Preparation method of cartilage acellular matrix composite scaffold and application thereof
An acellular matrix and composite scaffold technology, which is applied in the field of preparation of cartilage acellular matrix composite scaffolds, can solve the problem that the composition and structure of extracellular matrix cannot be completely simulated, and achieves good biocompatibility and biodegradability, and can Strong controllability and evenly distributed effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] This embodiment discloses a method for preparing extracellular matrix particles, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0053] 1) Scrape hyaline cartilage tissue from pig articular cartilage (within 24 hours after pig slaughter), cut it into small pieces, put it in PBS solution for 5 minutes of ultrasonication, vacuum freeze-dry, and put it in a -20°C refrigerator for later use.
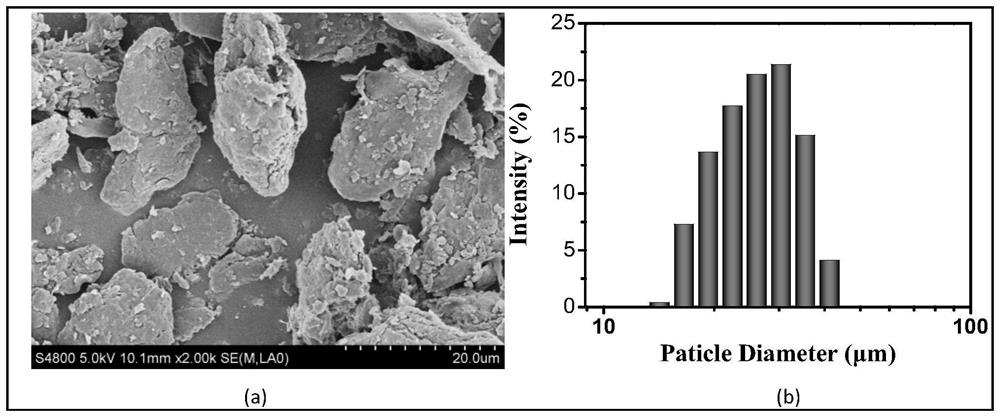
[0054] 2) Place the freeze-dried extracellular matrix obtained in step 1) in an EP tube, add grinding beads, and grind in a cryogenic grinder for 5-10 minutes. Wherein, the grinding temperature is -20° C., the frequency is 60 Hz, and the machine speed is 3000 r / min. The appearance and diameter of the particles after grinding are as follows: figure 1 As shown, its diameter is about 10-50 μm.
Embodiment 2
[0056] This embodiment discloses a gentle decellularization method, the specific steps are as follows:
[0057] 1) The granules prepared in Example 1 were placed in the hypotonic solution and the hypertonic solution, washed and shaken for 3 minutes, and repeated 3 times. Then the particles were frozen in liquid nitrogen, and then dissolved in a hot water bath at 37°C, and repeated 5 times.
[0058] 2) Move the particles into 1% CHAPS solution to wash 3 times, shake at 800r / min for 3h; then add to 100U / mL DNAse1 solution, shake for 9 at 37°C at 100r / min After 3 hours, change the fresh DNAse1 solution every 3 hours, and finally wash with 0.5% CHAPS solution for 15 minutes.
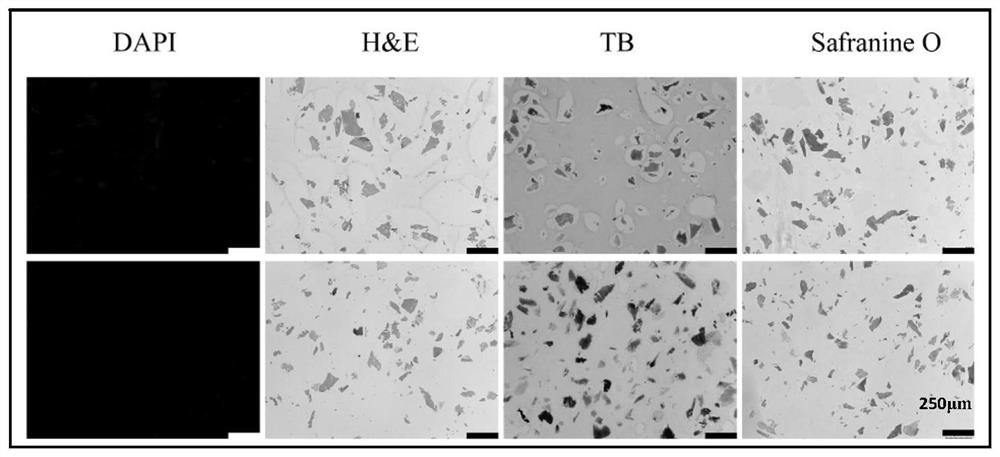
[0059] 3) Rinse the substrate well with distilled water to remove all detergent. The pelleted decellularized matrix (pdECM) was collected by centrifugation, lyophilized and stored at -20°C.
[0060] After decellularization treatment, no obvious cell debris remained, the cell removal rate reached 95% and a...
Embodiment 3
[0062] In this experiment, on the basis of Example 2, the effects of three different chemical reagents on the decellularization effect were compared (all the other conditions were in Example 2), which were polyethylene glycol octylphenyl ether (Triton X-100), ten Sodium dialkyl sulfate (SDS), 3-[(3-cholesteryl aminopropyl) dimethylamino]-1-propanesulfonic acid (CHAPS), the comparison method is as follows:
[0063] Table 1
[0064]
[0065] Among them, the concentrations of the three solutions are all 1%, and they are shaken under normal temperature conditions.
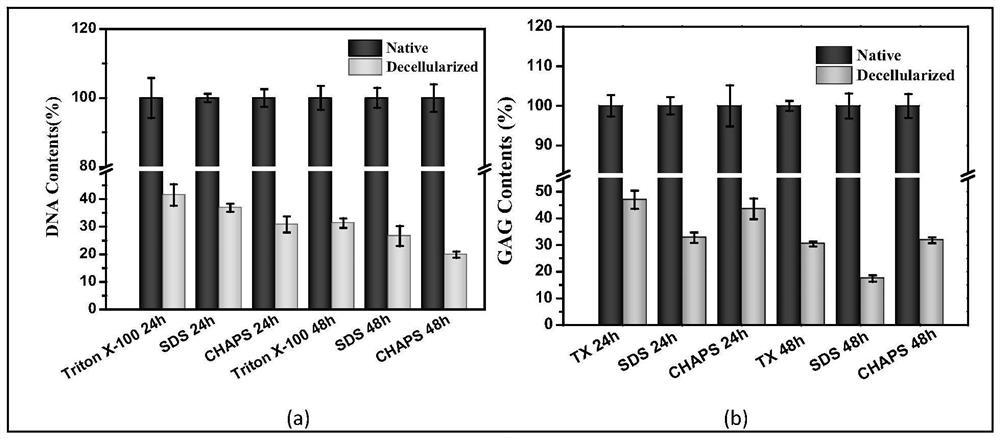
[0066] Quantitative analysis of DNA and GAG in six different ways, the results are as follows: figure 2 As shown, in general, under different time conditions, the decellularization effect of the CHAPS group is better than that of the other two groups, which is specifically manifested in the high DNA removal rate and the retention of more GAGs.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com