Preparation method of targeted adsorption in-situ regeneration hydrophilic nano molecularly imprinted material
An in-situ regeneration and nano-molecular technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, catalyst activation/preparation, water pollutants, etc., can solve problems such as easy collapse, small specific surface area, complex process, etc., to improve removal capacity and dosage The effect of less and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
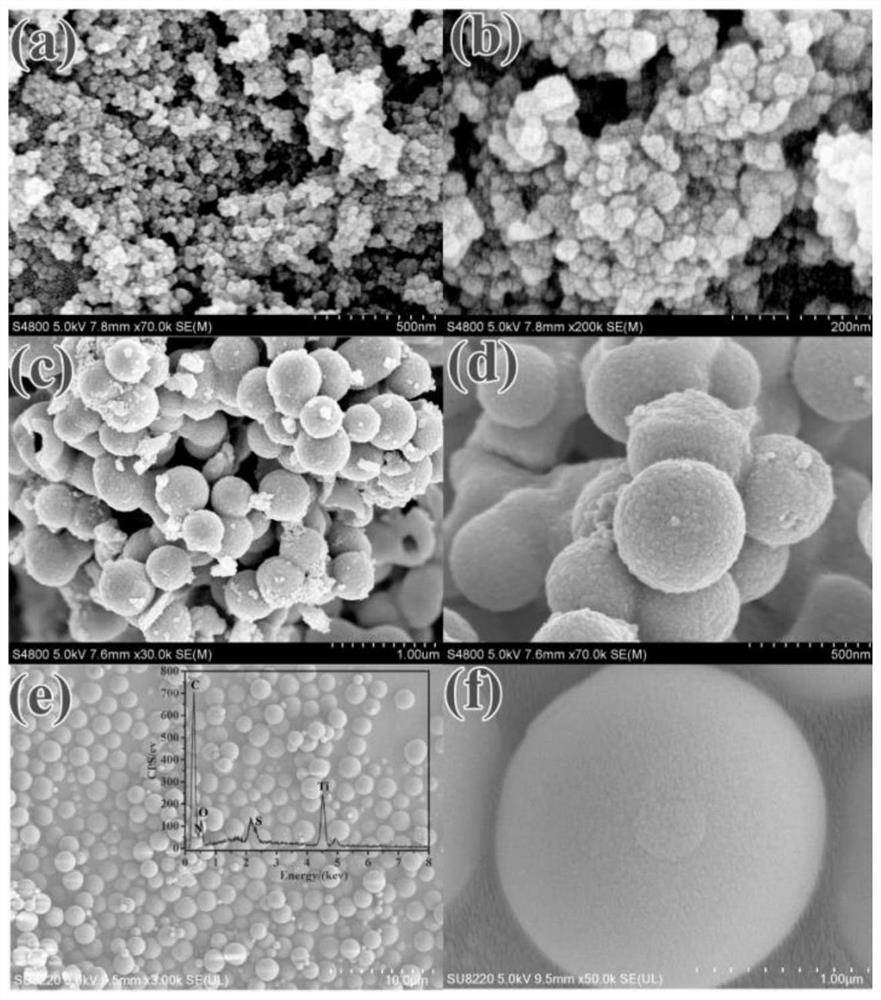
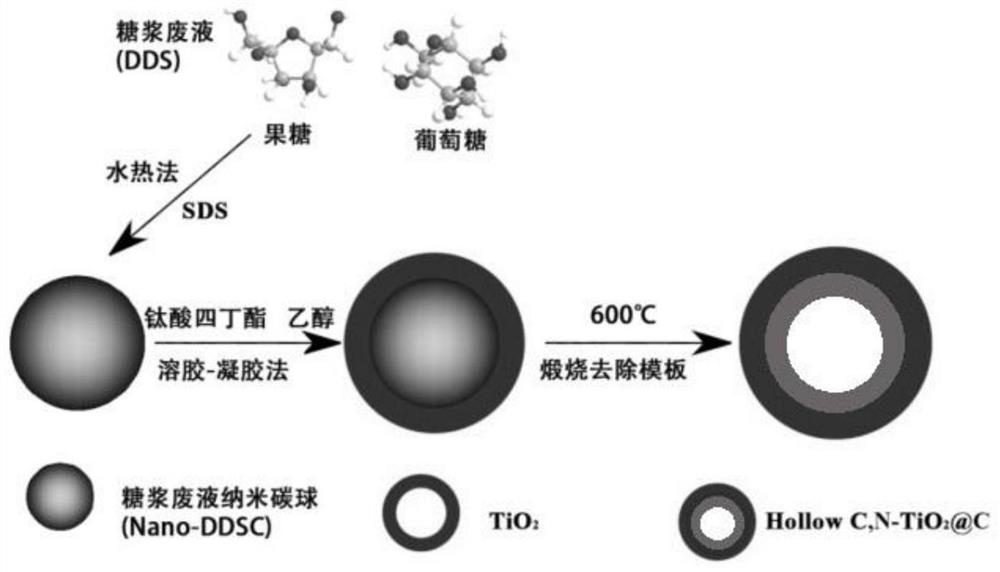
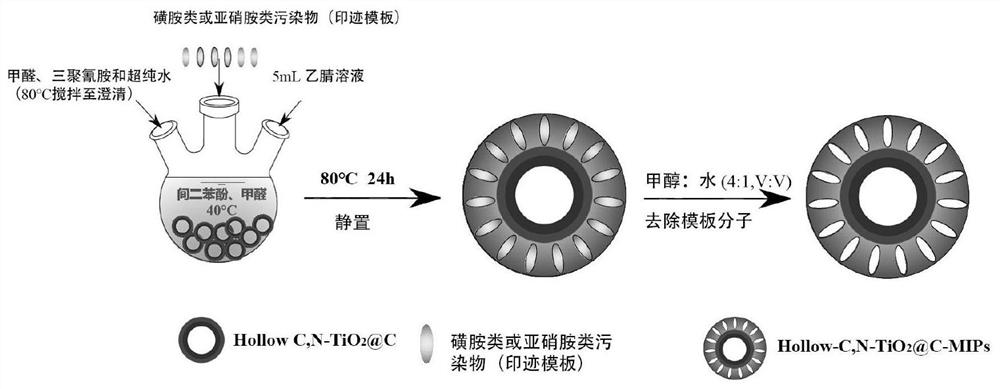
[0036] see figure 1 and figure 2 , a method for preparing a targeted adsorption in-situ regeneration hydrophilic nano-molecularly imprinted material, comprising the following steps:
[0037] S1, using syrup waste liquid and sodium lauryl sulfate to synthesize syrup nano-carbon spheres through hydrothermal reaction;
[0038] S2. Disperse 100 mg of syrup nanocarbon spheres (DDSC) in 20 mL of absolute ethanol, then add 2 mL of tetrabutyl titanate (TBOT), stir at room temperature for 24 hours, then suction filter, wash, and dry at 80 ° C. Dry under vacuum for more than 12 hours, and finally calcined at 400-600°C for 1-3 hours to obtain HollowC,N-TiO 2 @C microspheres; in the preparation process, in order to prevent HollowC, N-TiO 2 @C microspheres are oxidized, and a protective atmosphere (such as nitrogen) can be added during calcination.
[0039]S3. Add 1-2 parts of formaldehyde aqueous solution, 2-4 parts of resorcinol, and 40-60 parts of ultrapure water into a three-necke...
Embodiment 2
[0045] S1, using syrup waste liquid and sodium lauryl sulfate to synthesize syrup nano-carbon spheres through hydrothermal reaction;
[0046] The preparation process of the syrup nano-carbon spheres in this example is as follows: Weigh 50.00 g of syrup waste liquid and 0.05 g of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) in a beaker, stir for 30 min at a constant temperature of 40 ° C, and then transfer to a 100 mL high-pressure In the reaction kettle, heat at 180°C for 8h. After cooling to room temperature, filter with suction (0.22um water-based filter membrane), wash the product with distilled water and absolute ethanol three times, and vacuum-dry at 80°C for more than 12 hours to obtain syrup nanocarbon spheres.
[0047] S2. Disperse 100 mg of syrup nanocarbon spheres (DDSC) in 20 mL of absolute ethanol, then add 2 mL of tetrabutyl titanate (TBOT), stir at room temperature for 24 hours, and then suction filter (0.22 μm is used in this embodiment) water-based filter membrane), washed, a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com