Method for determining pesticide residues in edible plant enzymes
A technology for edible plants and pesticide residues, which is applied in measurement devices, instruments, scientific instruments, etc., can solve the problems of single type of testing items, complicated processing process, and large solvent consumption, and achieves solvent saving, strong selectivity, and elimination of The effect of matrix interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031]1. Principle of detection method:
[0032] The edible plant enzyme sample was extracted by 0.1% formic acid-acetonitrile (volume ratio 1:1) acidification system, and was extracted by compound C 18 and PSA filler QuEChERS dispersive extraction and purification, and finally use liquid chromatography triple quadrupole mass spectrometry to simultaneously determine the residues of 65 pesticides, use blank sample matrix as standard, retention and ion fragment abundance ratio time qualitative, quantitative ion peak area Quantification by standard method.
[0033] 2. Detection method procedure:
[0034] 3.1. Instruments and reagents
[0035] 3.1.1 Liquid chromatography triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometer (AB Triple Quad 4500)
[0036] 3.1.2 Standard substances: 65 pesticide standard substances were purchased from Ehrensyorfer, Germany
[0037] 3.1.3 Analytical reagent: formic acid (China Resources Chemical, 500mL)
[0038] 3.1.4 Chromatographically pure reagent: acet...
Embodiment 2
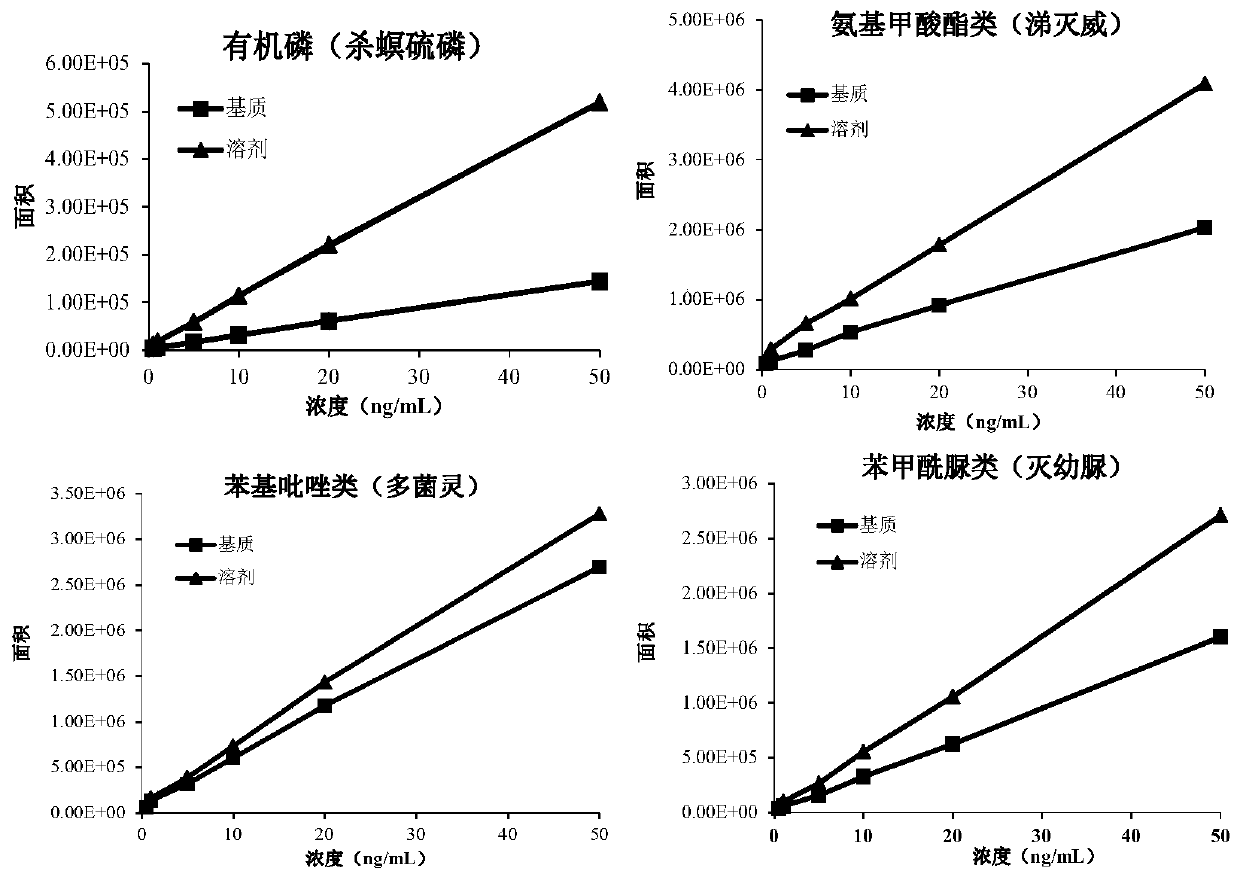
[0095] 1. In order to explore the influence of different extraction solvents on the extraction efficiency, find a better extraction solvent for the determination of 65 kinds of pesticides in edible plant enzymes, take 2g of edible plant enzyme powder samples, and compare 10mL acetonitrile, 0.1% formic acid water, The extraction effect of 0.1% formic acid water + acetonitrile (volume ratio 1:1) three kinds of extraction solvents on 65 kinds of pesticides, with 0.05mg / kg standard addition recovery experiment (extraction solution is not purified), compare the effect of different extraction solvents on pesticides See Table 10 for extraction efficiency and the recovery distribution of 65 kinds of pesticides in edible plant enzymes.
[0096] Table 10
[0097]
[0098] It can be seen from the above data that when 0.1% formic acid water + acetonitrile (volume ratio 1:1) is used as the extraction solvent of 65 kinds of pesticides in edible plant enzymes, the recoveries of 39 kinds o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com