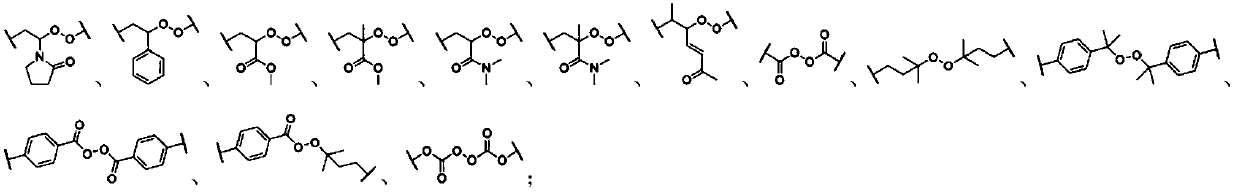
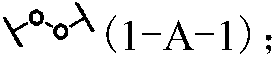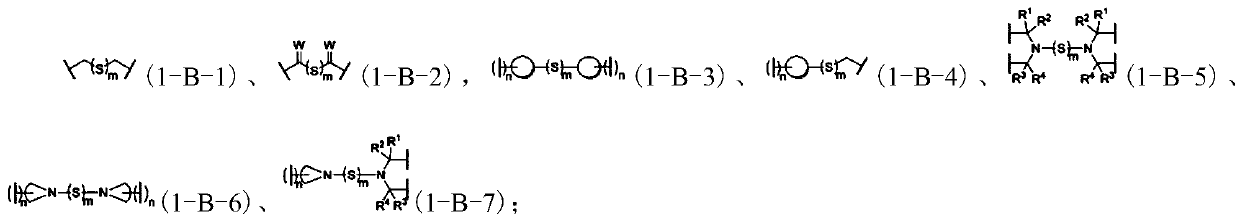Force-induced responsive cross-linked polymer with multiple networks
A technology of cross-linked polymers and responsiveness, which is applied in the field of mechano-responsive cross-linked polymers, mechano-responsive cross-linked polymers and their realization of mechano-response, which can solve the problem of limited improvement of mechanical strength and non-responsive mechanical force Sex, gel materials can not provide strength and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[1780] In the preparation process of the polymer, three methods of mechanical foaming, physical foaming and chemical foaming are mainly used to foam it.
[1781] Among them, the mechanical foaming method is to introduce a large amount of air or other gases into the emulsion, suspension or solution of the polymer with the help of strong stirring during the preparation of the polymer to make it a uniform foam, and then through physical or Chemical changes shape it into foam. In order to shorten the molding cycle, air can be introduced and emulsifiers or surfactants can be added.
[1782] Wherein, the physical foaming method is to use physical principles to realize the foaming of the polymer during the preparation of the polymer, which includes but is not limited to the following methods: (1) inert gas foaming method, that is, under pressure Under normal circumstances, the inert gas is pressed into the molten polymer or pasty material, and then the pressure is reduced and the te...
Embodiment 1
[1799]
[1800] Using triethylamine as a catalyst and dichloromethane as a solvent, a distyryl-sensitizing group cross-linking agent is prepared by reacting the sensitizing group diol (a) with excess 4-vinyl benzoyl chloride. Take 80 molar equivalents of styrene, 1 molar equivalent of the above-mentioned force-sensitive group crosslinking agent, 5 molar equivalents of divinylbenzene, and 5 wt% BPO, put them in a reaction vessel, dissolve them with an appropriate amount of toluene, and stir the reaction at 70°C under a nitrogen atmosphere After 24h, a single-network styrene was obtained. Then take 80 molar equivalents of styrene, 3 molar equivalents of divinylbenzene, 5wt% BPO, and 80wt% single-network styrene, place them in a reaction vessel, fully swell with an appropriate amount of toluene, and stir the reaction at 70°C under a nitrogen atmosphere After 24 hours, the product was poured into a mold, and the solvent was removed at 60°C to obtain a common solid. The solid m...
Embodiment 2
[1802]
[1803] Take 3.5 molar equivalents of polylactide diol (molecular weight: 5000), 1 molar equivalent of alkoxyamine dibromide (a), and 3 molar equivalents of 1,3,5-tris(bromomethyl)benzene, and dissolve them with an appropriate amount of DMF Finally, add 18 molar equivalents of sodium hydroxide catalyst, then stir the reaction at 50°C for 24 hours, remove impurities and solvent after the reaction is completed, and obtain single-network polylactide. Take 9 molar equivalents of polylactide diol (molecular weight is 5000), 36 molar equivalents of triethylamine, 50wt% single-network polylactide, fully swell with an appropriate amount of dichloromethane, cool in an ice bath for 30 minutes, then stir and drop into the solution There are 6 molar equivalents of 1,3,5-dichloromethane solution of benzenetricarboxylic acid chloride, after the dropwise addition is completed, stir and react at room temperature for 6h, then add 5wt% nano silver, 0.6wt% dibutyltin dilaurate, 0.3wt% ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com