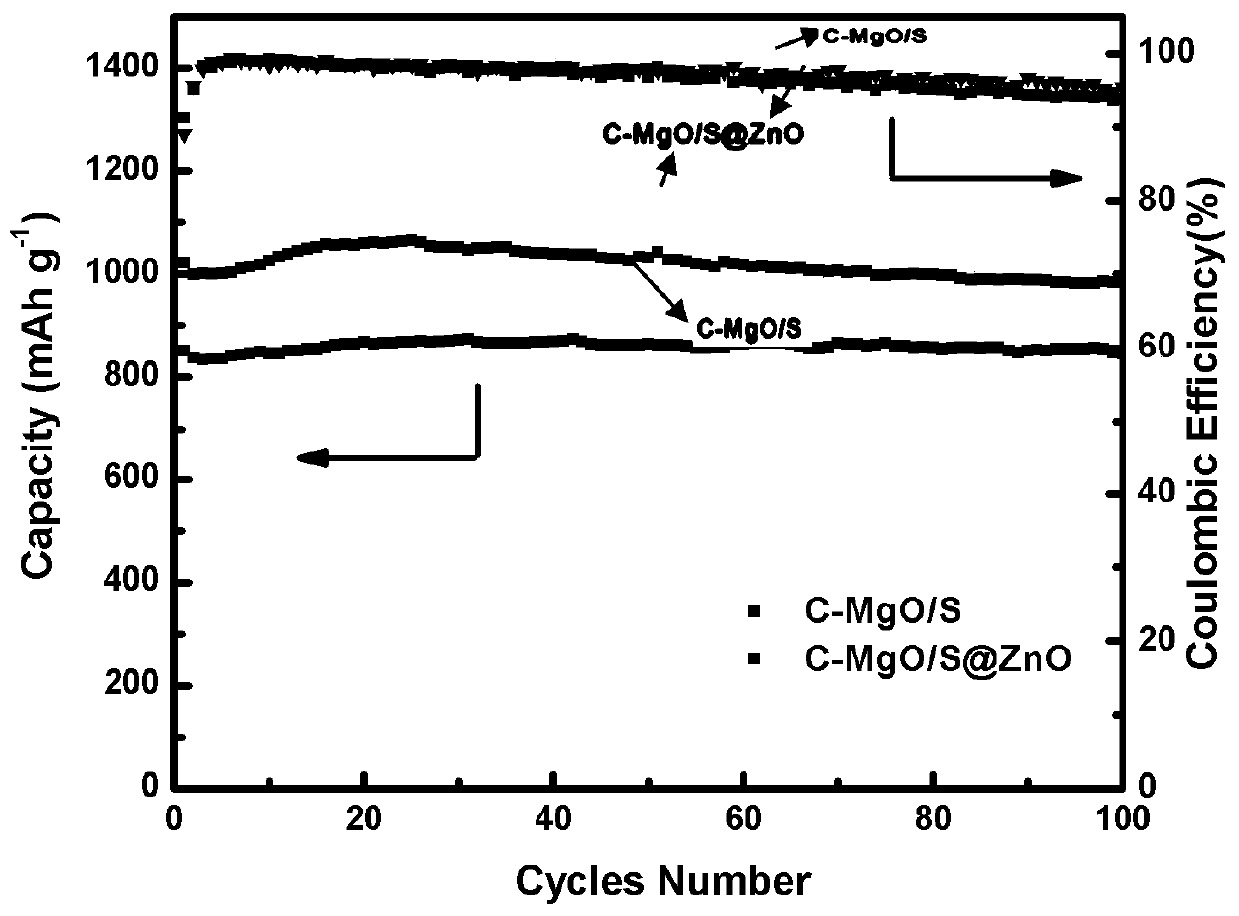
Method for preparing sulfur/carbon@metal oxide nanotube lithium-sulfur battery positive electrode material by using atomic layer deposition technology
A technology of atomic layer deposition and positive electrode materials, which is applied in metal material coating technology, battery electrodes, lithium batteries, etc., to achieve the effects of reducing loss, uniform coating layer, and reducing active material loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] 1) Mix 1.5g of polyacrylonitrile with a molecular weight of 150,000 and 0.6g of magnesium acetate with 11g of N,N-dimethylformamide solution and stir at room temperature for 10 hours to prepare a precursor polymer solution, and then pour the solution into a disposable syringe In the process, spinning under high pressure 13.5kV, low pressure -2.5kV, and rotation speed 200rpm for 8h to obtain a membrane;
[0026] 2) pre-oxidizing the film obtained in step 1) in air at 230°C for 3 hours, and then treating it in a nitrogen atmosphere at 900°C for 3 hours to obtain nanofibers;
[0027] 3) Under the environment of 1800Pa and 100℃, with diethylzinc and H 2 O is a reactant, with the nanofibers obtained in step 2) as the substrate, through 200 circles of ALD cycles, the growth thickness is a ZnO cladding layer of 40nm, to obtain nanofibers wrapped by zinc oxide;
[0028] 4) Mix the zinc oxide-wrapped nanofibers obtained in step 3) with sulfur in a weight ratio of 3:7, and keep ...
Embodiment 2
[0030] 1) Mix 1.5g of polyacrylonitrile with a molecular weight of 150,000 and 0.6g of magnesium acetate with 11g of N,N-dimethylformamide solution and stir at room temperature for 10 hours to prepare a precursor polymer solution, and then pour the solution into a disposable syringe In the process, spinning under high pressure 13.5kV, low pressure -2.5kV, and rotation speed 200rpm for 8h to obtain a membrane;
[0031] 2) pre-oxidizing the film obtained in step 1) in air at 230°C for 3 hours, and then treating it in a nitrogen atmosphere at 900°C for 3 hours to obtain nanofibers;
[0032] 3) Under the environment of 1800Pa and 100℃, with diethylzinc and H 2 O is a reactant, with the nanofibers obtained in step 2) as the substrate, through 250 circles of ALD cycles, the growth thickness is a ZnO cladding layer of 50nm, to obtain nanofibers wrapped by zinc oxide;
[0033] 4) Mix the zinc oxide-wrapped nanofibers obtained in step 3) with sulfur in a weight ratio of 3:7, and keep ...
Embodiment 3
[0035] 1) Mix 1.5g of polyacrylonitrile with a molecular weight of 150,000 and 0.6g of magnesium acetate with 11g of N,N-dimethylformamide solution and stir at room temperature for 10 hours to prepare a precursor polymer solution, and then pour the solution into a disposable syringe In the process, spinning under high pressure 13.5kV, low pressure -2.5kV, and rotation speed 200rpm for 8h to obtain a membrane;
[0036] 2) pre-oxidizing the film obtained in step 1) in air at 230°C for 3 hours, and then treating it in a nitrogen atmosphere at 900°C for 3 hours to obtain nanofibers;
[0037] 3) Under the environment of 1800Pa and 100℃, with diethylzinc and H 2 O is a reactant, with the nanofibers obtained in step 2) as the substrate, through 300 circles of ALD cycles, the growth thickness is a ZnO cladding layer of 60nm, to obtain nanofibers wrapped by zinc oxide;
[0038]4) Mix the zinc oxide-wrapped nanofibers obtained in step 3) with sulfur in a weight ratio of 3:7, and keep s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com