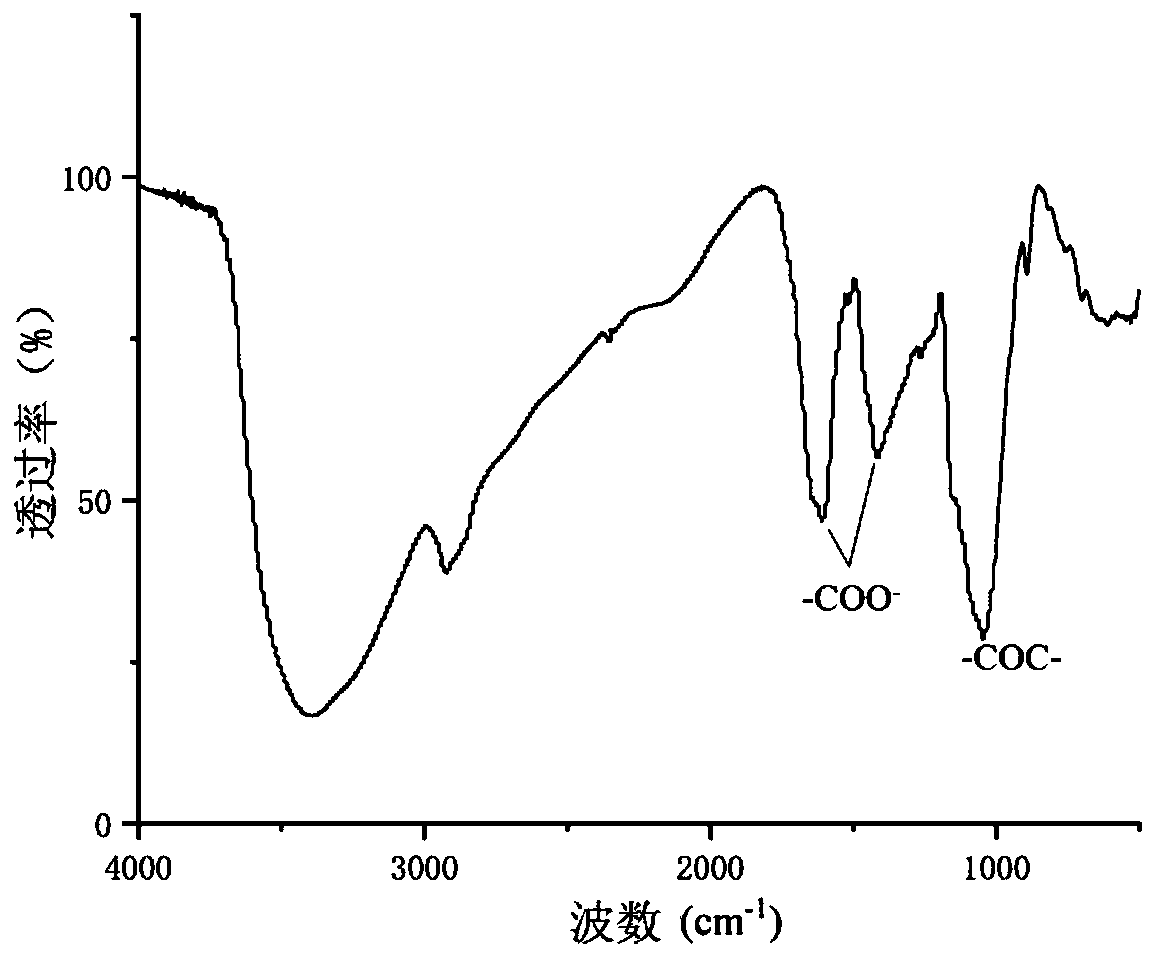
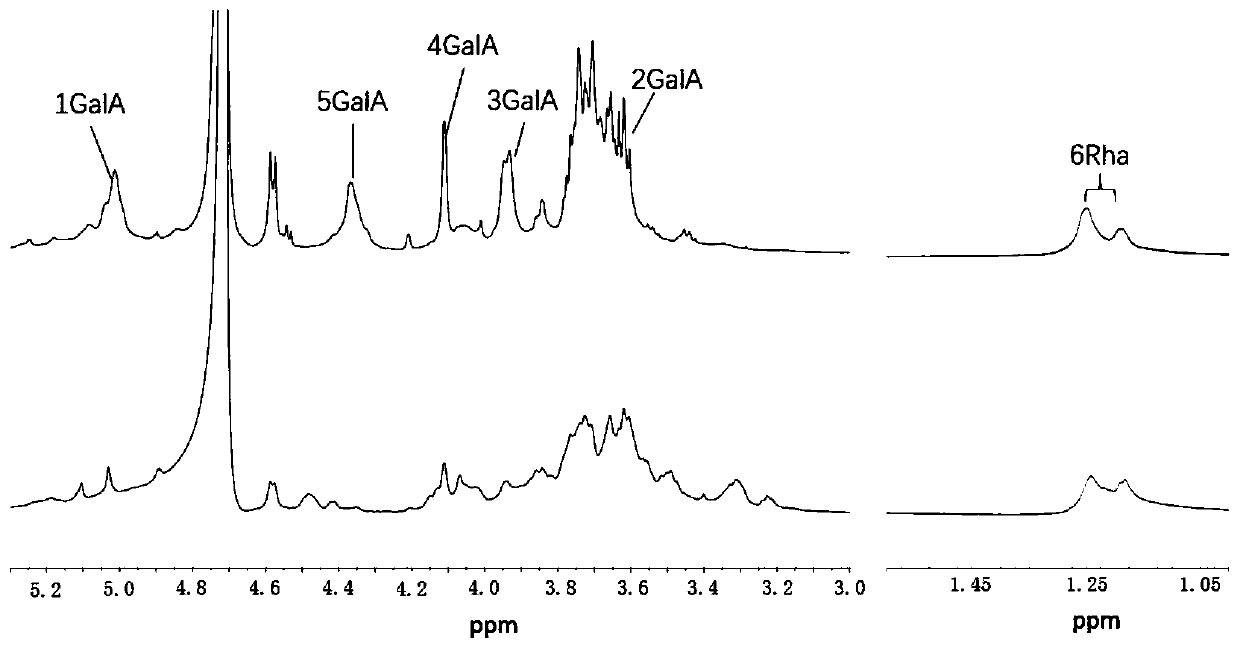
Method for extraction of RG-I pectic polysaccharide rich in galactose side chain
A technology of RG-I, pectin polysaccharide, applied in the field of extracting RG-I pectin polysaccharide rich in galactose side chain, to achieve good emulsification potential, improve food texture, and good anti-tumor effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Wet potato residues were provided by a starch processing factory in Ningxia, China. After natural air-drying, they were crushed and passed through a 40-mesh sieve. Take 300g and put it into 6000mL pH 6.5 phosphate buffer solution heated to 95°C, add 6000U of high-temperature-resistant α-amylase, and keep at 95°C for 25min. Add about 6000mL of pH 6.5 phosphate buffer solution, drop the temperature of the mixture to 45°C, add 24000U of liquefied glucoamylase to hydrolyze for 20 hours, filter to obtain the filter residue, freeze-dry to obtain 98g of starch-removed potato dry residue, and measure the starch content was 1.2%. Mix the above 98g of starch-removed potato dry residue with 1000mL of potassium hydroxide solution with a mass fraction of 0.4mol / L, react at 45°C for 18h under magnetic stirring conditions, filter through a 500-mesh filter cloth to obtain a clear night, and neutralize with hydrochloric acid. Add absolute ethanol three times the volume of the filtrate,...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Wet potato residues were provided by a starch processing factory in Ningxia, China. After natural air-drying, they were crushed and passed through a 40-mesh sieve. Take 20g and put it into 500mL of pH 6.5 phosphate buffer solution heated to 80°C, add about 300U of high temperature resistant α-amylase, and keep at 95°C for 30min. Then add 300mL of pH 6.8 phosphate buffer solution, the temperature of the mixture is lowered to 45°C, and about 2400U of liquefaction-type glucoamylase is added; after hydrolysis for 20 hours, the filter residue is obtained by filtration, freeze-dried, and 5.7g of starch-removed potato dry residue is obtained, and the starch The content is 0.7%. Mix the above 5.7g of starch-removed potato dry residue with 80mL of potassium hydroxide solution with a mass fraction of 0.8mol / L, react at 40°C for 24h under magnetic stirring conditions, filter through qualitative filter paper and then pass through a 0.45μm water film to obtain clear night, use 2mol...
Embodiment 3
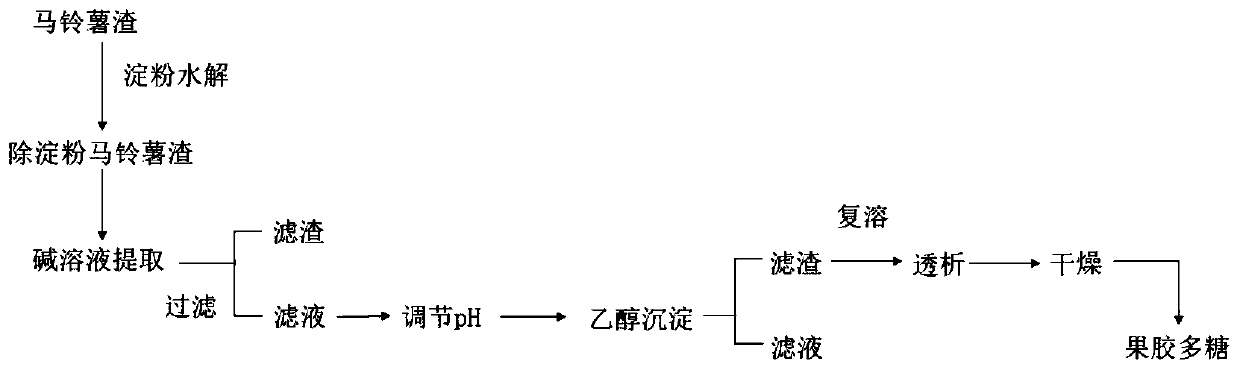
[0037] Potato residues were provided by a potato starch processing factory in Ningxia. After centrifugal dehydration, vacuum freeze-drying, crushing, and passing through a 40-mesh sieve. The method for extracting pectic polysaccharides from potato residues is as follows: figure 1 As shown, specifically, take 20g of potato dregs, add 300mL of pH 6.5 phosphate buffer heated to 95°C, add 300U of high temperature resistant α-amylase, and keep at 95°C for 20min. Then continue to add 300mL of pH 6.5 phosphate buffer solution, and after the temperature of the mixture drops to 45°C, add 2000U of liquefied glucoamylase; after hydrolysis for 20 hours, the filter residue is obtained by filtration, freeze-dried, and 6.5g of starch-removed potato dry residue is obtained. The starch content is 0.9%. Mix the above 6.5g of starch-removed potato dry residue with 90mL of 0.4mol / L potassium hydroxide solution, react for 20h under magnetic stirring conditions at 38°C, filter through qualitative ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Weight average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Number average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Dispersion | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com