Method for improving yield of erythromycin by modifying saccharopolyspora erythraea SACE_4682 gene
A technology of saccharopolyspora and erythromycin, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve problems such as being unsuitable for wide application, time-consuming, uneconomical and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Construction of SACE_4682 gene deletion mutants:
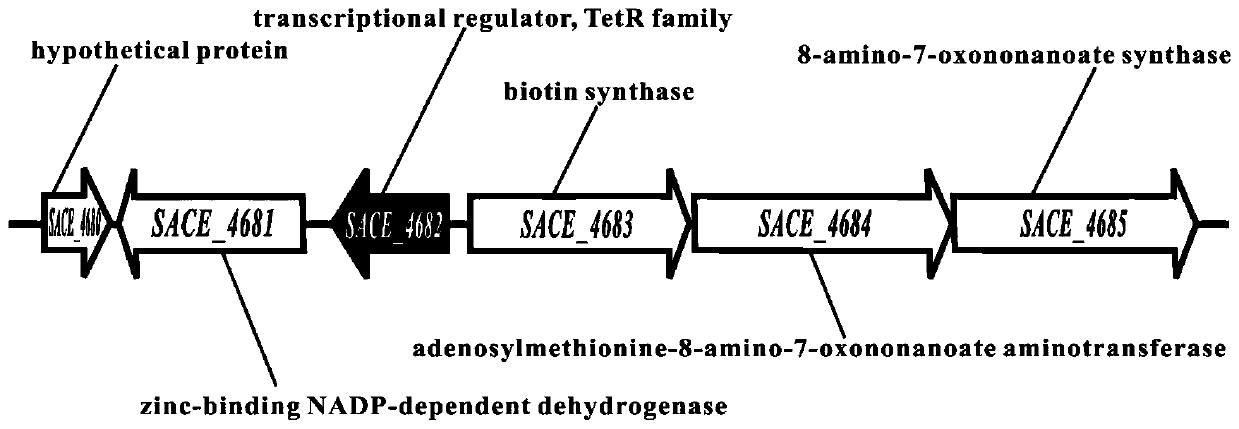
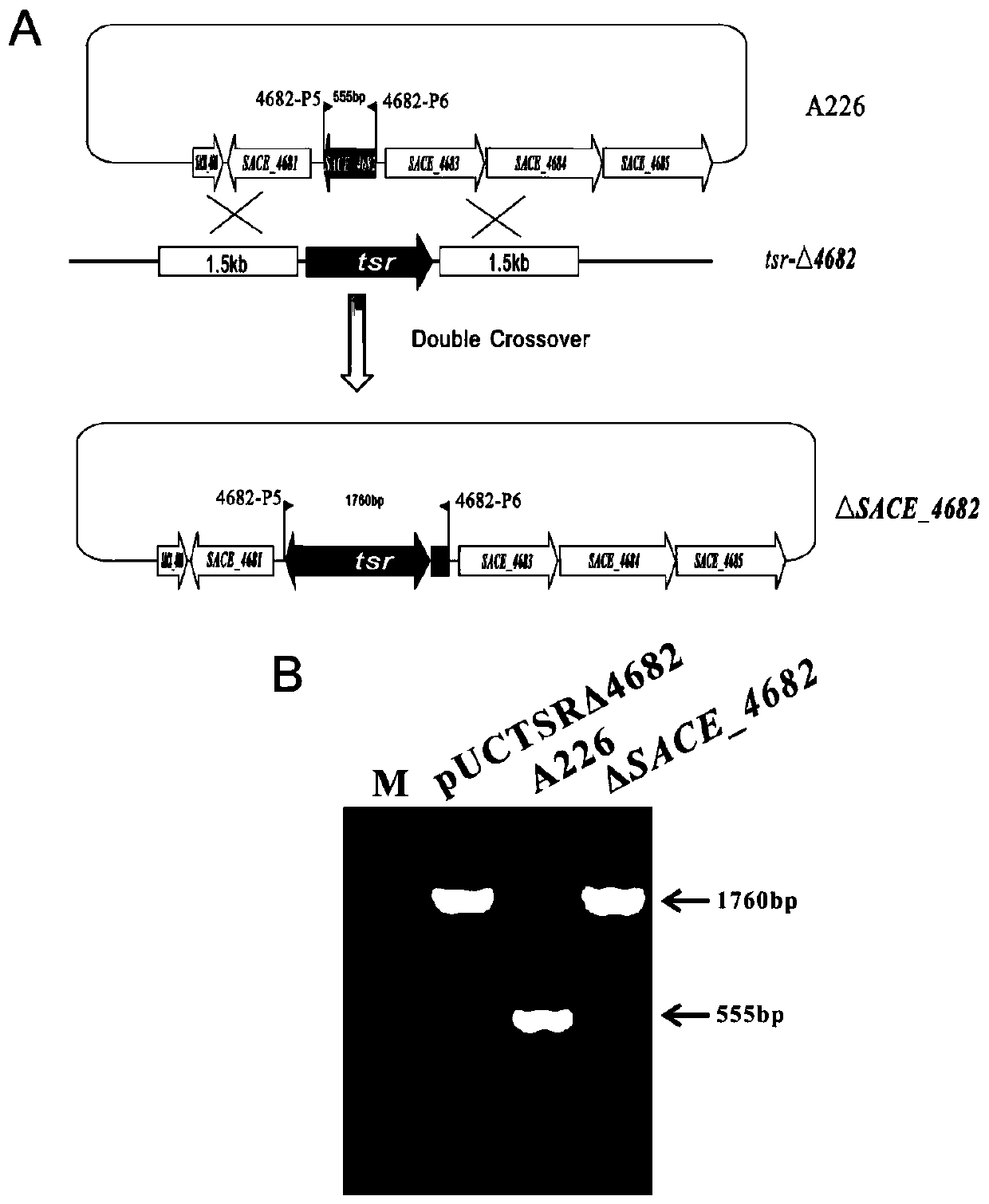
[0036] Such as figure 2 As shown, in order to knock out the SACE_4682 gene in Saccharopolyspora red mold, use 4682-P1, 4682-P2, 4682-P3 and 4682-P4 as primers, Saccharopolyspora red mold A226 genome as template, PCR amplify SACE_4682 Homologous fragments of about 1.5 kb upstream and downstream of the gene.
[0037]The upstream and downstream fragments of the above SACE_4682 were respectively connected to the pUCTSR vector to complete the construction of the plasmid pUCTSRΔ4682. Using PEG-mediated protoplast transformation technology, the large fragment of tsr-Δ4682 was transformed into protoplasts of Rhodomycetes saccharopolyspora. Based on homologous recombination technology of chromosome fragments, positive mutants were screened by thiostrepton resistance, and SACE_4682 was obtained. Genetically engineered strains whose genes are replaced by tsr. 4682-P5 and 4682-P6 were used as identification primers, the plasmid...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Construction of SACE_4682 gene reversion and overexpression strains:
[0040] The SACE_4682 gene was amplified using the designed primers 4682-P5 and 4682-P6, and recovered by electrophoresis. The recovered SACE_4682 gene fragment and pIB139 were double-enzymatically digested and recovered using NdeI and XbaI endonucleases, and then extracted by T4DNA ligase. The SACE_4682 gene fragment was connected to pIB139, and the plasmid pIB139-4682 was successfully obtained. Then pIB139 and pIB139-4682 plasmids were introduced into A226 and ΔSACE_4682 protoplasts by PEG-mediated protoplast transformation technology. Through preliminary screening with apramycin, the apramycin resistance gene (apr) was identified by PCR. The obtained positive reverting strain was named ΔSACE_4682 / pIB139-4682, the positive reverting empty control strain was named ΔSACE_4682 / pIB139; the obtained positive overexpression strain was named A226 / pIB139-4682, and the positive overexpressing empty control ...
Embodiment 3
[0042] HPLC detection of fermentation products of Saccharopolyspora red mold:
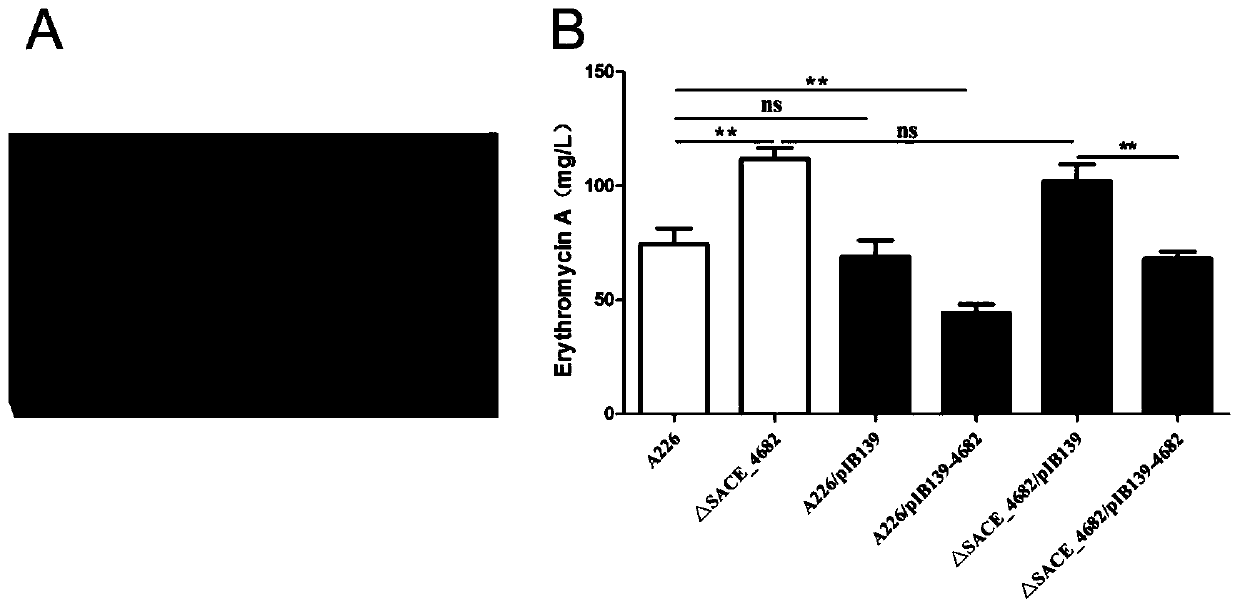
[0043] Inoculate Saccharopolyspora red mold series strains into TSB medium, and after shaking culture at 30°C for 48 hours, transfer to R5 liquid medium, shake culture at 30°C for 6 days, then use organic solvent to extract the fermentation broth, use a water bath After the pot is evaporated to dryness, add 1mL of methanol to dissolve and use a 0.22μm organic filter membrane to process, and then use the machine to detect the content of erythromycin A in the sample, such as image 3 Shown in B.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com