Loose nanofiltration membrane and preparation method and application thereof
A nanofiltration membrane and loose technology, which is applied in the field of membrane separation, can solve the problems of low water flux and long preparation time of composite nanofiltration membranes, and achieve the effects of short time consumption, stable membrane performance and stable performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
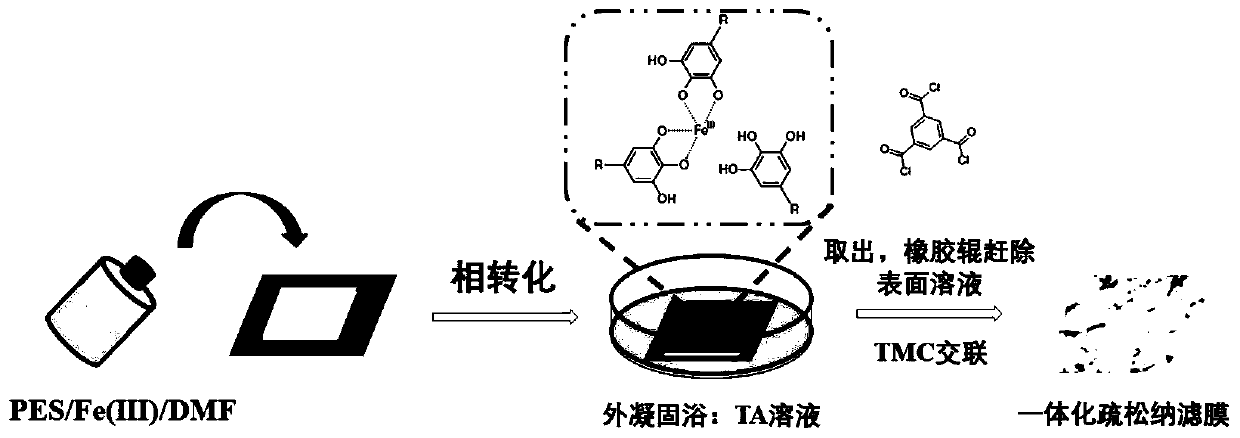
[0044] The embodiment of the present invention proposes a method for preparing a loose nanofiltration membrane applied to the reuse of printing and dyeing wastewater, comprising the following steps:
[0045] S1. First, mix a certain amount of ferric chloride with the organic solvent -N,N'-dimethylformamide, and shake until uniform before use. Then weigh a certain amount of polyethersulfone particles and add to the above solution, heat and stir to obtain a uniform and stable casting solution.
[0046] S2. Configure a certain concentration of tannic acid aqueous solution as the external coagulation bath, paste the non-woven fabric on the glass plate with transparent glue, pour the casting solution evenly on the edge of the glass plate, use a scraper to scrape the film, and make the casting solution in the absence of Forms an even coating on the spun fabric. Thereafter, the glass plate and the cast film liquid layer are immersed in the external coagulation bath for a period of t...
Embodiment 1
[0058] First, mix a certain mass of ferric chloride with the organic solvent-N,N'-dimethylformamide, wherein the mass fraction of ferric chloride is 0.5wt.%, shake until uniform, and then weigh a certain amount of poly Ethersulfone particles were added to the above solution, the mass fraction of polyethersulfone in the casting solution was 18wt.%, and heated and stirred at 45°C to obtain a uniform and stable casting solution. An aqueous solution of tannic acid (adjusted to pH 5 with sodium hydroxide and sulfuric acid) with a mass fraction of 1.0 wt.% was used as an external coagulation bath. Stick the non-woven fabric on the glass plate with transparent glue, pour the casting solution evenly on the edge of the glass plate, scrape the film with a 200 μm scraper, and let the casting solution form a uniform coating on the non-woven fabric. Thereafter, the glass plate together with the cast film layer was immersed in the external coagulation bath for 10 minutes. Take out the base...
Embodiment 2
[0063] The difference between this example and Example 1 is that the mass fraction of polyethersulfone in the casting solution is 21wt.%. Others are the same as in Example 1.
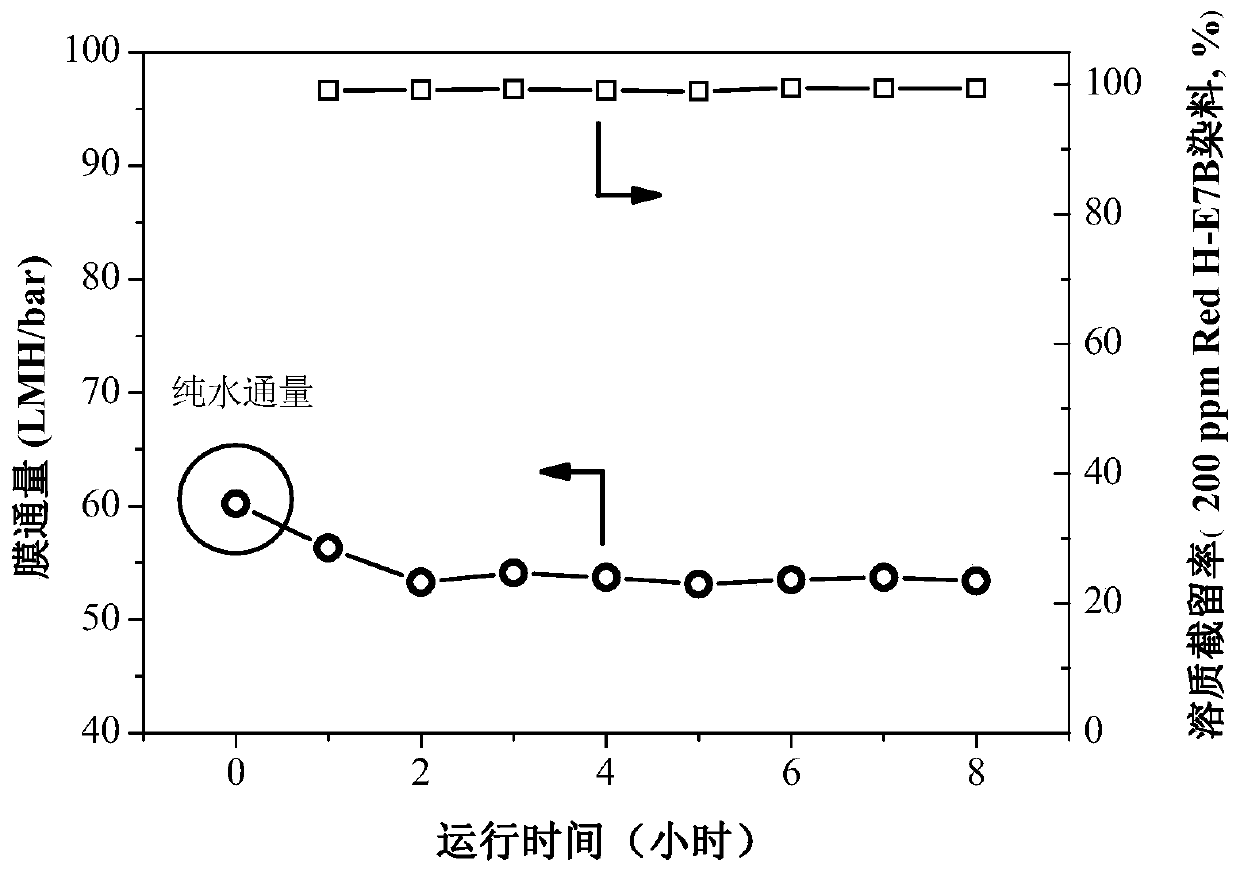
[0064] Use pure water as the raw material liquid, run it at 3.0bar for 1 hour, and obtain the water flux of the prepared loose nanofiltration membrane, which is 22.4LMH / bar. After that, change the raw material liquid into 200ppm reactive dye Ec Red H-E7B H / C aqueous solution was used as the feed liquid, and the test was carried out continuously for 8 hours at a test temperature of 25°C and a pressure of 2.0 bar, and the changes of membrane flux and dye retention rate during the test were investigated. see results Figure 6 . Depend on Figure 6 It can be seen that the pure water flux of the loose nanofiltration membrane prepared in Example 2 has decreased compared to Example 1, only 22.4LMH / bar, and the rejection rate of reactive dye Ec Red H-E7BH / C was tested in 8 hours. Both remain above 99.4%, w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com