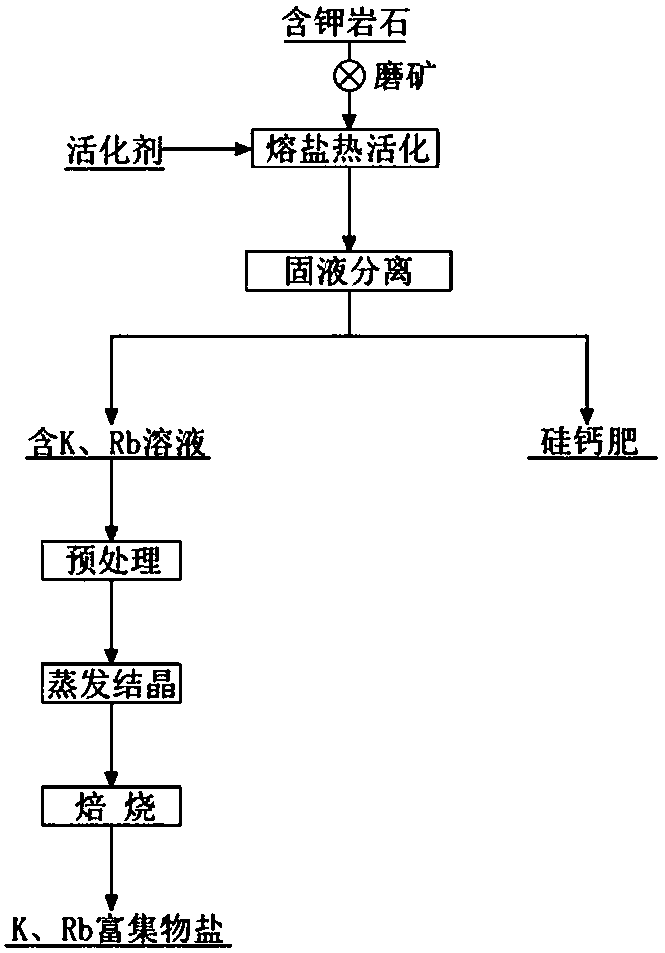
Method for cooperatively extracting potassium and rubidium from potassium-containing rock
A potash rock and ore technology, applied in the field of mineral processing and hydrometallurgy, can solve the problems of poor economic benefit, low added value, single product, etc., and achieve the effects of less equipment, less impurities and easier technology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] The embodiment uses potassium-bearing shale and analytically pure CaO as raw materials. Among them, the potassium-containing rock samples come from the potassium-bearing sand shale mining area in Pingshun District, Changzhi City, Shanxi Province, and the analyzed pure CaO contains 98% of CaO. The results of chemical analysis of the ore are shown in Table 1.
[0065] Table 1 Main composition and content (%) of potassium-bearing rock ore
[0066] components SiO 2
K 2 o
CaO Na 2 o
TF Al 2 o 3
MgO TiO 2
Rb 2 o
content% 66.26 10.48 1.44 0.081 1.78 14.01 1.12 0.48 0.022
[0067] Specific steps include:
[0068] Step 1: crush 500 grams of potassium-containing rock, add 400 milliliters of water and grind in a ball mill for 15 minutes, filter, and dry to obtain a potassium-containing rock sample passing through a 200-mesh sieve;
[0069] Step 2: Take 50 grams of potassium-containing rock samples, add 70 g...
Embodiment 2
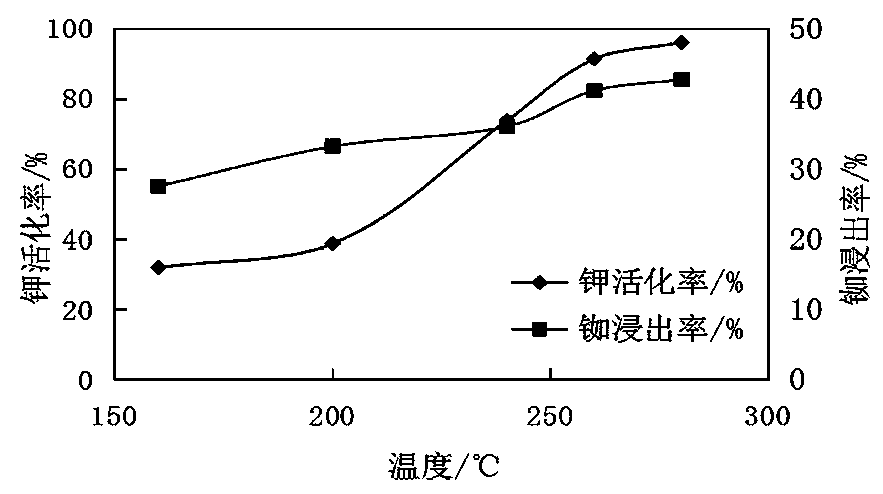
[0074] Example 2: Effect of molten salt thermal activation temperature on potassium activation rate and rubidium leaching rate
[0075] The steps of the method described in Example 1 are adopted, but the reaction temperatures of thermal activation of molten salt in step 2 are adjusted to 160°C, 200°C, 240°C, 260°C and 280°C respectively, and tests are carried out at different reaction temperatures. For the results, see figure 2 .
[0076] From figure 2 It can be seen that as the temperature increases, the effective potassium activation rate and rubidium leaching rate increase gradually. The higher the temperature, the more intense the reaction. At 260°C, the effective potassium activation rate is 91%, and the rubidium leaching rate is 42%. The rate of activation then slows down. Excessively high temperature requires high equipment materials and consumes a lot of energy. Considering comprehensively, the optimum temperature is selected as 260°C.
Embodiment 3
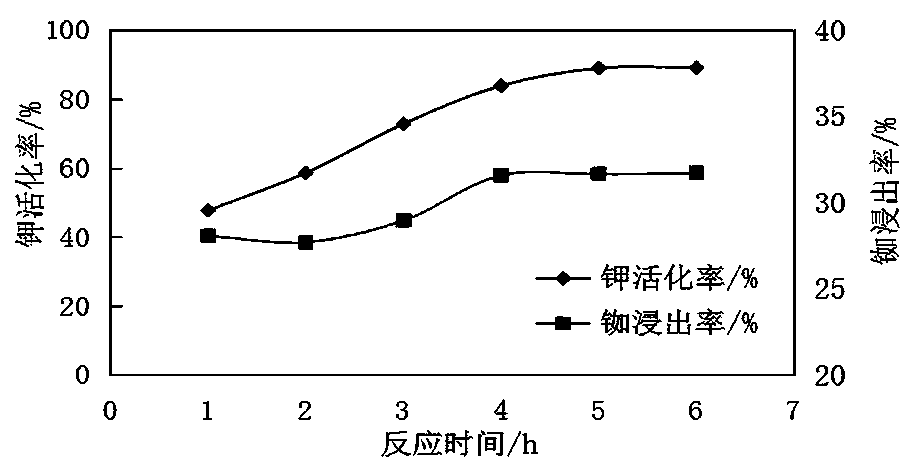
[0077] Example 3: Effect of molten salt thermal activation reaction time on potassium activation rate and rubidium leaching rate
[0078] Using the steps of the method described in Example 1, set the reaction temperature of thermal activation of molten salt to be 260°C, but adjust the reaction time of thermal activation of molten salt in step 2 to 1h, 2h, 3h, 4h, 5h and 6h respectively. Experiments were carried out under different reaction times, and the results can be found in image 3 .
[0079] From image 3 It can be seen that the activation rate of effective potassium and the leaching rate of rubidium increase with the increase of time, and remain basically unchanged with the extension of reaction time after 4 hours. The hydrothermal system has complex phases. In order to save costs, reduce energy consumption, and avoid side reactions, the time should not be too long. The optimal reaction time is 4 hours.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com