A Tribocatalytic Design Method for Realizing Ultra-low Friction of Carbon Thin Films
A technology of ultra-low friction and design method, which is applied in the direction of nano-carbon, mechanical equipment, engine lubrication, etc., can solve the problems of short wear life, easy oxidation, and restriction of tribological performance of diamond-like carbon film, and realize the frictional contact area , low cost, improved effect of high friction coefficient
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] Example 1 A tribocatalytic design method to achieve ultra-low friction of carbon thin films: firstly, disperse 0.125 g 50 nm Cu nanoparticles in 1 L of absolute ethanol, and ultrasonically disperse for 30 min to obtain a Cu nanoparticle solution; then use a 1 mL dropper to 8 drops / 2.5 cm of Cu nanoparticles solutions with different concentrations 2 Spin coating on the surface of an amorphous carbon-based film with a hydrogen content of 20 at.% and a surface roughness of ≤5 nm. After vacuum evaporation of absolute ethanol, a uniformly distributed coating of metal nanoparticles can be obtained.
[0019] The obtained metal nanoparticle coating and aluminum oxide dual balls constitute a friction pair, the lower module is fixed, and the upper module is rotated, and the friction experiment is carried out in UMT under vacuum.
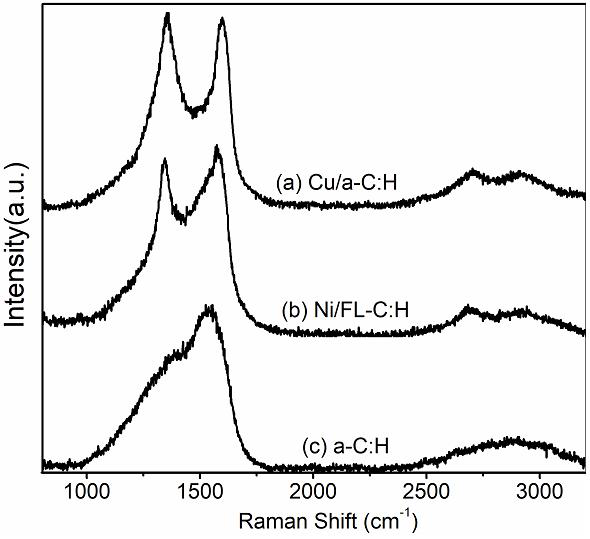
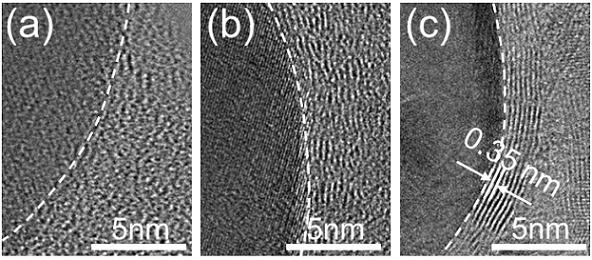
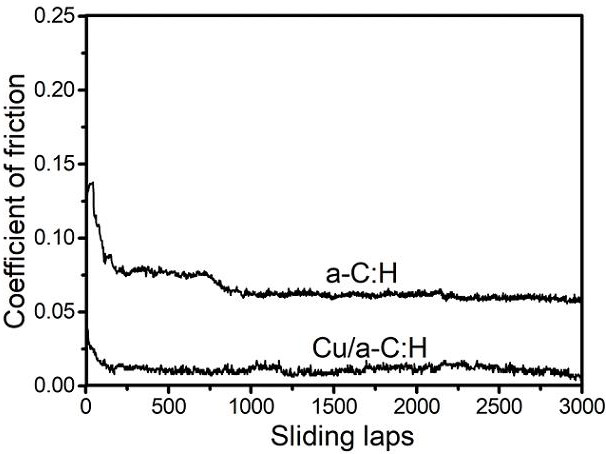
[0020] The Cu metal nanoparticle coating and the dual ball form a friction pair. Through the TEM and Raman analysis of the wear debris, it is found tha...
Embodiment 2
[0021] Example 2 A tribocatalytic design method for realizing ultra-low friction of carbon thin films: firstly, disperse 0.25 g of 100 nm Ni nanoparticles in 1 L of absolute ethanol, and ultrasonically disperse for 30 min to obtain a Ni nanoparticle solution; then use a 1 mL dropper to Ni nanoparticle solutions with different concentrations were placed in 10 drops / 2.5 cm 2 Spin-coat on the surface of a fullerene-like carbon-based film with a hydrogen content of 15 at.% and a surface roughness of ≤5 nm. After evaporating absolute ethanol in a vacuum, a uniformly distributed coating of metal nanoparticles can be obtained.
[0022] The obtained metal nanoparticle coating and aluminum oxide dual balls form a friction pair, the lower module is fixed, the upper module is rotated, and the UMT is in the N 2 The friction experiment was carried out under the atmosphere.
[0023] On the Raman spectrum of the fullerene-like carbon-based film, there is an obvious D peak (1360 cm -1 ) and...
Embodiment 3
[0024] Example 3 A tribocatalytic design method for achieving ultra-low friction of carbon thin films: firstly, disperse 0.025 g of 200 nm Co nanoparticles in 1 L of absolute ethanol, and ultrasonically disperse for 30 min to obtain a Co nanoparticle solution; then use a 1 mL dropper to Ni nanoparticle solutions of different concentrations were placed in 12 drops / 2.5 cm 2 Spin coating on the surface of graphite-like carbon-based film with hydrogen content of 10 at.% and surface roughness ≤ 5 nm. After vacuum evaporation of absolute ethanol, a uniformly distributed coating of metal nanoparticles can be obtained.
[0025] The obtained metal nanoparticle coating and silicon carbide form a friction pair, the lower module is fixed, the upper module is rotated, and the reciprocating friction experiment is carried out on the CSM under the condition of 40% atmospheric humidity.
[0026] The orderly transformation of the thin film structure to graphene can also be observed, forming a b...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com