Treatment method for recovering magnesium salt from copper-containing wastewater
A treatment method and technology for waste water, applied in the field of water treatment, can solve the problem that magnesium salts contain a lot of miscellaneous salts, and achieve the effects of good adsorption effect, saving operation cost and reducing dosage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
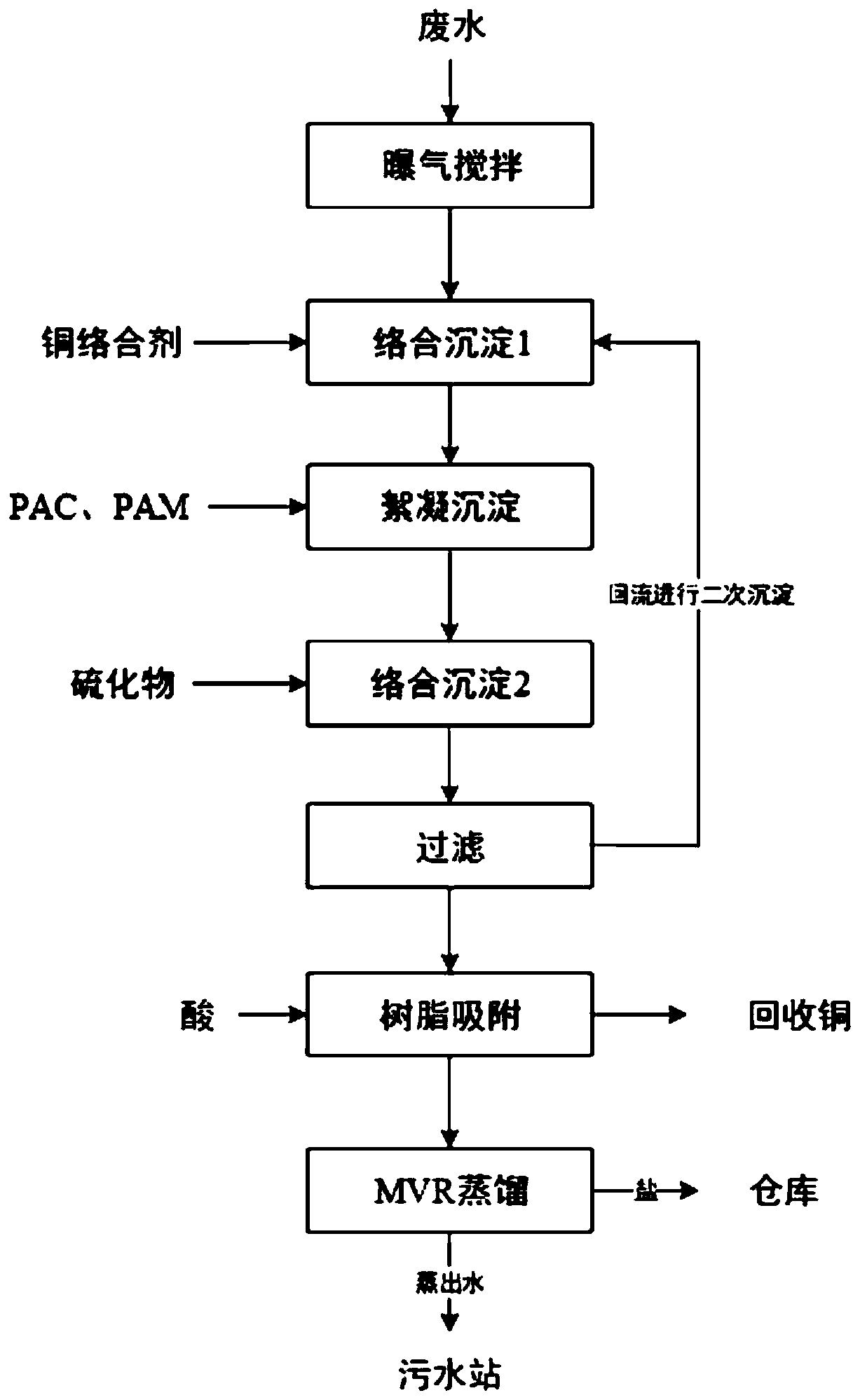
[0037] A treatment method for recovering magnesium salts from copper-containing wastewater according to the present invention, the treated wastewater is high-concentration magnesium salt-containing copper wastewater, the concentration of copper ions in the wastewater is 500-2000 mg / L, and the concentration of magnesium ions is 20000-100000 mg / L L. Specific steps are as follows:
[0038]S100. Pass the wastewater into the aeration tank and add air, oxygen or hydrogen peroxide and other oxidizing agents for aeration and stirring; convert the monovalent copper in the wastewater into divalent copper, the cost of aeration oxidation is low and easy to operate, and can be used Significantly improve the removal effect of copper complex sedimentation agent on copper ions, and remove most of the copper ions; it is worth noting that it can be determined whether the conversion of monovalent copper ions is complete through iodometric method and instrument detection;
[0039] S200, adjust t...
Embodiment 2
[0058] The basic content of this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 1, and its difference is that the specific steps are as follows:
[0059] S100, passing the waste water into the aeration tank and passing air into it for aeration and stirring;
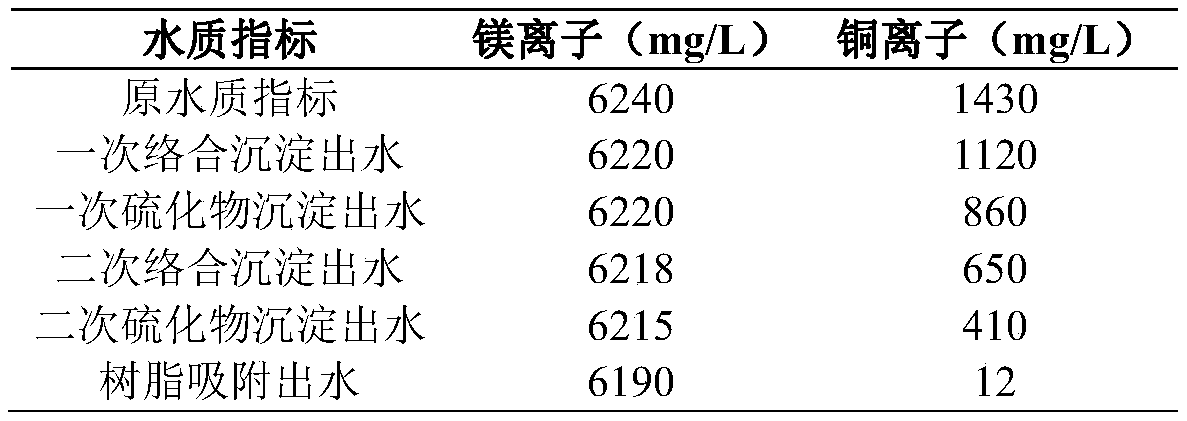
[0060] S200, adjust the pH of the effluent in S100 to 6, add heavy metal complexing agent TMT-15 for complexation and stirring; the dosage of primary precipitation is 1.0g per kilogram of wastewater, and the dosage of secondary precipitation is per kilogram of wastewater Add 0.5g in the medium dosage;
[0061] S300, pass the effluent in S200 into the flocculation tank, add flocculant to carry out flocculation, sedimentation, and filtration in sequence; the flocculant used is PAC;
[0062] S400. Add a precipitant to the effluent in S300 for precipitation, stir to precipitate copper sulfide precipitation, and filter after precipitation; the precipitant used is sodium sulfide, and the dosage of the primary precipitation is 1g...
Embodiment 3
[0070] The basic content of this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 1, and its difference is that the specific steps are as follows:
[0071] S100, passing the wastewater into the aeration tank and adding oxygen for aeration and stirring;
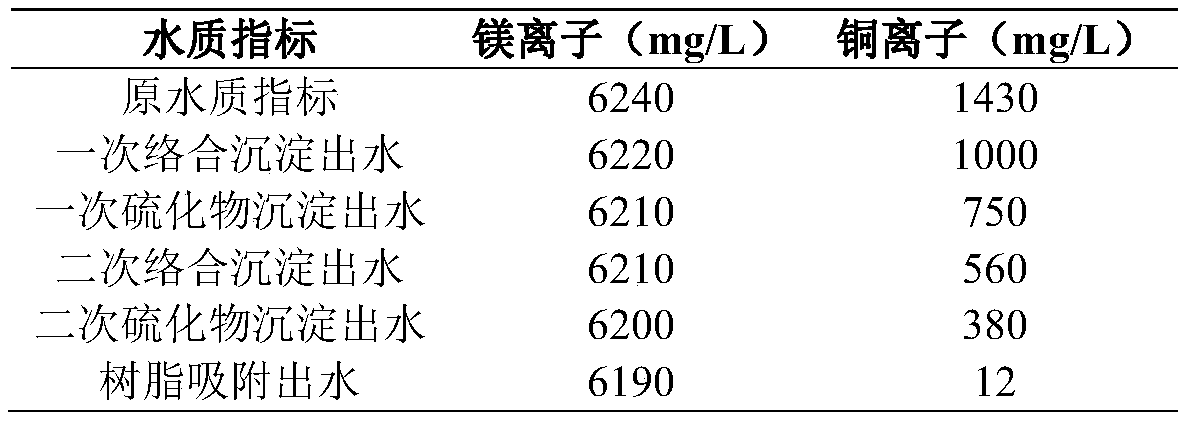
[0072] S200, adjust the pH of the effluent in S100 to 8, add heavy metal complexing agent TMT-15 for complexation and stirring; the dosage of primary precipitation is 0.2g per kilogram of wastewater, and the dosage of secondary precipitation is per kilogram of wastewater Add 0.1g in the medium dosage;
[0073] S300, pass the effluent in S200 into the flocculation tank, add flocculant to carry out flocculation, sedimentation, and filtration in sequence; the flocculant used is PAM;
[0074] S400, add a precipitant to the effluent in S300 for precipitation, stir and precipitate copper sulfide precipitation, and filter after precipitation; the precipitant used is sodium sulfide, and the dosage of the primary precipitation is 0.5g per...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com