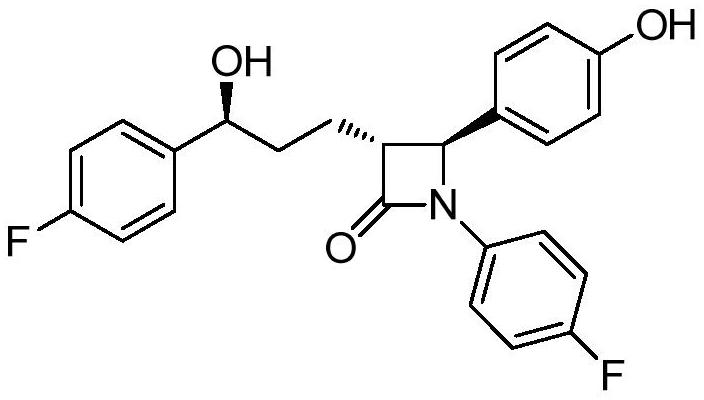
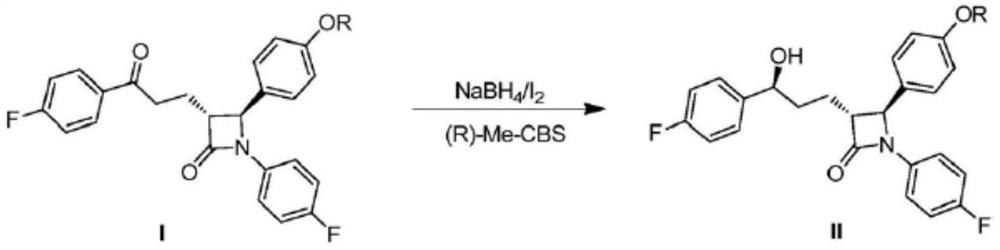
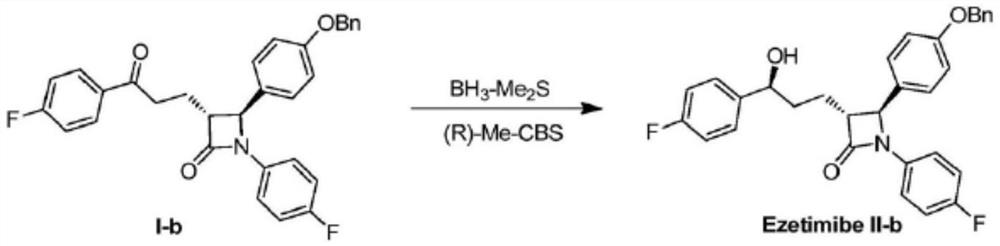
Ezetimibe intermediate and preparation method of ezetimibe
A compound and catalyst technology, applied in the field of preparation of ezetimibe intermediates and ezetimibe, can solve the problems of potential safety hazards, low asymmetric conversion rate, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0046] The preparation method of the compound shown in the formula (I) of one embodiment of the present invention, comprises the following steps:
[0047] S101: providing a compound represented by formula (II);
[0048]
[0049] Among them, the compound represented by formula (II) can be commercially available raw materials, or prepared by existing methods, which are not particularly limited here, and should be understood as being within the protection scope of the present invention.
[0050] Further, S101 includes the following steps:
[0051]
[0052] S1011: providing a compound represented by formula (III);
[0053] S1012: Condensing the compound represented by formula (III) and the compound represented by formula (IV) to obtain the compound represented by formula (II);
[0054] Wherein, in step S1012, existing condensation reaction reagents, such as DDC / DMAP, can be used.
[0055] In one embodiment, in step S1012, the compound represented by the formula (III) is f...
Embodiment 1
[0099] (1) Add 200g of the compound represented by formula (III) into 2.5L of dichloromethane, cool to -10°C, slowly add 220mL of oxalyl chloride dropwise, after the dropwise addition is completed, stir for 30min, rise to room temperature for reaction, and wait until the reaction is complete After concentrating to obtain the crude product, the crude product was dissolved in 500 mL of toluene to obtain the first solution; 2.5 L of toluene, 170g and 265mL of triethylamine were mixed to obtain the second solution; the first solution was slowly dripped into the second solution, and after the addition was completed, it was reacted at 75°C. The solution was washed, the organic phase was concentrated, and recrystallized with isopropanol to obtain the compound represented by formula (II).
[0100] (2) In a 5L autoclave, under an argon atmosphere, add 100g of the compound shown in formula (II) from the feeding port, then add 1L of toluene to fully dissolve the raw material, continue t...
Embodiment 2
[0102] In a 5L autoclave, under an argon atmosphere, add 100g of the compound represented by the formula (II) through the feeding port, then add 1L of toluene to fully dissolve the raw material, continue bubbling with argon for degassing, and continue bubbling for 1h , the degassing is completed. Under argon atmosphere, add the structure catalyst shown in 0.1g formula (C) ( n is 50), finally add 10g of potassium tert-butoxide, after the feeding is finished, close the feeding port quickly. Replace the argon with hydrogen, slowly introduce hydrogen to 4MPa, and close the inflation valve. The rapidly stirred reaction was carried out at 30-40°C. When the pressure drops to 1-2 MPa, the hydrogen pressure is added back to 4 atm, and the reaction is considered to be stopped when the pressure drops to a constant value. Sampling was sent for liquid phase analysis to confirm the conversion rate. The catalyst was removed, and the filtrate was washed successively with 0.3 L of water a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com