Laser taking perovskite quantum dot microcrystalline glass as gain medium
A glass-ceramic and gain medium technology, applied in the field of lasers, can solve the problems of poor wavelength tunability, poor reliability and mechanical stability of all-solid-state lasers, and high cost of electrically pumped lasers, and is suitable for mass production and performance. Excellent, environmentally stable and mechanically stable results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
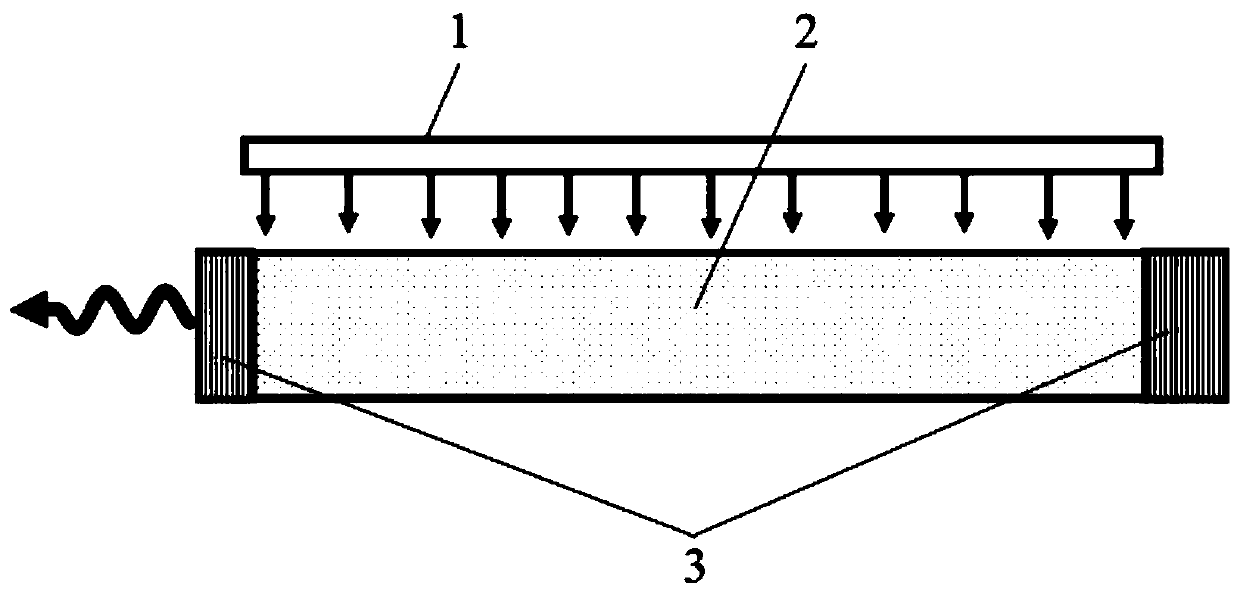
[0043] Such as figure 1 Shown is a schematic diagram of a laser with a perovskite quantum dot glass ceramic whose resonant cavity structure is Fabry-Perot (FP) as the gain medium in the present invention. Such as figure 1 As shown, in this embodiment, the laser with perovskite quantum dot glass ceramics as the gain medium includes:
[0044] The pump source 1 is used to excite the laser gain medium 2 so that the laser gain medium 2 emits photons;
[0045] The laser gain medium 2 is used to receive the radiation of the pump source 1 and emit photons;
[0046] The resonant cavity 3 is used to amplify the photons emitted by the laser gain medium 2 to output continuous laser or pulsed laser.
[0047] The perovskite quantum dot glass ceramic material of the laser gain medium 2 is CsPbX 3 (X=Cl,Br,I), or CsPb(Cl x Br 1-x ) 3 (x=0-1), or CsPb(Br x I 1-x ) 3 (x=0-1), or CsPb 2 Br 5 The Pb ions in the perovskite quantum dot glass-ceramic material can be replaced in whole or in part with tin ion...
Embodiment 2
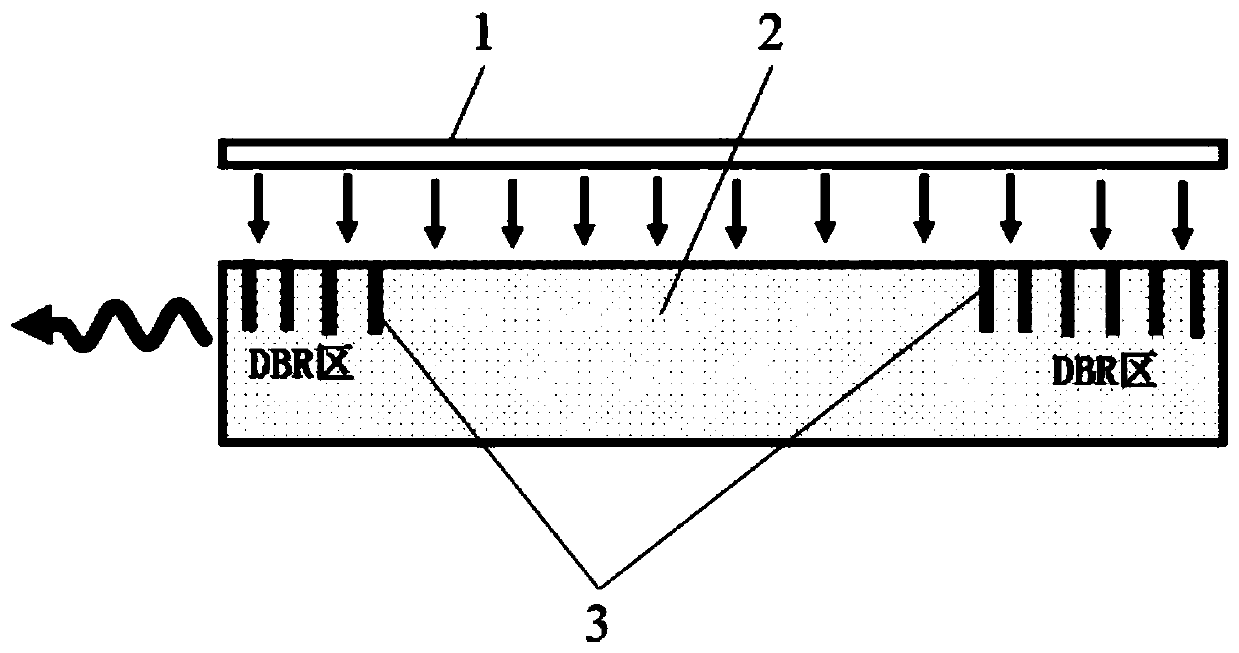
[0054] figure 2 It is a schematic diagram of a laser with a perovskite quantum dot glass ceramic whose resonant cavity structure is a distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) as a gain medium in the present invention. Such as figure 2 As shown, in this embodiment, the laser with perovskite quantum dot glass ceramics as the gain medium includes:
[0055] The pump source 1 is used to excite the laser gain medium 2 so that the laser gain medium 2 emits photons;
[0056] The laser gain medium 2 is used to receive the radiation of the pump source 1 and emit photons;
[0057] The resonant cavity 3 is used to amplify the photons emitted by the laser gain medium 2 to output continuous laser or pulsed laser.
[0058] The difference from Embodiment 1 is that in the laser with the perovskite quantum dot glass ceramics of Embodiment 2 as the gain medium, the resonator 3 is a distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) structure resonator in a periodic structure resonator. . The laser gain medium 2 is formed b...
Embodiment 3
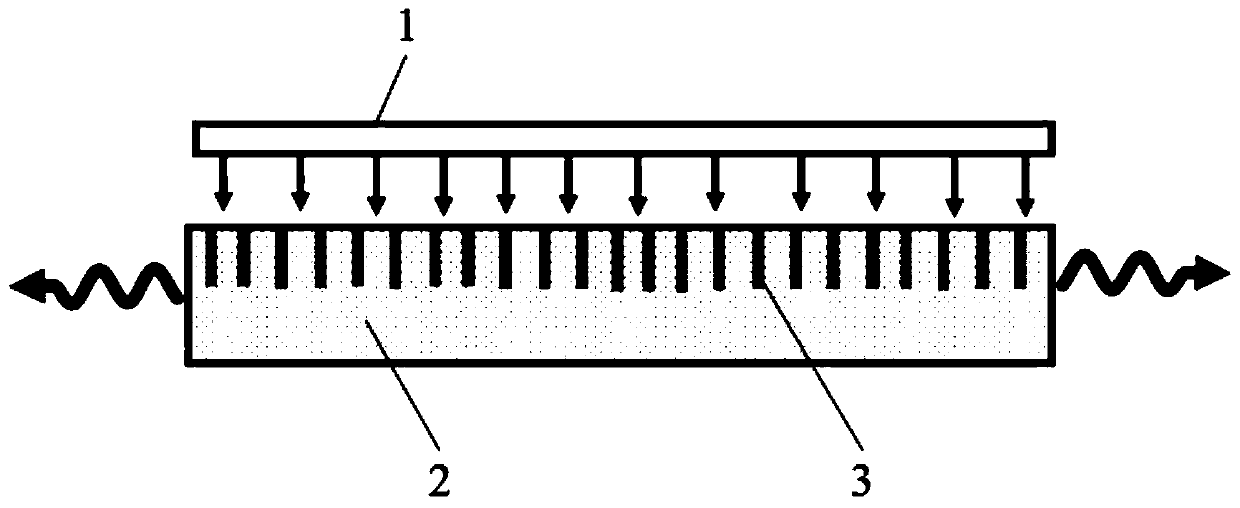
[0061] image 3 It is a schematic diagram of the laser with the perovskite quantum dot glass ceramics as the gain medium with the distributed feedback (DFB) cavity structure in the present invention. Such as image 3 As shown, in this embodiment, the laser with perovskite quantum dot glass ceramics as the gain medium includes:
[0062] The pump source 1 is used to excite the laser gain medium 2 so that the laser gain medium 2 emits photons;
[0063] The laser gain medium 2 is used to receive the radiation of the pump source 1 and emit photons;
[0064] The resonant cavity 3 is used to amplify the photons emitted by the laser gain medium 2 to output continuous laser or pulsed laser.
[0065] The difference from Embodiment 1 is that in the laser with the perovskite quantum dot glass ceramics of Embodiment 3 as the gain medium, the resonator 3 is a distributed feedback (DFB) structure resonator in a periodic structure resonator. Make the laser emit laser light in both directions.
[0066...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com