Rapid-charge microcrystalline graphite negative electrode material and production method thereof
A technology of microcrystalline graphite and negative electrode materials, applied in the direction of negative electrodes, chemical instruments and methods, battery electrodes, etc., can solve the problems that the yield of powder making is difficult to exceed 40%, high production costs, and poor circulation of natural graphite, etc., to achieve Excellent fast charging performance and cycle performance, low production cost, and small specific surface area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
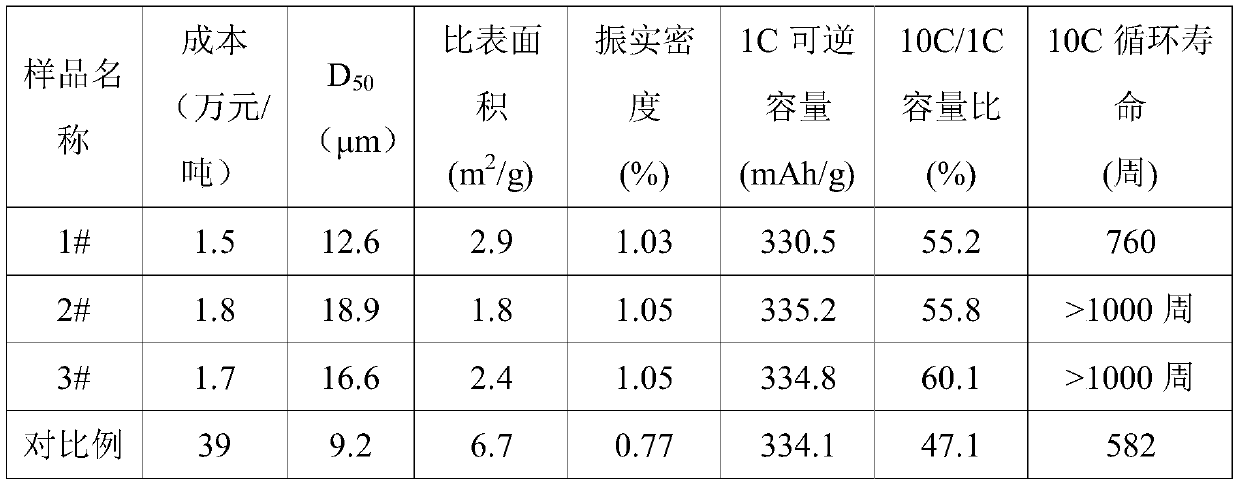
[0041] Microcrystalline graphite waste with a degree of graphitization of 93.2% and petroleum pitch (particle size 4.8 μm) with a softening point of 120° C. were mixed with VC machinery at a ratio of 10:3.
[0042] The mixed material was transferred into a vertical kettle, and composite granulated at 400° C. in a nitrogen atmosphere. The rotation speed of the material in the granulation equipment was 90 rpm, and the granulation time was 3 hours to obtain composite granules.
[0043] After the composite particles are cooled, they are classified twice by the classifier. The first classification takes 2# as the target outlet. feed port. The particle size of the composite particle after twice classification is 13~22 μm, PSD is 0.9~1.1, and described PSD calculation method is (D 90 -D 10 ) / D 50 .
[0044] Finally, the composite particles classified twice were transferred into a carbonization furnace, and the temperature was rapidly raised to 350°C at a rate of 10°C / min under a ni...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Microcrystalline graphite waste with a degree of graphitization of 93.2% and coal tar pitch (particle size 3.9 μm) with a softening point of 280° C. were mixed with VC machinery at a ratio of 10:1.5.
[0047] The mixed material was transferred into a drum furnace, and compositely granulated at 600° C. in an argon atmosphere. The rotation speed of the material in the granulation equipment was 15 rpm, and the granulation time was 8 hours.
[0048] After the composite particles are cooled, they are classified twice by a classifier, and the process is similar to that of Example 1.
[0049] Finally, the composite particles classified twice were transferred into a carbonization furnace, and the temperature was rapidly raised to 500°C at a rate of 5°C / min under an argon atmosphere, kept for 4 hours, and then slowly raised to 1250°C at a rate of 3°C / min , after 1 hour of heat preservation, it was naturally cooled, and then the 2# sample was obtained by breaking up, demagnetizin...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Microcrystalline graphite waste with a degree of graphitization of 93.2% and biomass pitch (particle size 3.3 μm) with a softening point of 200°C were mixed with VC machinery at a ratio of 10:2.3.
[0052] The mixed material was transferred into a horizontal furnace, and compositely granulated at 500° C. in an argon atmosphere. The rotation speed of the material in the granulation equipment was 40 rpm, and the granulation time was 5 hours.
[0053] After the composite particles are cooled, they are classified twice by the classifier F1, and the process is similar to that of Example 1.
[0054] Finally, the composite particles classified twice were transferred into a carbonization furnace, and the temperature was rapidly raised to 450°C at a rate of 7°C / min under an argon atmosphere, kept for 7 hours, and then slowly raised to 1100°C at a rate of 2°C / min , After heat preservation for 1h, cool naturally, and then disperse, demagnetize, and sieve to obtain 3# samples.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Softening point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com