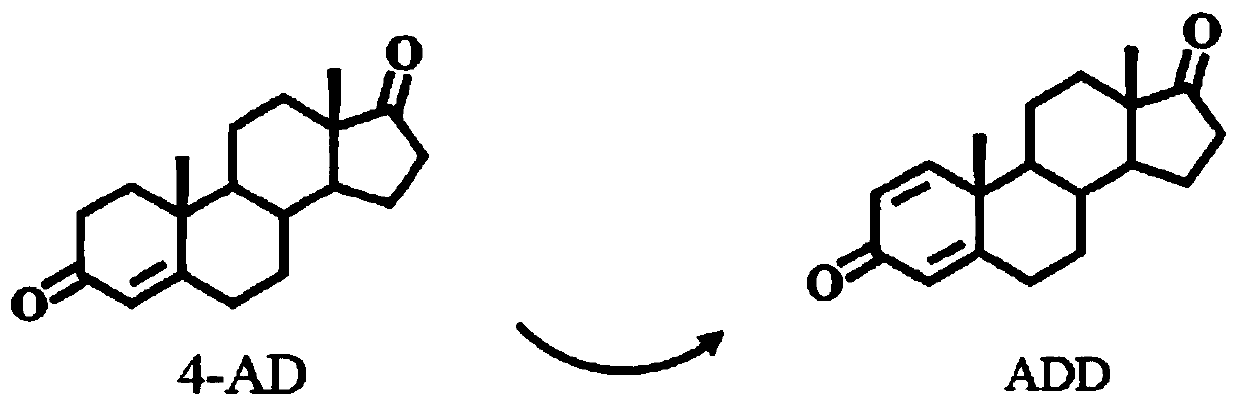
Method for preparing C1,2-position dehydrogenated steroid compound
A steroidal compound and dehydrogenation technology, applied in the field of biochemistry, can solve the problem of difficult solubility of membrane proteins, etc., and achieve the effect of single product and high-efficiency conversion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Embodiment 1, construction and shake flask expression of recombinant KstD fusion enzyme plasmid:
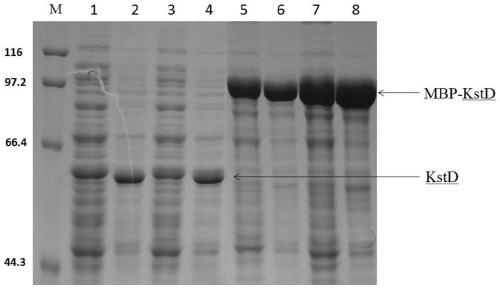
[0034] Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) cells containing the recombinant plasmid were cultured in LB medium containing 35 μg / ml kanamycin and rotated at 37° C. at 200 rpm. When OD600nm reached 0.8, 0.4 mM isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactopyranoside (final concentration) was added, the culture temperature was lowered to 20° C., and culture was continued for 18-20 hours. It was found by SDS-PAGE that the expression of the soluble target enzyme protein was significantly increased ( figure 2 ).
Embodiment 2
[0035] Embodiment 2, high-density fermentation prepares KstD fusion enzyme:
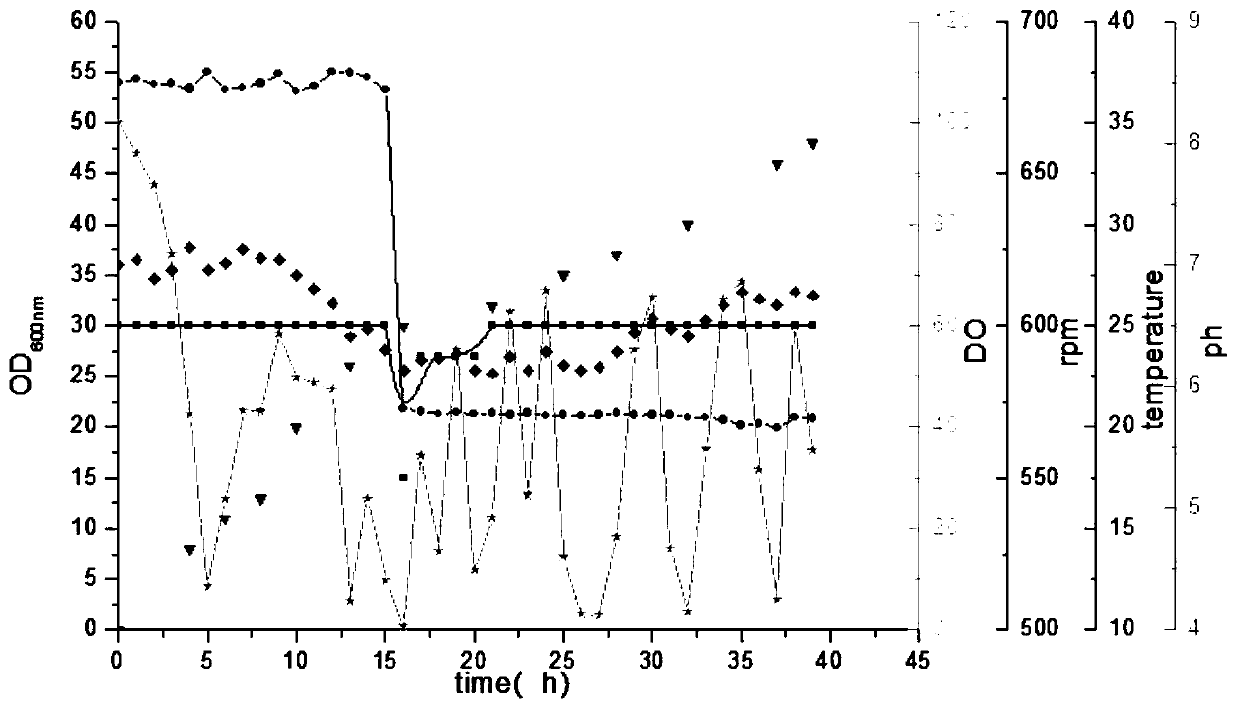
[0036] In order to obtain a high-density cell culture with a large amount of enzymes, the high-density medium was optimized, and the cells were cultured in a 15L fermenter with some modifications, such as replacing glucose by glycerol, yeast powder as a nitrogen source, induced by lactose, etc. At the beginning of the fermentation, the temperature of the fermentor was controlled at 37 °C to allow rapid cell growth. During the fed-batch phase, the dissolved oxygen was controlled between 10% and 30%, and the pH was controlled between 6.2 and 7.8. Before the induction phase, the cell culture temperature was lowered to 20°C and maintained for a period of time, then lactose mother solution was added until the final concentration reached 0.4mM, and the induction time was 18h-20h. Induce protein expression. After fermentation, collect E. coli cells by centrifugation at 4°C, resuspend in 50mM Tris-HCl buff...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Embodiment 3, KstD fusion enzyme activity
[0039] Take an appropriate amount of the centrifuged supernatant of 2.3, Mbp-KstD2 at 30 °C with a Nano Drop 2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific) at 600 nm (ξ600 nm = 18.7 × 103
[0040] cm-1M-1) using phenazine methyl sulfate (PMS) and 2,6-dichlorophenol-diphenol (DCPIP). The reaction mixture (1 ml) consisted of 50 mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 7.0), 150 mM PMS, 8 mM DCPIP, appropriate concentration of supernatant or cell extract and 100 mM AD methanol. Activity is expressed as units per milligram of protein; 1 U is defined as a reduction of 1 μmolmin-1 DCPIP. No activity was detected in the reaction mixture without 4-androstenone-3,17-dione (AD). The remaining supernatant was subjected to SDS-PAGE electrophoresis analysis, and SDS-PAGE used 8% separating gel and 5% stacking gel to identify whether the protein was expressed correctly. Protein expression in the fermenter as Figure 4 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com