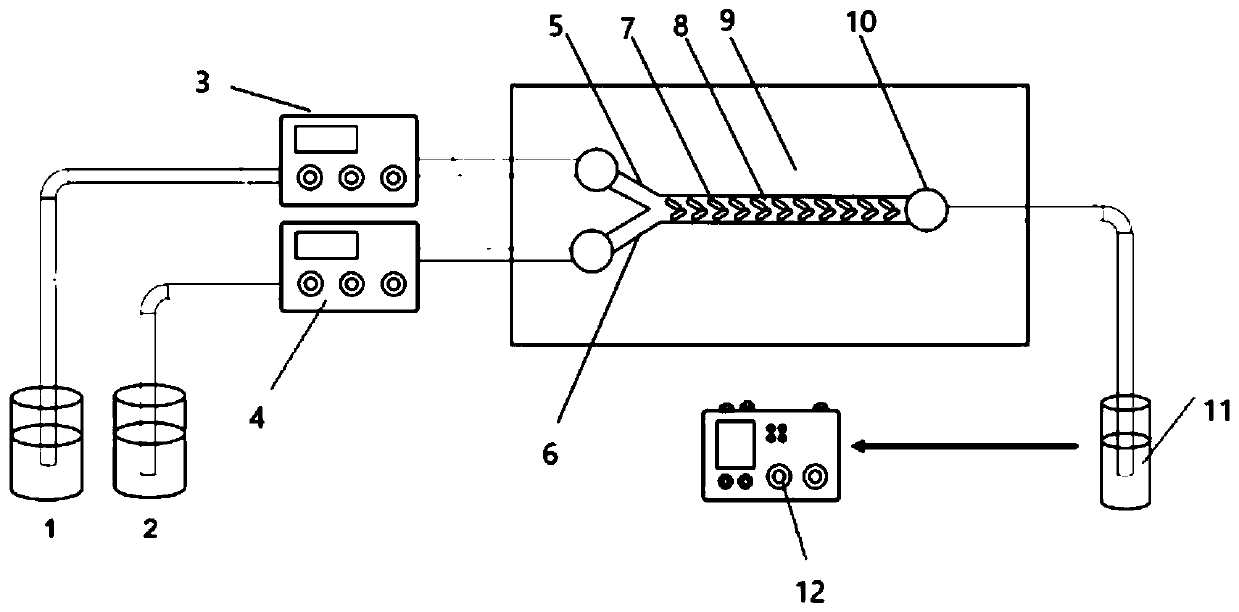
System and method for synthesizing methyl ethyl oxalate based on micro-channel reactor
A microchannel reactor, methyl ethyl oxalate technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, ester group and hydroxyl reaction preparation, chemical/physics/physicochemical reactors, etc., can solve the problem of long production cycle, complex production process, Affecting problems such as synthesis efficiency, to achieve the effect of reducing human accidents, high yield and high selectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
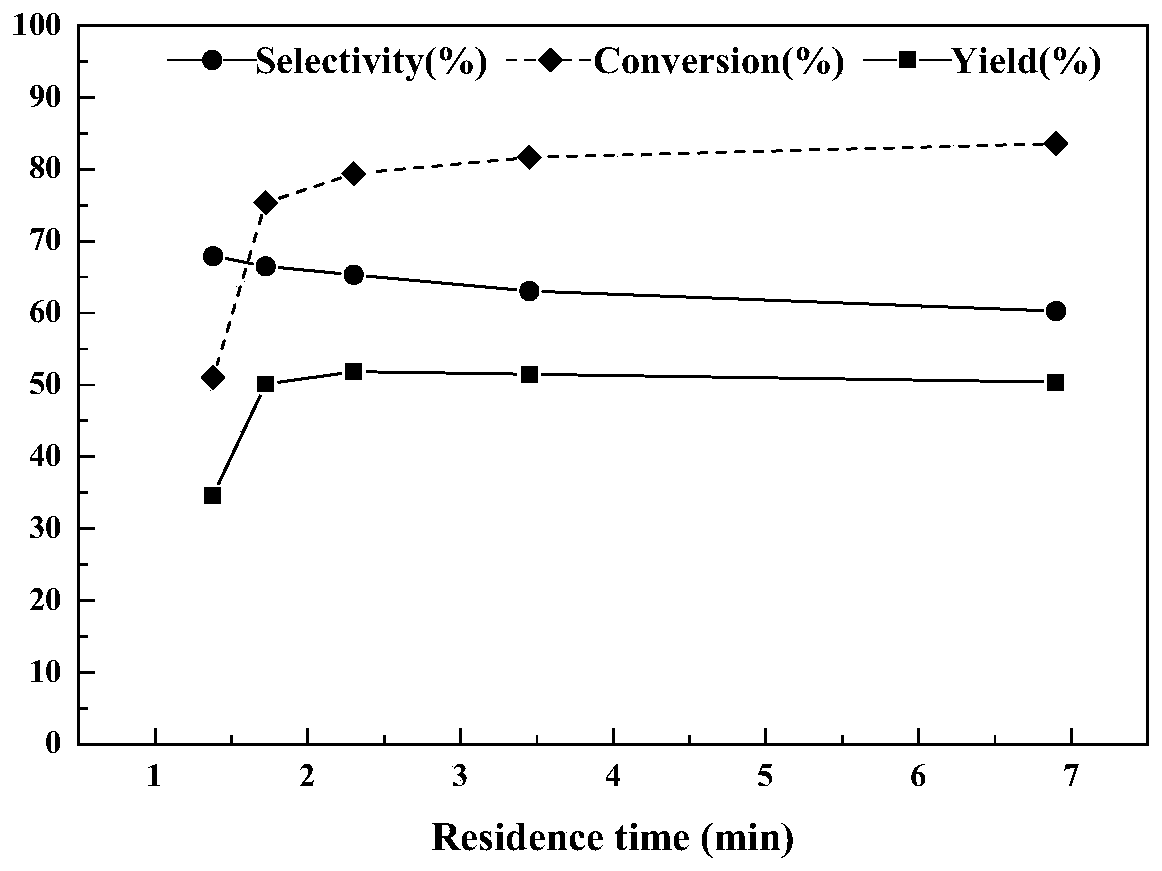
[0053] Continuously pump methanol and diethyl oxalate into the microreactor from a high-pressure infusion pump, and control the reaction at a temperature of 20°C, control the molar ratio of methanol to diethyl oxalate to 3.3:1, and the catalyst concentration to 5mg / mL , by controlling the total flow rate of the liquid to change the residence time of the reaction, the residence time of the two materials in the reactor is 1.38min, 1.73min, 2.3min, 3.45min, 6.9min respectively.
[0054] Collect the output liquids of different flow rates respectively, and all collect the output liquid of 1h, analyze and calculate the transformation rate of diethyl oxalate, the selectivity and productive rate of methyl ethyl oxalate with gas chromatography, the result is as attached figure 2 Shown in, under the microchannel reactor used in this implementation and reaction condition, the flow velocity that improves feed liquid is beneficial to the conversion of diethyl oxalate, but for the selectivi...
Embodiment 2
[0056] The process is the same as in Example 1, with the residence time being 2.3min (total feed flow rate 40μL / min), the molar ratio of methanol to diethyl oxalate being 3.3:1, the catalyst concentration being 5mg / mL, and the reaction temperature being 20°C respectively , 30°C, 40°C, 50°C. The products were analyzed by gas chromatography and the reaction results were shown in the attached image 3 shown. The results are attached image 3 As shown, the change trend of the conversion rate of diethyl oxalate by changing the temperature of the reaction is to decrease first and then remain unchanged slightly, while the conversion rate and selectivity of methyl ethyl oxalate are first increased and then decreased, and are obtained at 40 ° C. The highest, and therefore preferred, reaction temperature is 40°C.
Embodiment 3
[0058] The process is the same as in Example 1, with the residence time being 2.3min, the reaction temperature (total feed flow rate 40μL / min) being 40°C, the catalyst concentration being 5mg / mL, and the molar ratio of methanol to diethyl oxalate being 1.3:1 respectively , 2:1, 3.3:1, 5:1. The product was analyzed by gas chromatography, and the conversion rate of diethyl oxalate, selectivity and yield of methyl ethyl oxalate were calculated. The results are based on the attached Figure 4 It can be known that when the molar ratio is between 1.3:1 and 5:1, the conversion rate of diethyl oxalate has an upward trend first, while the selectivity of methyl ethyl oxalate shows a downward trend, and the yield change trend is first increased and then decreased. When the molar ratio is 2:1, both of them achieve the maximum value, so the better molar ratio is 2:1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com