Method for recovering valuable metals in waste nickel-cobalt-manganese lithium ion battery by ion exchange method
An ion exchange method, nickel-cobalt-manganese-lithium technology, applied in the chemical industry, can solve the problems of complex metal separation process, and achieve the effect of short process flow, strong operability, and avoiding the introduction of impurity ions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
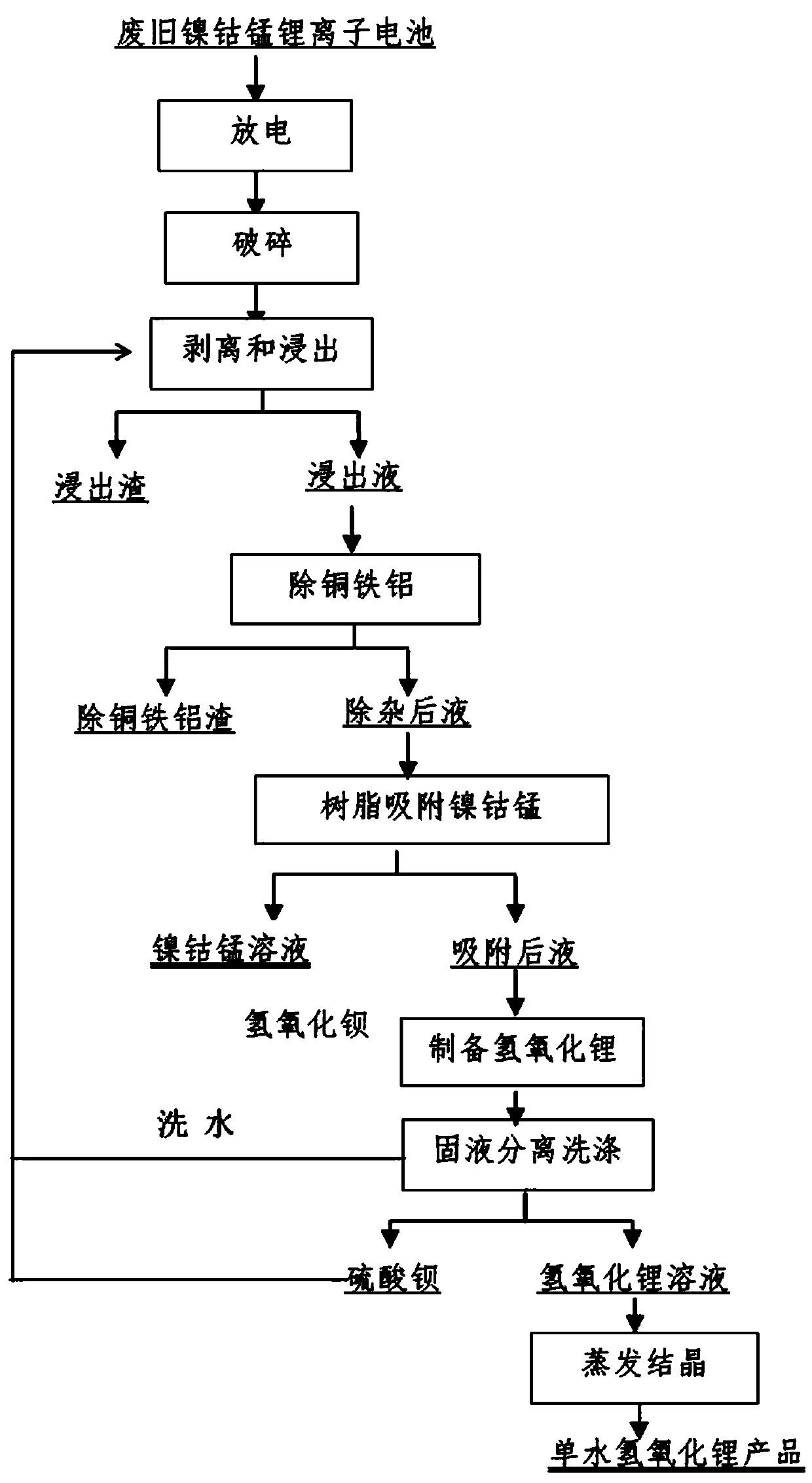
[0028] A method for recycling valuable metals in waste nickel-cobalt-manganese lithium-ion batteries by ion exchange, comprising the steps of:
[0029] Step (1). Collect waste nickel-cobalt-manganese lithium-ion batteries, disassemble them manually, discharge them in 5% sodium chloride solution, and crush them mechanically. Weigh 1500g of anhydrous sodium sulfite, dissolve it for later use; add 15L of 1.8M sulfuric acid into the reactor and heat to 50~65°C; weigh 5kg of the crushed waste lithium-ion battery and add it, stir at a low speed, and slowly add sulfuric acid solution to adjust the pH value of the solution 1.0 or so, add sodium sulfite solution dropwise after 10 minutes, react for 30~100 minutes after the dropwise addition, and filter.
[0030] Step (2). Raise the temperature of the leaching solution to 80~90°C, stop heating, add 50g / L lithium hydroxide solution to adjust the pH value of the solution to 2.0, add 10g of nickel powder, react for 15min, add 100mL of 30% ...
Embodiment 2
[0034] A method for recycling valuable metals in waste nickel-cobalt-manganese lithium-ion batteries by ion exchange, comprising the steps of:
[0035] Step (1). Collect waste nickel-cobalt-manganese lithium-ion batteries, manually disassemble them, discharge the batteries in 5% sodium chloride solution, and mechanically crush them. Add 15L of 2M sulfuric acid to the reactor, raise the temperature to 50~65°C, weigh 5kg of the crushed waste lithium-ion battery and add it into it, soak for 10min, stir at a low speed, measure a certain amount of 98% concentrated sulfuric acid, and slowly add it to the reaction vessel. Adjust the pH value of the solution to about 1.0, add 2.5L of 30% hydrogen peroxide, react for 30-100min after the dropwise addition, and filter.
[0036] Step (2). Raise the temperature of the leaching solution to 85°C, add 50g / L nickel hydroxide solution to adjust the pH value of the solution to 1.8, add 12g nickel powder, react for 15 minutes, add 80mL of 30% hyd...
Embodiment 3
[0040] A method for recycling valuable metals in waste nickel-cobalt-manganese lithium-ion batteries by ion exchange, comprising the steps of:
[0041] Step (1). Collect waste nickel-cobalt-manganese lithium-ion batteries, manually disassemble them, discharge the batteries in 5% sodium chloride solution, and mechanically crush them. Add 15L of 2M sulfuric acid to the reactor, raise the temperature to 50~65°C, weigh 5kg of the crushed waste lithium-ion battery and add it into it, soak for 10min, stir at a low speed, measure a certain amount of 98% concentrated sulfuric acid, and slowly add it to the reaction vessel. Adjust the pH value of the solution to about 1.0, add 2.5L of 30% hydrogen peroxide, react for 30-100min after the dropwise addition, and filter.
[0042] Step (2). Raise the temperature of the leaching solution to 85°C, add 50g / L cobalt hydroxide solution to adjust the pH value of the solution to 1.8, add 12g nickel powder, react for 15min, add 30% hydrogen peroxid...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com