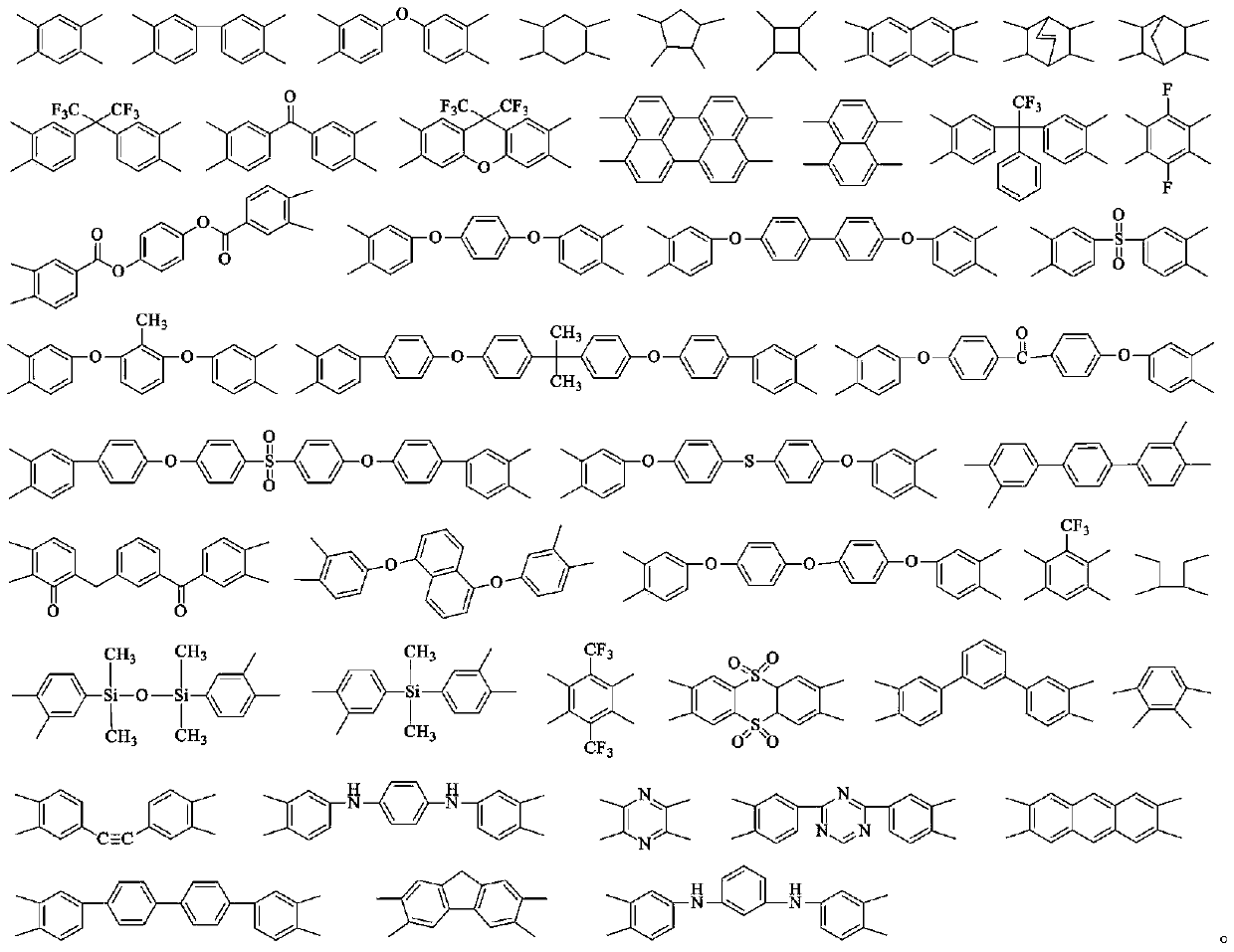
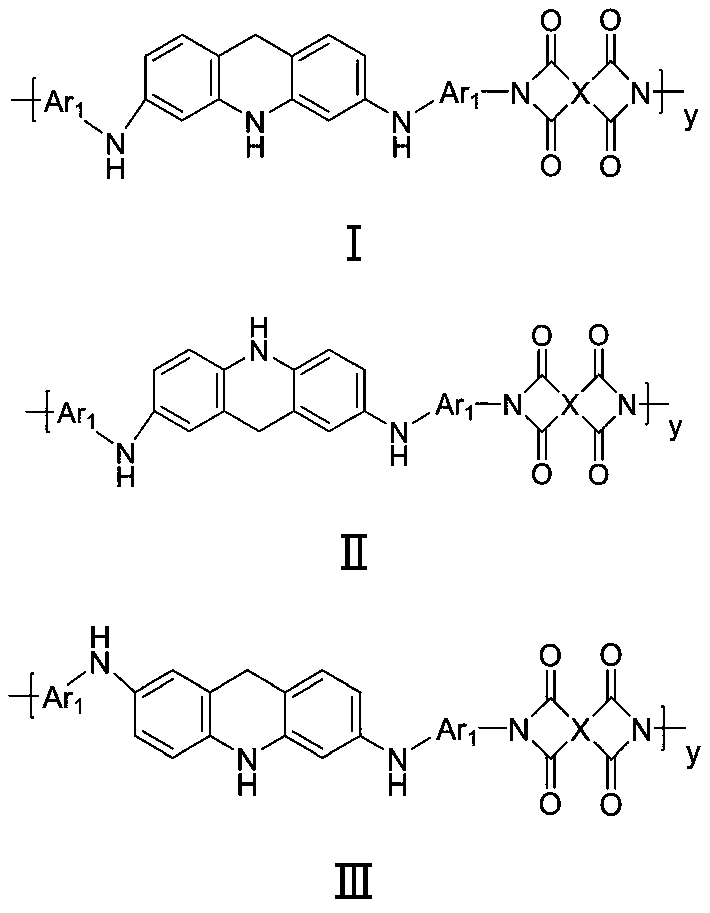
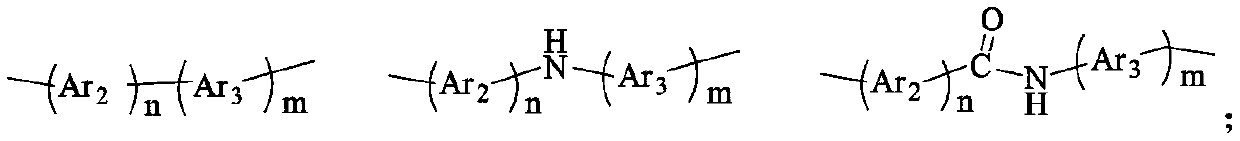Polyimide containing 9,10-dihydroacridine structure, and preparation method and application thereof
A dihydroacridine and polyimide technology, applied in the field of material science, can solve problems such as inability to meet, and achieve the effects of improving barrier properties, compact stacking, high glass transition temperature and thermal stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] This example provides the synthesis of N1,N1'-(9,10-dihydroacridine-3,6-diyl)bis(benzene-1,4-diamine):
[0040]
[0041] S1. Synthesis of intermediate 9,10-dihydroacridine-3,6-diamine:
[0042] Add 3.39g (0.01mol) of 3,6-dibromo-9,10-dihydroacridine, an appropriate amount of cuprous oxide, 50ml of NMP, and 13ml of ammonia water (29%, 0.2mol) into a 200ml pressure bottle, under argon protection, and react at 100°C After the reaction is completed, the reaction solution is poured into ice water, extracted with dichloromethane, and the solvent is removed under reduced pressure. The product uses dichloromethane:n-hexane=2:1 (volume ratio) as the mobile phase and silica gel as the stationary phase After chromatographic purification, the product was collected and spin-dried, and dried in vacuum at 80°C for 24 hours to obtain an intermediate. The intermediate structure is as follows:
[0043]
[0044] S2. Synthetic intermediate N3, N6-bis(4-nitrophenyl)-9,10-dihydroacri...
Embodiment 2
[0050] This example provides the synthesis of N6-(5-aminopyridin-2-yl)-N2-(6-aminopyridin-3-yl)-9,10-dihydroacridine-2,6-diamine:
[0051]
[0052] S1. Synthesis of intermediate 9,10-dihydroacridine-2,6-diamine:
[0053] Add 3.39g (0.01mol) of 2,6-dibromo-9,10-dihydroacridine, an appropriate amount of cuprous oxide, 50ml of NMP, and 13ml of ammonia water (29%, 0.2mol) into a 200ml pressure bottle, under argon protection, and react at 100°C After the reaction is completed, the reaction solution is poured into ice water, extracted with dichloromethane, and the solvent is removed under reduced pressure. The product uses dichloromethane:n-hexane=2:1 (volume ratio) as the mobile phase and silica gel as the stationary phase After chromatographic purification, the product was collected and spin-dried, and dried in vacuum at 80°C for 24 hours to obtain an intermediate. The intermediate structure is as follows:
[0054]
[0055] S2. Synthetic intermediate N6-(5-nitropyridin-2-y...
Embodiment 3
[0061] This example provides the synthesis of N1,N1'-(9,10-dihydroacridine-2,7-diyl)bis(benzene-1,3-diamine):
[0062]
[0063] S1 synthetic intermediate 9,10-dihydroacridine-2,6-diamine:
[0064] Add 3.41g (0.01mol) of 3,7-dibromo-10H-phenoxazine, an appropriate amount of cuprous oxide, 50ml of NMP, and 13ml of ammonia water (29%, 0.2mol) into a 200ml pressure bottle, under argon protection, and react at 100°C. After the reaction was completed, the reaction solution was poured into ice water, extracted with dichloromethane, the solvent was removed under reduced pressure, and the product was purified by column chromatography using dichloromethane:n-hexane=2:1 (volume ratio) as the mobile phase and silica gel as the stationary phase. , the product was collected and spin-dried, and dried in vacuum at 80°C for 24h to obtain an intermediate. The intermediate structure is as follows:
[0065]
[0066] S2. Synthesis of intermediate N2, N7-bis(3-nitrophenyl)-9,10-dihydroacrid...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com