Low-dimensional inorganic-organic hybrid metal halide perovskites
A perovskite and halogen technology, applied in tin organic compounds, organic chemistry, tin halide, etc., can solve the problems of material and substrate limitations, inability to achieve uniform coating with luminous quality, harsh synthesis conditions, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0260] As mentioned above, the conditions required for fabrication are convenient and can be performed at room temperature. In view of this, also provide a kind of preparation method of above-mentioned formula I zero-dimensional perovskite, comprise the steps:
[0261] (a) tin halide and / or pseudotin halide and formula II compound:
[0262]
[0263] mixed in a solvent, where, A, L, R 1 ~R 3 , X, n, m and p are as defined above for formula I, and y is equal to p; and
[0264] (b) adding an anti-solvent to the mixture to precipitate the zero-dimensional perovskite of formula I.
[0265] It can be understood that the perovskites of formula Ia, formula Ib, formula III and formula IV can be produced in a manner similar to the above method.
[0266] In this application, "solvent" means capable of maintaining a raw material in solution when provided in an appropriate amount (such as an economically feasible amount of solvent) readily determined by a person skilled in the art i...
Embodiment 1
[0297] Example 1: Single Crystal Growth and Structural Characterization of m-xylylenedimethylammonium tin (II) bromide (m-XDATB)
[0298] synthesis
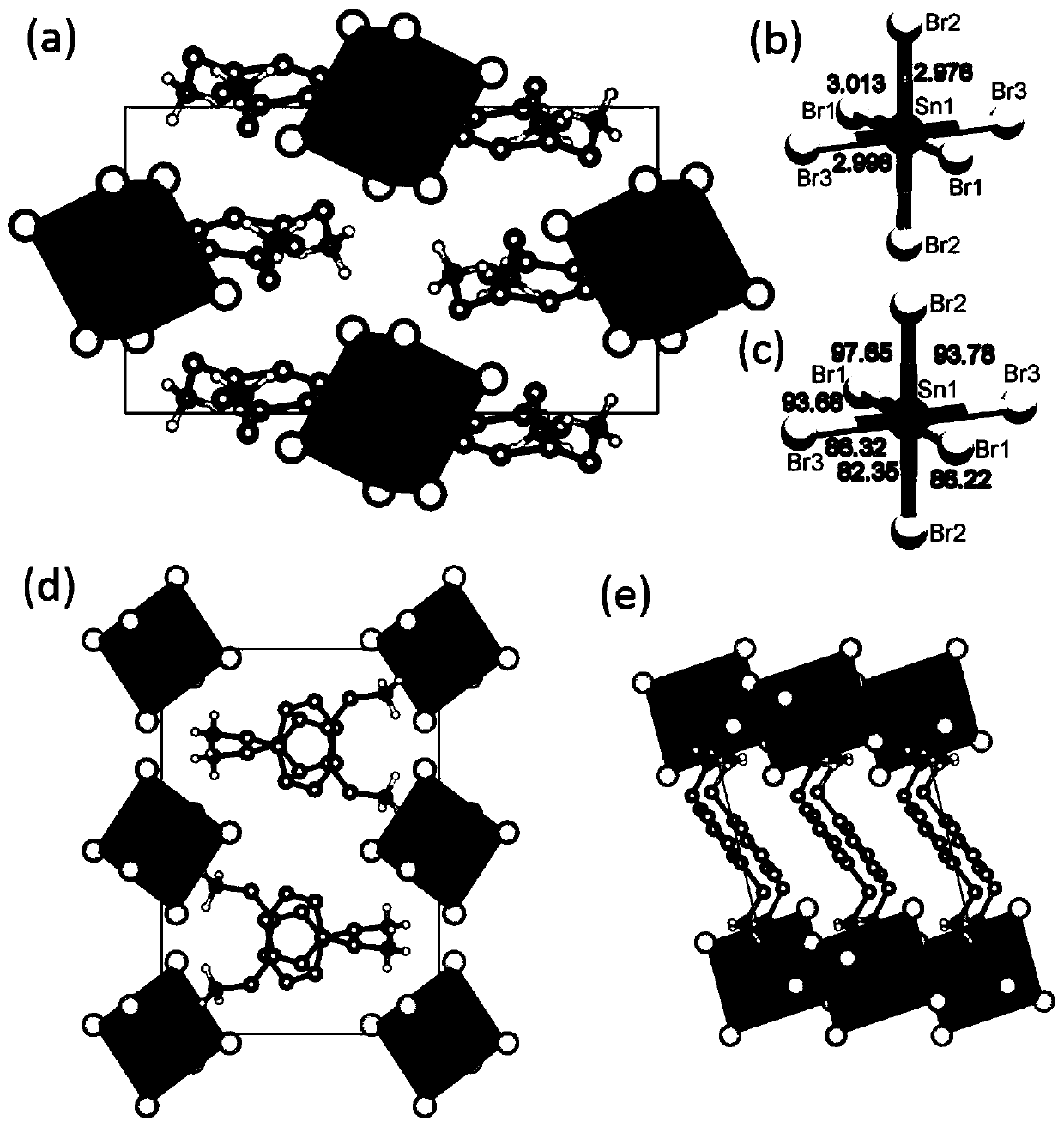
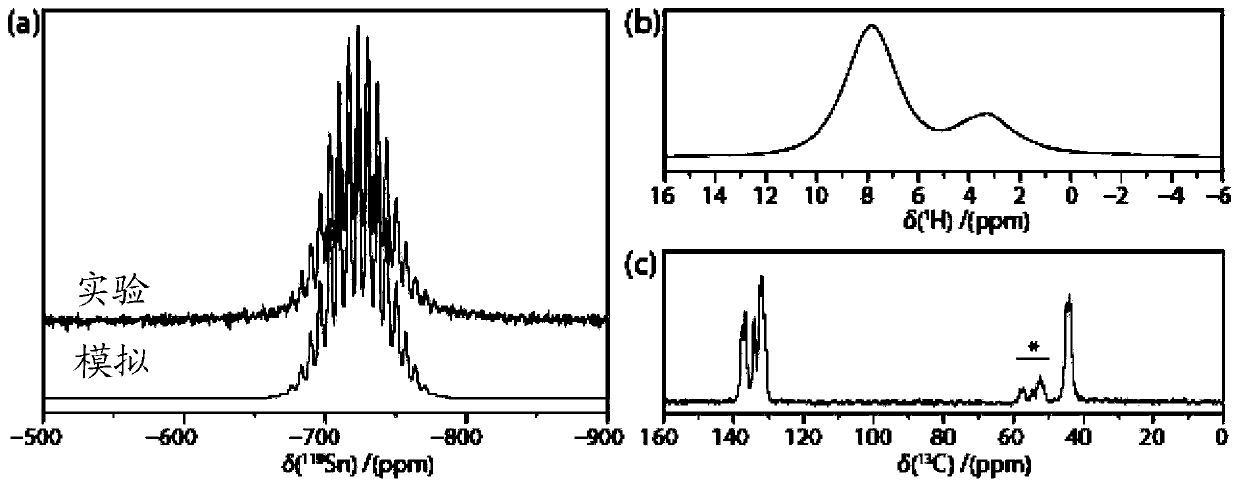
[0299] Prepare m-xylylenedimethylammonium bromide (m-XDABr) as described above 2 ), and m-XDATB single crystals were grown by anti-solvent vapor-assisted crystallization. 1 equivalent of tin halide (SnX 2 ) and 2 equivalents of m-XDABr 2 Ammonium halide was dissolved in a minimum amount of N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) to obtain a saturated solution. Subsequently, the vapor of dichloromethane (DCM) as an anti-solvent was diffused into the perovskite solution, resulting in the formation of m-XDATB single crystals (molecular formula (m-XDA) determined by X-ray diffraction) after several days 2 SnBr 6 ). The obtained crystals were washed with DCM and used for single crystal X-ray diffraction (XRD) measurements and ultrafast spectroscopy studies.
[0300] Single Crystal X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Characterization
[0301] m-XD...
Embodiment 2
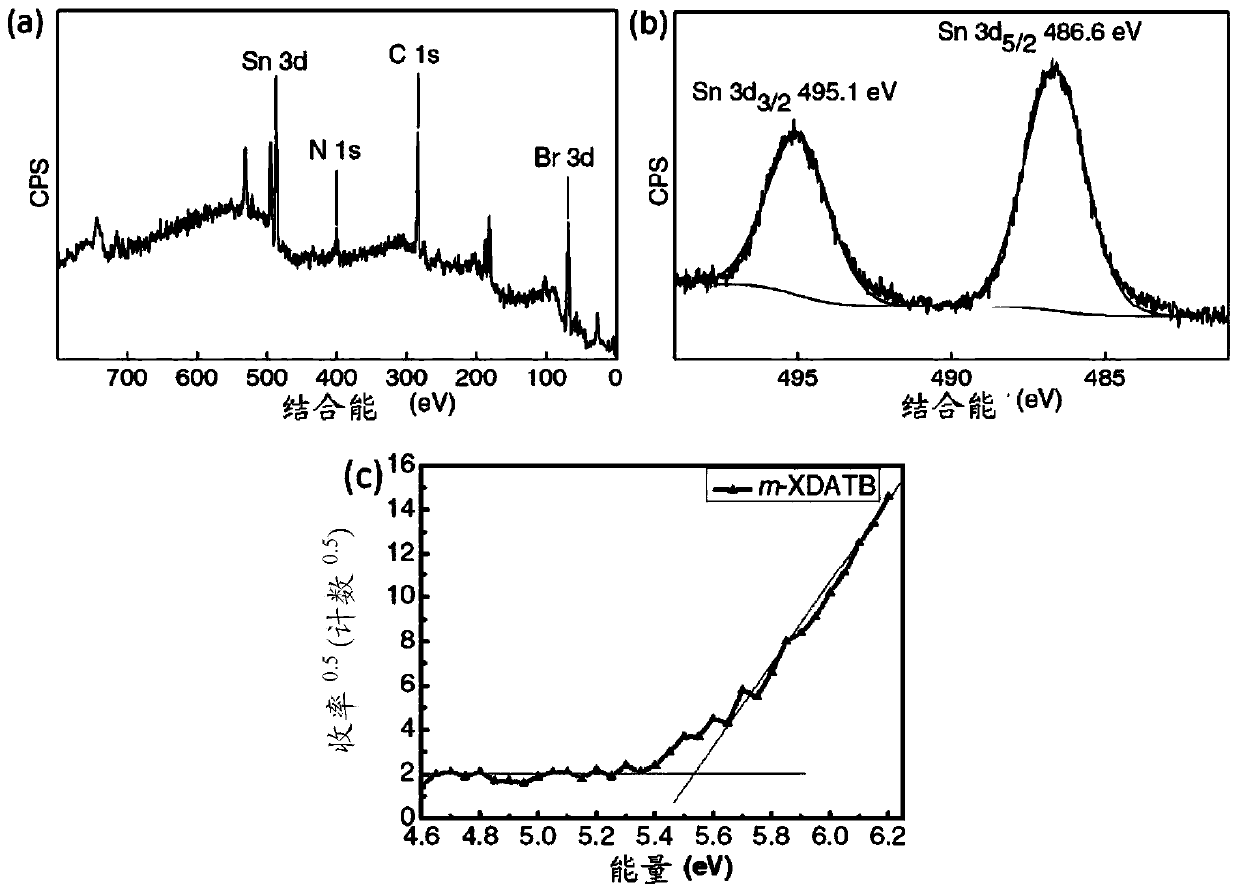
[0312] Example 2: Oxidative stability and thermal stability of m-XDATB characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), photoelectron spectroscopy in air (PESA), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) sex
[0313] Such as image 3 As shown in a, the oxidation stability of m-XDATB was investigated by performing full-spectrum scanning of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) in the binding energy range of 0 to 800 eV. As shown in the figure, since the core level peaks of Sn, Br, C, and N elements are observed, it can be confirmed that all these elements are contained in m-XDATB. snd 3 / 2 and d 5 / 2 Electron binding energy XPS narrow-spectrum scanning results prove that metal Sn( image 3 b). However, due to Sn 4+ and Sn 2+ 3d 5 / 2 The binding energies are relatively close, so the oxidation state of Sn cannot be determined clearly. The molecular formula of m-XDATB determined by single crystal X-ray crystallography is (m-XDA) 2 Sn...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum luminescence wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Half width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Maximum absorption wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com