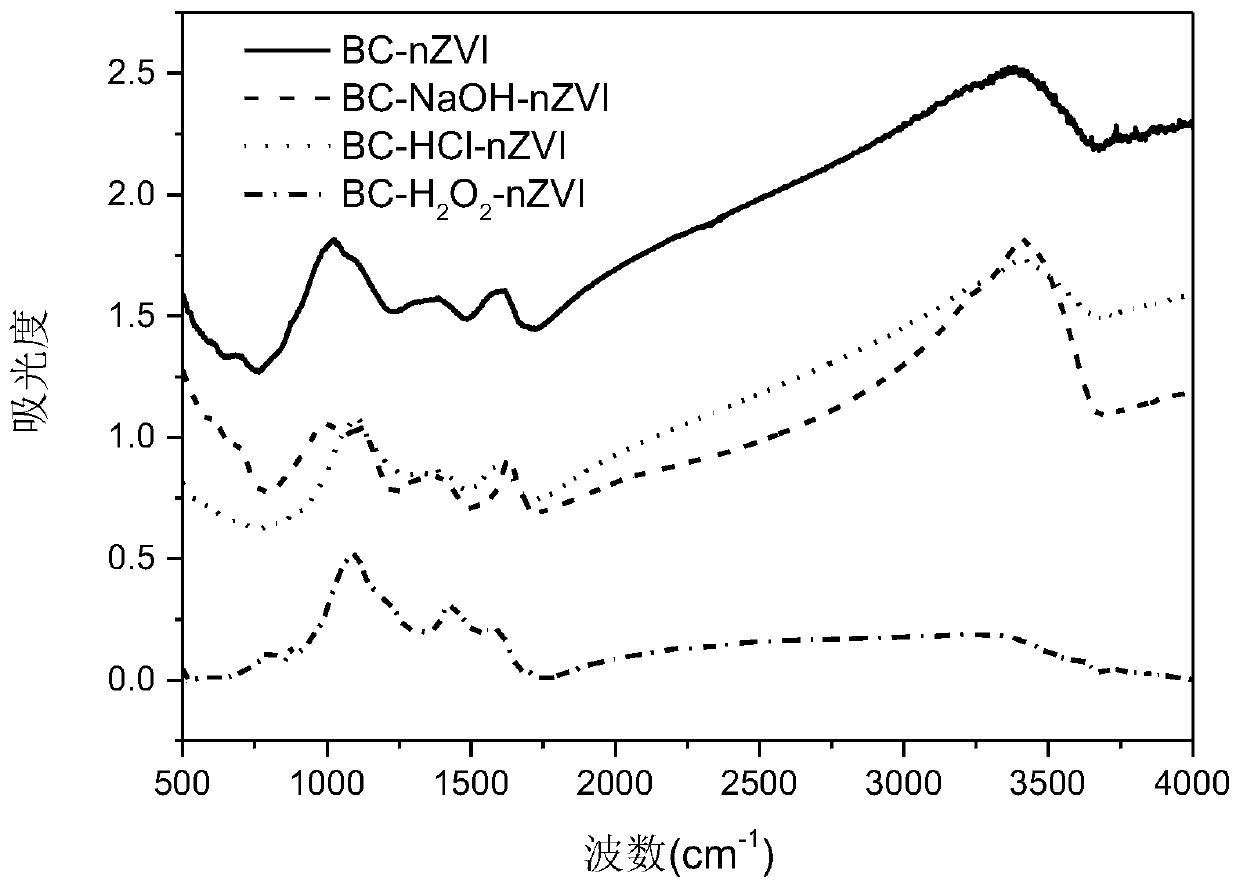
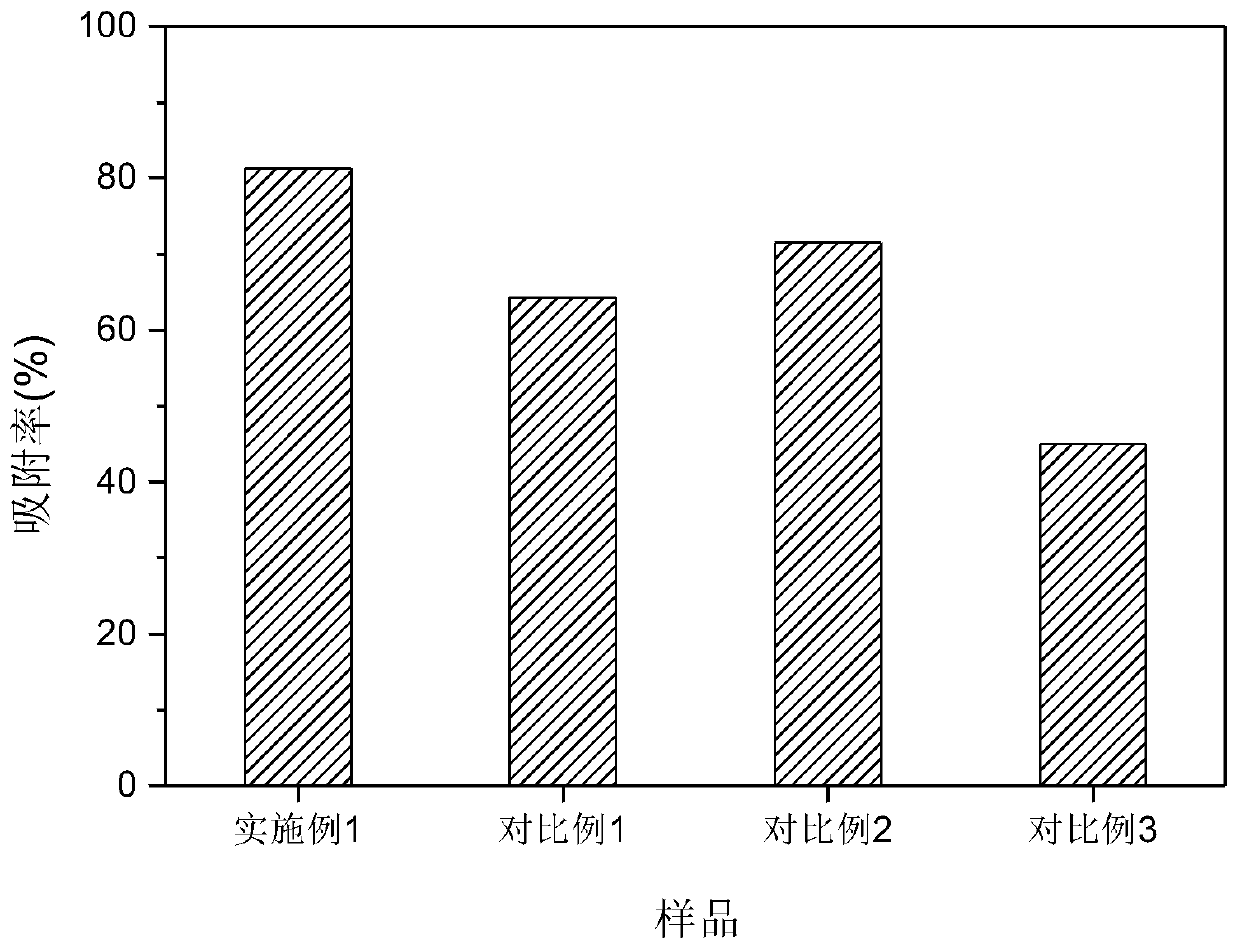
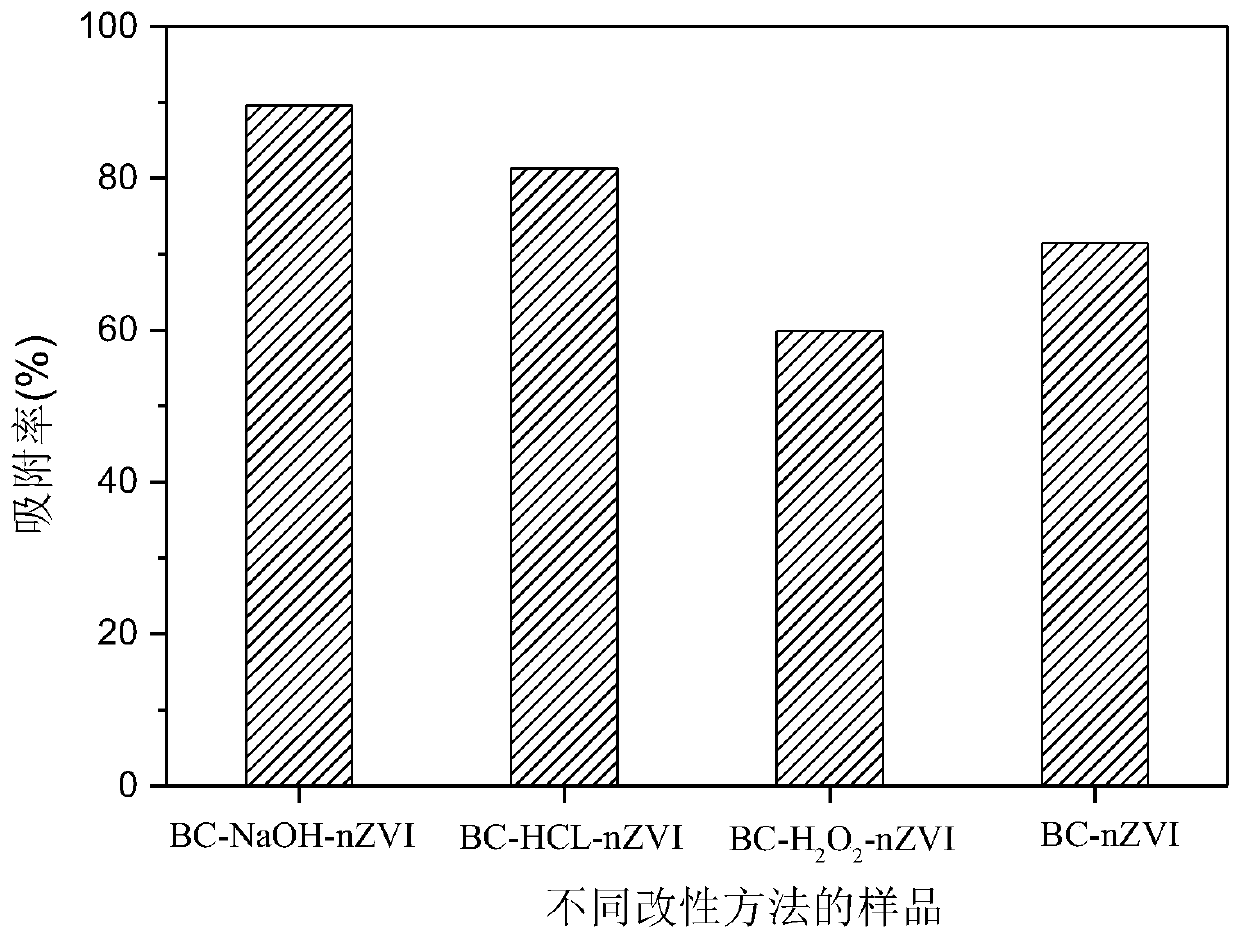
Biochar-loaded nano zero-valent iron material and application thereof
A technology of nano-zero-valent iron and biochar, which is applied in the direction of water pollutants, other chemical processes, gaseous effluent wastewater treatment, etc., can solve the problems that nano-zero-valent iron is easy to agglomerate and difficult to separate, so as to improve adsorption efficiency and improve efficiency effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] 1. Crush the washed and dried rice straw and pass through a 100-mesh sieve to obtain rice straw powder;
[0035] 2. Soak the rice straw powder with 0.5mol / L hydrochloric acid and stir it at a constant speed for 8 hours. The solid-to-liquid ratio is 1:50. Wash it with ultrapure water until the filtrate is neutral, then put it in a drying oven, and dry it at 105°C for 12 hours. Obtain modified rice straw powder;
[0036] 3. First raise the temperature of the pyrolysis furnace to 500°C, and at the same time feed nitrogen gas into the pyrolysis furnace, so that the pyrolysis furnace is in a nitrogen atmosphere, then weigh 5g of modified rice straw powder and place it in the pyrolysis furnace, and then add 2 The temperature is raised to 700°C at the rate of ℃ / min, and then cooled to room temperature to obtain biochar;
[0037] 4. Soak the biochar with 1mol / L hydrochloric acid and stir it at a constant speed for 24 hours. The solid-to-liquid ratio is 1:50. Wash it with ultra...
Embodiment 2
[0041] 1. Crush the washed and dried rice straw and pass through a 100-mesh sieve to obtain rice straw powder;
[0042] 2. Soak the rice straw powder with 15wt% hydrogen peroxide hydrochloric acid and stir it at a constant speed for 8 hours. The solid-to-liquid ratio is 1:50. Wash it with ultrapure water until the filtrate is neutral, then put it in a drying oven, and dry it at 105°C for 12 hours. Obtain modified rice straw powder;
[0043] 3. First raise the temperature of the pyrolysis furnace to 500°C, and at the same time feed nitrogen gas into the pyrolysis furnace, so that the pyrolysis furnace is in a nitrogen atmosphere, then weigh 5g of modified rice straw powder and place it in the pyrolysis furnace, and then add 2 The temperature is raised to 700°C at the rate of ℃ / min, and then cooled to room temperature to obtain biochar;
[0044] 4. Soak the biochar with 30wt% hydrogen peroxide and stir it at a constant speed for 24 hours. The solid-to-liquid ratio is 1:50. Wash...
Embodiment 3
[0048] 1. Crush the washed and dried rice straw and pass through a 100-mesh sieve to obtain rice straw powder;
[0049] 2. Soak the rice straw powder with 0.5mol / L sodium hydroxide and stir at a constant speed for 8 hours. The solid-to-liquid ratio is 1:50. Wash with ultrapure water until the filtrate is neutral, then put it in a drying oven, and dry it at 105°C 12h, obtain the modified rice straw powder;
[0050] 3. First raise the temperature of the pyrolysis furnace to 500°C, and at the same time feed nitrogen gas into the pyrolysis furnace, so that the pyrolysis furnace is in a nitrogen atmosphere, then weigh 5g of modified rice straw powder and place it in the pyrolysis furnace, and then add 2 The temperature is raised to 700°C at the rate of ℃ / min, and then cooled to room temperature to obtain biochar;
[0051] 4. Soak the biochar with 1mol / L sodium hydroxide and stir it at a constant speed for 24 hours. The solid-to-liquid ratio is 1:50. Wash it with ultrapure water un...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com