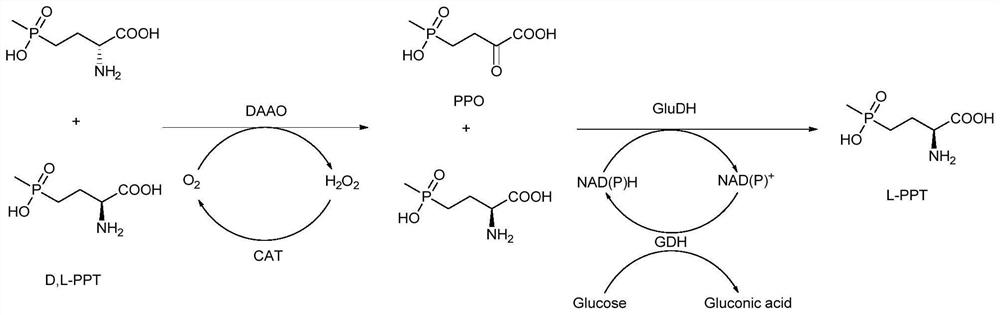
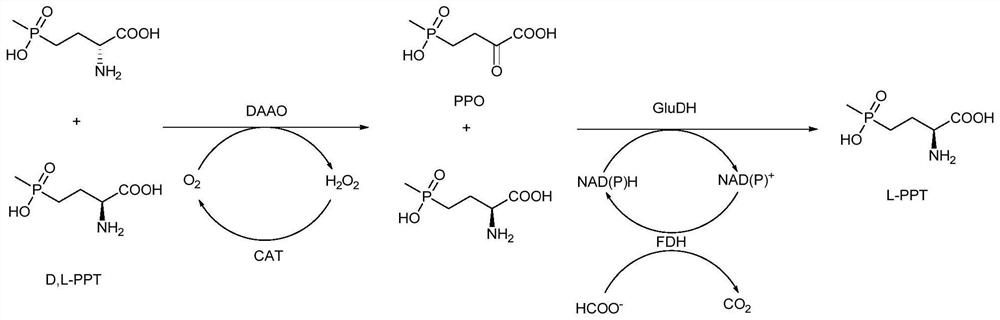
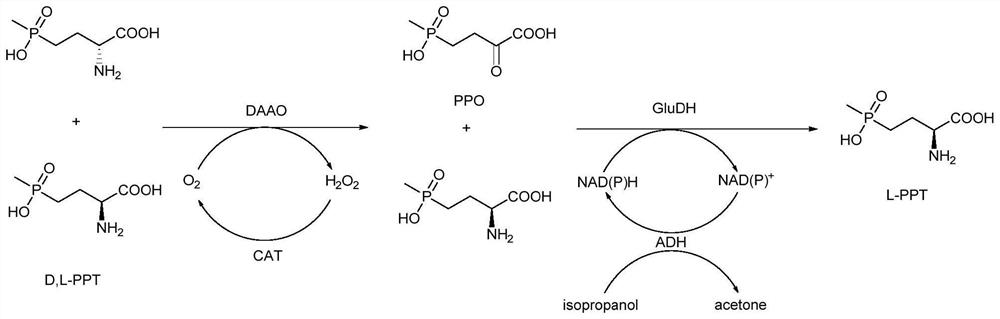
A method for preparing l-glufosinate-ammonium by deracemization by biological enzymatic method, glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase mutant and application
A biological enzyme method, glufosinate-ammonium technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of complex process, expensive chiral resolution reagents, low single resolution rate, etc., and achieve the effect of good catalytic efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] 1. Cultivation of engineered bacteria
[0042] After the engineered bacteria were activated by streaking on a plate, a single colony was inoculated into 10 mL of LB liquid medium containing 50 μg / mL kanamycin, and incubated at 37°C with shaking for 10 h. Transfer to 50 mL of LB liquid medium containing 50 μg / mL kanamycin at 2% of the inoculum, and shake to OD at 37 °C. 600 When it reached about 0.8, IPTG with a final concentration of 0.5 mM was added, and the culture was shaken at 28 °C for 12 h. After the cultivation, the culture solution was centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 10 min, the supernatant was discarded, the cells were collected, and stored in a -80°C ultra-low temperature refrigerator until use.
[0043] 2. Preparation of crude enzyme solution
[0044] The cells collected after the culture were washed twice with pH 8 phosphate buffer (50 mM pH=8 phosphate buffer), and then the cells were resuspended by adding pH=8 phosphate buffer (50 mM). Cells were disrupted ...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Determination of specific enzyme activity of glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase and its mutants.
[0050] The unit of enzyme activity (U) is defined as: the amount of enzyme required to generate 1 μmol of L-glufosinate per minute at 35° C. and pH 7.4 is defined as one unit of enzyme activity, U. Specific enzyme activity is defined as the unit of activity per milligram of enzyme protein, U / mg.
[0051] Standard conditions for enzyme activity detection: 100 mM 2-carbonyl-4-(hydroxymethylphosphinyl)-butyric acid, 10 mM NADPH, appropriate amount of enzyme solution, 30 °C, pH 7.4, 600 rpm for 10 minutes, sample treatment And carry out HPLC detection and analysis. The protein concentration was determined with a BCA protein assay kit (Nanjing Keygen Biotechnology Development Co., Ltd., Nanjing).
Embodiment 3
[0053] Construction and screening of glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase mutant library.
[0054] 1. Construction of genetically engineered bacteria
[0055] The gene sequence of glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase (GenBank No.: WP_101496154) derived from polyculture denitrifying sulfur bacteria (Thiopseudomonas denitrificans) was codon-optimized and sent to Sangon Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. for full gene synthesis, And cloned into the recombinant expression plasmid pETduet-1 to construct the plasmid pETduet-1-GluDH. After the recombinant plasmid was verified by sequencing, it was transferred into the expression host E. coli BL21 (DE3) for subsequent expression of recombinant glufosinate dehydrogenase. The codon-optimized glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase gene sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.1, and the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.2.
[0056] 2. Construction of a library of glufosinate dehydrogenase mutants
[0057] The first step is to construct a glufo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com