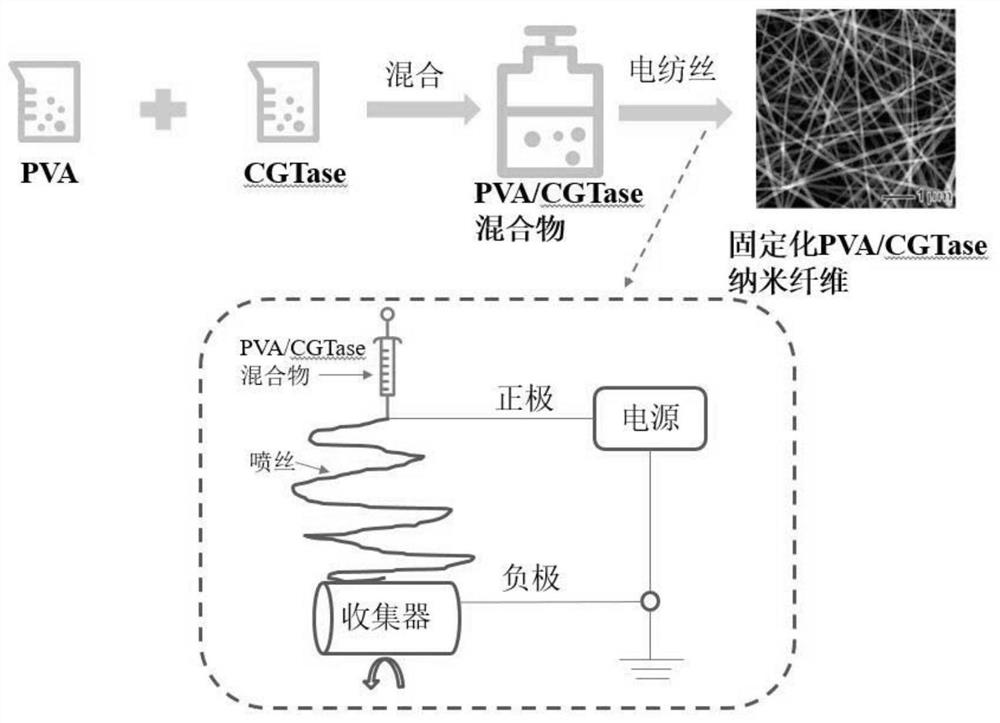
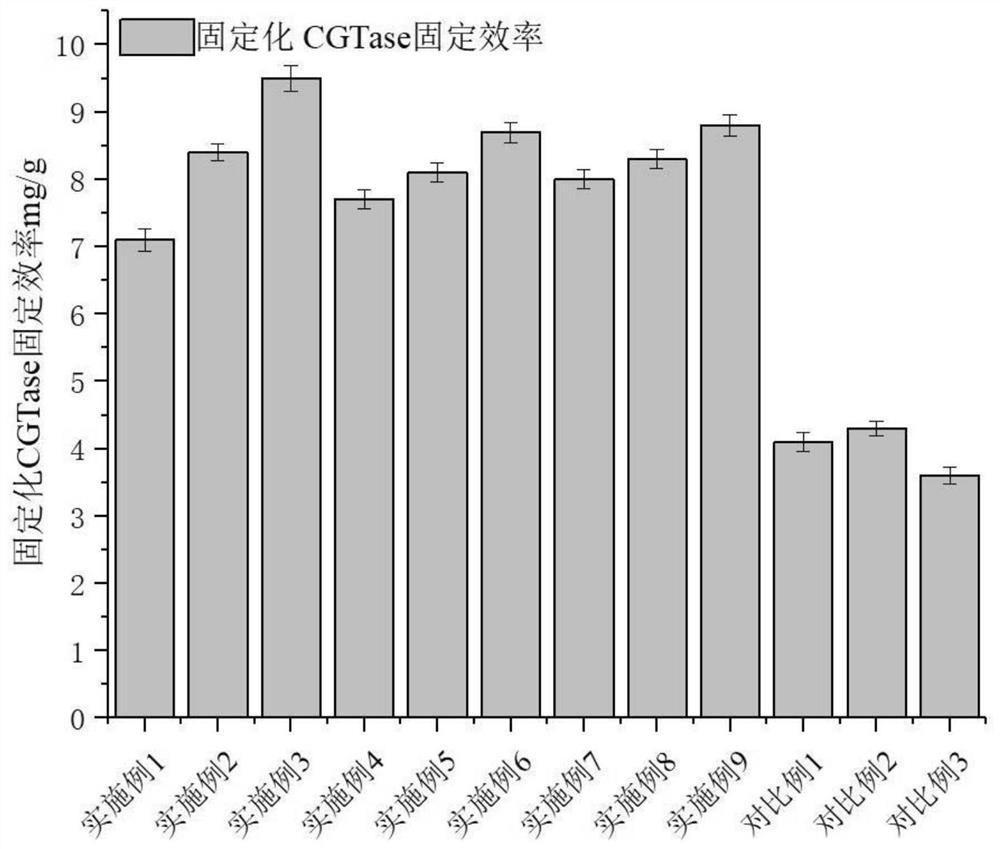
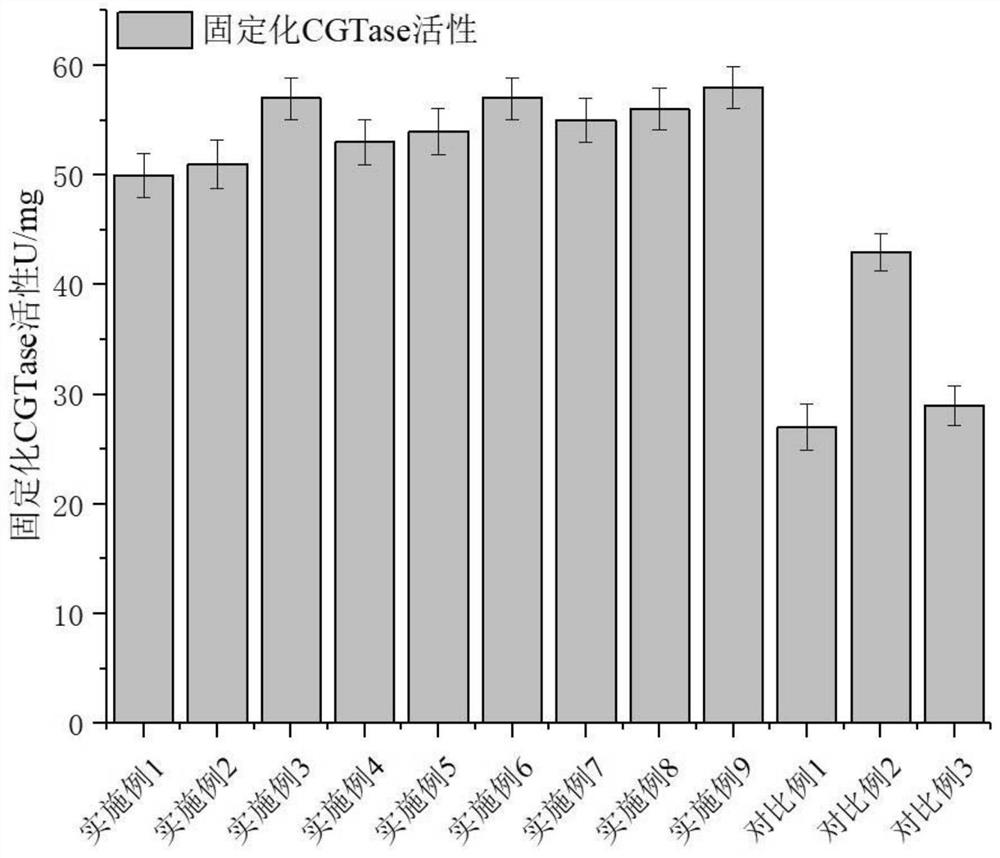
A method for immobilizing enzymes on nanofibers
A nanofiber and enzyme immobilization technology, applied in the direction of immobilized enzymes, biochemical equipment and methods, enzymes, etc., can solve the problems of weak binding force between immobilized materials and enzymes, difficulty in repeated use of immobilized enzymes, and mechanical strength of immobilized enzymes Low-level problems, to achieve the effect of improving the amount and stability of enzyme immobilization, improving the utilization rate of enzyme, and improving biocompatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0095] (1) Dissolve PSF powder in DMAC (100 mM, pH 6), at 85 °C, dissolve PSF in the solvent at a mass concentration of 75 g / L PSF while stirring, at 90 °C, according to the mass concentration ratio PSF:PVA=2:1 PVA was added, and the PVA was dissolved in the solution with stirring. The solution was cooled at room temperature and then mixed with the CGTase solution to obtain a PSF / PVA mixed solution with a final enzyme concentration of 1 mg / ml.
[0096]The enzyme was purchased from Japan Amano Company, the enzyme activity preservation rate was 99%, the effective substance content was 99%, white crystal, and the solubility in water increased with the increase of temperature. Not hygroscopic, but easy to form various stable hydrates.
[0097] (2) inject the PSF / PVA solution prepared in step (1) into the syringe respectively, use the flattened needle as the capillary for spinning, fix the syringe on the micro-extrusion pump, and control the solution flow rate to 0.2ml / h. The pos...
Embodiment 2
[0100] (1) Dissolve PSF powder in DMAC (100 mM, pH 6), at 85 °C, dissolve PSF in the solvent at a mass concentration of 75 g / L PSF while stirring, at 90 °C, according to the mass concentration ratio PSF:PVA=2:1 PVA was added, and the PVA was dissolved in the solution with stirring. The solution was cooled at room temperature and then mixed with the CGTase solution to obtain a PSF / PVA mixed solution with a final enzyme concentration of 2 mg / ml.
[0101] The enzyme was purchased from Japan Amano Company, the enzyme activity preservation rate was 99%, the effective substance content was 99%, white crystal, and the solubility in water increased with the increase of temperature. Not hygroscopic, but easy to form various stable hydrates.
[0102] (2) inject the PSF / PVA solution prepared in step (1) into the syringe respectively, use the flattened needle as the capillary for spinning, fix the syringe on the micro-extrusion pump, and control the solution flow rate to 0.2ml / h. The po...
Embodiment 3
[0105] (1) Dissolve PSF powder in DMAC (100 mM, pH 6), at 85 °C, dissolve PSF in the solvent at a mass concentration of 75 g / L PSF while stirring, at 90 °C, according to the mass concentration ratio PSF:PVA=2:1 PVA was added, and the PVA was dissolved in the solution with stirring. The solution was cooled at room temperature and then mixed with the CGTase solution to obtain a PSF / PVA mixed solution with a final enzyme concentration of 3 mg / ml.
[0106] The enzyme was purchased from Japan Amano Company, the enzyme activity preservation rate was 99%, the effective substance content was 99%, white crystal, and the solubility in water increased with the increase of temperature. Not hygroscopic, but easy to form various stable hydrates.
[0107] (2) inject the PSF / PVA solution prepared in step (1) into the syringe respectively, use the flattened needle as the capillary for spinning, fix the syringe on the micro-extrusion pump, and control the solution flow rate to 0.2ml / h. The po...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com