Purple monascus, method and application thereof for producing lovastatin through co-fermentation
A purple monascus and strain technology, applied in microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, bacteria and other directions, can solve problems such as few reports, and achieve the improvement of color and luster, increase fermentation capacity, and strengthen lipid-lowering health care functions. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
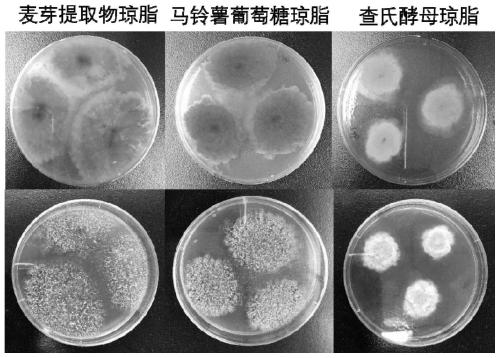
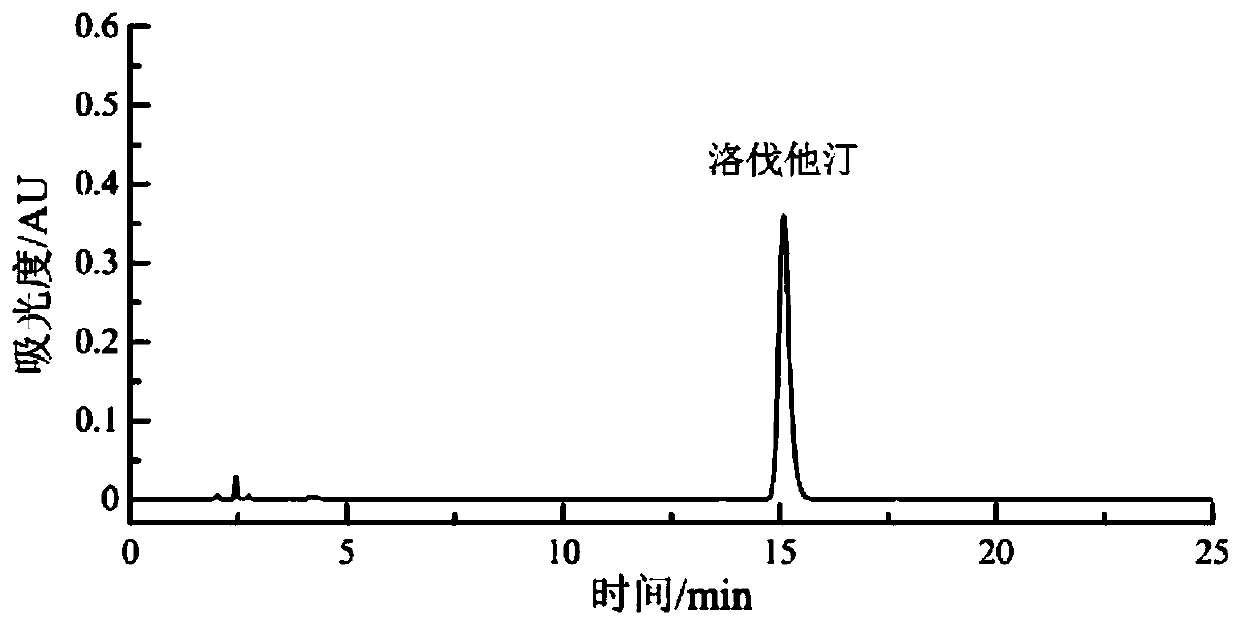
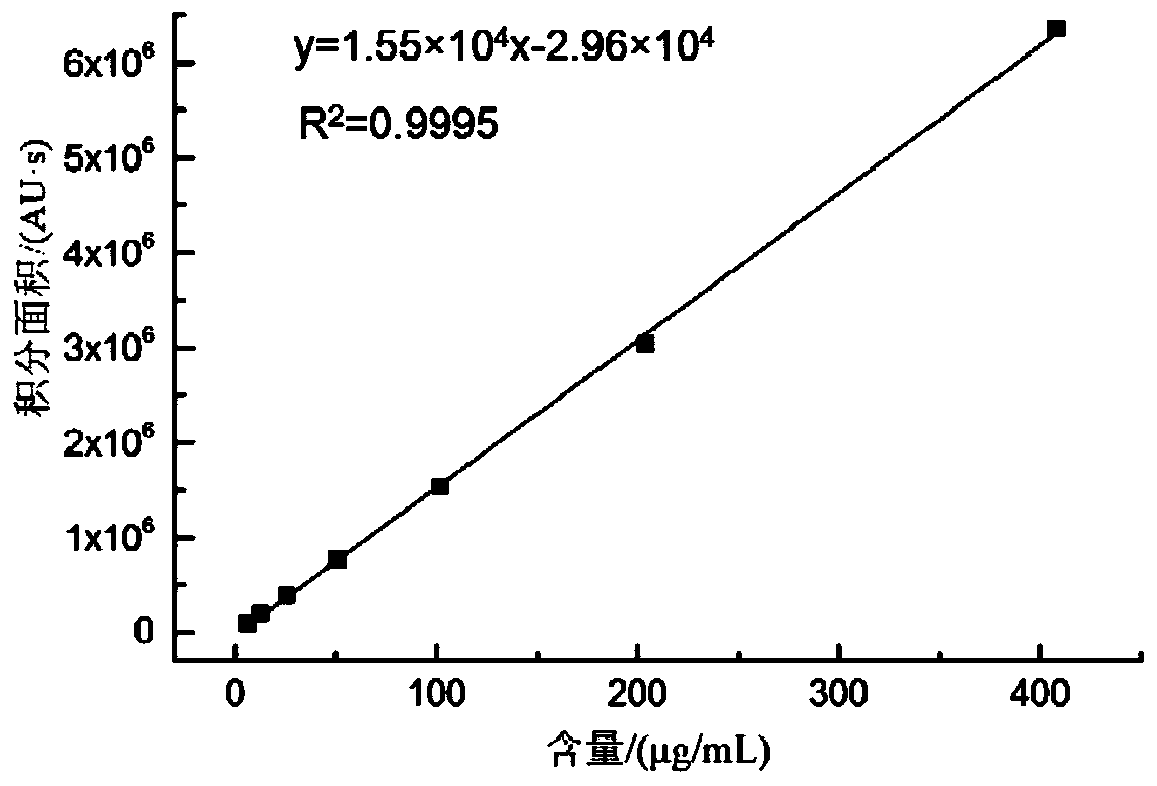
[0033] Example 1: Screening and identification of high-yield lovastatin strains in red yeast rice
[0034] Step 1, sample collection and processing:
[0035] Red yeast rice was collected from Gutian County, Ningde City, Fujian Province, and the collected red yeast rice was stored in sealed sterile plastic bags at 4°C. Weigh 5 g of red yeast rice, grind it into powder in a sterile mortar, place it in a 95 mL Erlenmeyer flask of sterile saline with glass beads, and shake it on a shaker for 30 min. followed by serial dilution.
[0036] PDA medium: 200 grams of potatoes, 20 grams of glucose, 15-20 grams of agar, 1000 ml of distilled water, natural pH, sterilized at 121°C for 15 minutes.
[0037] Step 2, screening of strains:
[0038] Under the aseptic operating environment, shake the Erlenmeyer flask evenly, draw 5mL of bacterial suspension from it and perform serial gradient dilution with sterile water to obtain 10 -2 、10 -3 、10 -4 、10 -5 、10 -6 、10 -7 times sample dilue...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Embodiment 2: co-fermentation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Monascus to prepare Monascus starter
[0050] Preparation of starter cultures containing Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Monascus. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae CCTCC NO:M 2015119 has been disclosed in the patent with publication number CN104911116B.
[0051] Saccharomyces cerevisiae CCTCC NO:M 2015119 was inoculated into potato dextrose water liquid medium, and cultured at 28±2°C for 24-32 hours to obtain the fermentation broth.
[0052] Use the sterile inoculation loop to scrape the Monascus strains in the preservation tube and streak them on the wort slope. Cultivate at 30°C for 7 days until Monascus grows spores.
[0053] Wash the spores on the slope with 0.1% sterile Tween water, soak 30g of indica rice for 2 hours, transfer to a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask, seal and sterilize at 121°C, 0.08MPa for 20 minutes, beat the rice grains while hot, and inoculate for 10 6 spores / g (dry weight of rice) were inoculated ...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Embodiment 3: Lactic acid bacteria and Monascus co-fermentation prepare Monascus starter
[0055] Taking Lactobacillus plantarum as an example, a starter containing Lactobacillus plantarum and Monascus was prepared. The Lactobacillus plantarum is Lactobacillus plantarum CGMCC No.8097, which has been disclosed in a patent with publication number CN103421723B.
[0056] Inoculate lactic acid bacteria into potato dextrose water liquid culture medium and culture at 28±2°C for 24-32 hours to obtain the fermentation broth.
[0057] Use the sterile inoculation loop to scrape the Monascus strains in the preservation tube and streak them on the wort slope. Cultivate at 30°C for 7 days until Monascus grows spores.
[0058] Wash the spores on the slope with 0.1% sterile Tween water, soak 30g of indica rice for 2 hours, transfer it to a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask, seal it, and sterilize it at 121°C and 0.08MPa for 20 minutes, beat the rice grains while they are hot, and inoculate for ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com